Intro
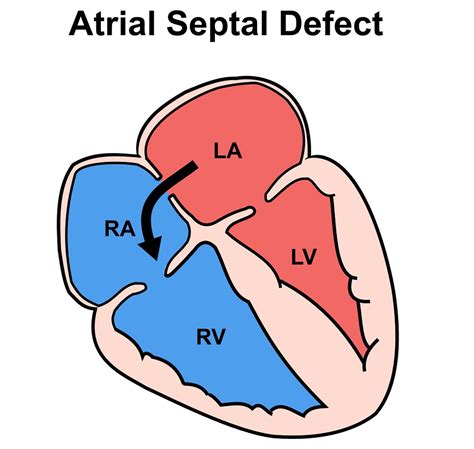
Atrial septal defects, commonly referred to as ASDs, are a type of congenital heart defect that affects the septum, which is the wall of tissue that separates the heart's upper chambers, known as the atria. This condition occurs when there is an abnormal opening in the septum, allowing blood to flow between the left and right atria. ASDs can be present at birth or develop later in life due to various factors. Understanding the importance of ASDs and their impact on the heart's functioning is crucial for providing proper care and treatment to individuals affected by this condition.
The prevalence of ASDs is relatively high, with approximately 1 in every 1,500 births being affected by this condition. ASDs can occur in isolation or in combination with other heart defects. The severity of the condition varies greatly among individuals, with some experiencing mild symptoms while others may have more severe complications. In some cases, ASDs may not be diagnosed until later in life, when symptoms become more apparent or when other health issues arise. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of ASDs to ensure timely medical intervention.
The diagnosis and treatment of ASDs have undergone significant advancements in recent years, offering new hope for individuals affected by this condition. With the help of modern medical technology and surgical techniques, it is now possible to repair or close ASDs, greatly improving the quality of life for those affected. Furthermore, increased awareness and understanding of ASDs have led to better preventive measures and early detection, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall health outcomes. As research continues to uncover the complexities of ASDs, it is crucial to stay informed about the latest developments and advancements in the field.
Atrial Septal Defect Types
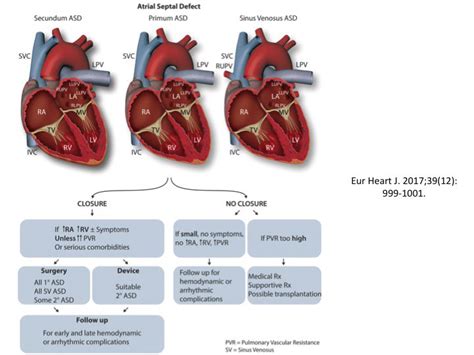
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of atrial septal defects are still not fully understood, but several factors are thought to contribute to their development. These include: * Genetic factors: Family history and genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing an ASD. * Environmental factors: Exposure to certain substances during pregnancy, such as tobacco smoke and alcohol, may increase the risk of ASDs. * Heart disease: Individuals with a history of heart disease or other heart defects are more likely to develop an ASD.Symptoms and Complications
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing atrial septal defects typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as: * Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the heart's electrical activity. * Chest X-ray: Shows the size and shape of the heart. * Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart. * Cardiac catheterization: Inserts a catheter into the heart to measure blood pressure and oxygen levels. Treatment for ASDs depends on the size and location of the defect, as well as the individual's overall health. Common treatment options include: * Watchful waiting: Monitoring the defect for changes or complications. * Medications: To manage symptoms and prevent complications. * Surgery: To repair or close the defect. * Catheter-based procedures: To close the defect using a catheter.Living with Atrial Septal Defects
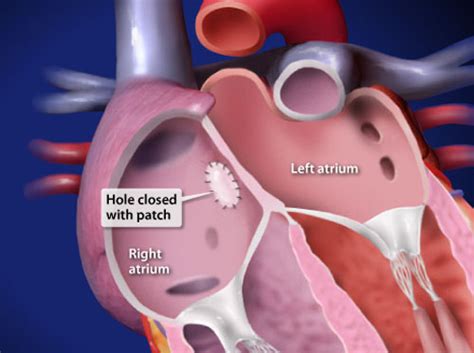
Lifestyle Modifications
Making healthy lifestyle choices can help individuals with ASDs manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications. These include: * Regular exercise: To improve cardiovascular health and reduce stress. * Balanced diet: To maintain a healthy weight and prevent conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes. * Stress management: To reduce stress and anxiety, which can exacerbate symptoms. * Avoiding smoking and tobacco products: To reduce the risk of heart disease and other complications.Atrial Septal Defect Repair
Postoperative Care
After ASD repair, it is essential to follow a comprehensive postoperative care plan to ensure a smooth and successful recovery. This includes: * Rest and relaxation: To allow the body to heal and reduce the risk of complications. * Pain management: To manage pain and discomfort after surgery. * Follow-up appointments: To monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed. * Lifestyle modifications: To promote overall health and well-being and reduce the risk of future complications.Atrial Septal Defect Complications
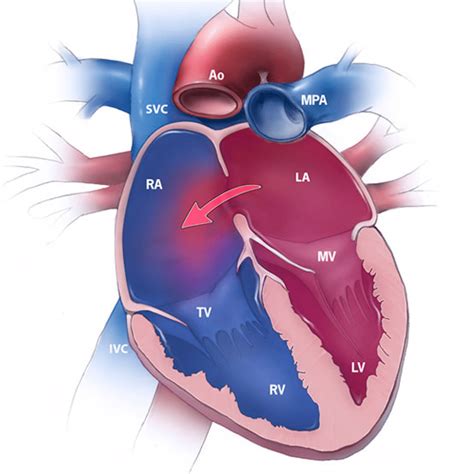
Prevention and Screening
Preventing atrial septal defects is not always possible, but there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing this condition. These include: * Genetic counseling: For individuals with a family history of ASDs or other heart defects. * Prenatal care: Regular prenatal check-ups to monitor fetal development and detect potential heart defects. * Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and tobacco products.Atrial Septal Defect Prognosis
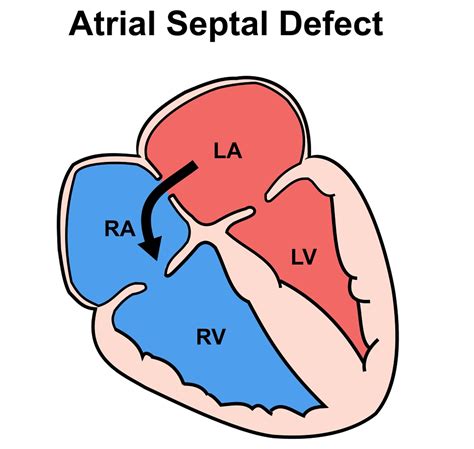
Future Directions
Research into atrial septal defects is ongoing, with a focus on developing new and innovative treatments, improving diagnostic techniques, and enhancing our understanding of the condition. Future directions include: * Minimally invasive procedures: Developing new catheter-based procedures to close ASDs. * Tissue engineering: Creating artificial tissue to repair or replace damaged heart tissue. * Gene therapy: Using genetic engineering to repair or replace faulty genes that contribute to ASDs.What are the symptoms of atrial septal defects?
+The symptoms of atrial septal defects can vary greatly among individuals, but common symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, palpitations, swelling in the legs and feet, and chest pain.
How are atrial septal defects diagnosed?
+Diagnosing atrial septal defects typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, echocardiogram, and cardiac catheterization.
What are the treatment options for atrial septal defects?
+Treatment for atrial septal defects depends on the size and location of the defect, as well as the individual's overall health. Common treatment options include watchful waiting, medications, surgery, and catheter-based procedures.
Can atrial septal defects be prevented?
+While preventing atrial septal defects is not always possible, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing this condition, such as genetic counseling, prenatal care, and healthy lifestyle choices.
What is the prognosis for individuals with atrial septal defects?
+The prognosis for individuals with atrial septal defects is generally good, especially with prompt and proper treatment. However, the outcome depends on various factors, including the size and location of the defect, the presence of other heart defects, and the individual's overall health.
In conclusion, atrial septal defects are a complex and multifaceted condition that requires careful diagnosis, treatment, and management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ASDs, individuals can take an active role in managing their condition and reducing the risk of complications. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with atrial septal defects in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support. By working together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of ASDs and improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
