Intro
Discover the process of Autism Diagnosis in Adults, including signs, symptoms, and assessment tools, to facilitate early detection and intervention, improving mental health outcomes for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a neurological and developmental disorder that affects communication, social interaction, and behavior. While autism is often associated with children, it is essential to recognize that adults can also be diagnosed with autism. In recent years, there has been an increase in awareness and understanding of autism in adults, leading to more diagnoses and a better quality of life for those affected. The importance of autism diagnosis in adults cannot be overstated, as it can have a significant impact on their daily lives, relationships, and overall well-being.
The prevalence of autism in adults is a topic of ongoing research, with estimates suggesting that approximately 1 in 54 adults in the United States may have autism. Despite this, many adults with autism remain undiagnosed or misdiagnosed, often due to a lack of awareness and understanding among healthcare professionals. This can lead to delayed diagnoses, which can have significant consequences for the individual, including delayed access to appropriate support and services. Furthermore, the stigma surrounding autism can also prevent adults from seeking a diagnosis, fearing that it may impact their relationships, employment, or social status.
The process of diagnosing autism in adults is complex and involves a comprehensive evaluation of the individual's behavior, communication, and social interactions. This typically involves a team of professionals, including psychologists, psychiatrists, and speech therapists, who use a range of diagnostic tools and assessments to determine whether the individual meets the diagnostic criteria for autism. The diagnostic criteria for autism, as outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), include persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction, as well as restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities.
Autism Diagnosis Process

Diagnostic Tools and Assessments
The diagnostic tools and assessments used to diagnose autism in adults may include: * Autism Quotient (AQ) test: a self-report questionnaire that assesses autistic traits and behaviors * Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS): a rating scale that evaluates social awareness, social cognition, and social communication * Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS): a semi-structured assessment that evaluates social interaction, communication, and play * Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS): a cognitive test that assesses intelligence quotient (IQ)Benefits of Autism Diagnosis

Common Challenges
Despite the benefits of an autism diagnosis, adults may face several challenges, including: * Stigma and discrimination: many adults with autism report experiencing stigma and discrimination, which can impact their mental health and well-being * Lack of awareness and understanding: many healthcare professionals and employers may not be aware of the needs and challenges of adults with autism * Limited access to services and support: adults with autism may have limited access to services and support, particularly in rural or underserved areas * Co-occurring mental health conditions: adults with autism are at increased risk of developing co-occurring mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depressionAutism Treatment and Support

Accommodations and Modifications
Adults with autism may also be eligible for accommodations and modifications in the workplace or educational setting, such as: * Extra time to complete tasks or assignments * A quiet workspace or flexible work arrangements * Use of assistive technology, such as text-to-speech software or a communication device * Provision of written instructions or visual aids * Regular breaks and self-care activities to manage stress and anxietyAutism and Employment

Disclosure and Accommodations
Adults with autism may need to disclose their diagnosis to their employer to access accommodations and support. This can be a challenging and sensitive process, but it can also be an opportunity to educate employers and colleagues about autism and promote acceptance and inclusion.Autism and Relationships
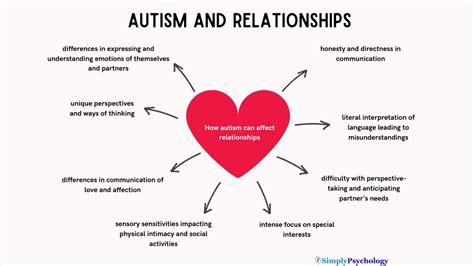
Communication and Emotional Intelligence
Adults with autism may need to develop strategies to improve their communication and emotional intelligence, such as: * Using visual aids or written communication to support verbal interactions * Practicing active listening and empathy to improve social understanding * Developing self-awareness and self-regulation skills to manage emotions and behaviors * Seeking feedback and support from trusted friends, family, or mental health professionalsAutism and Mental Health

Self-Care and Stress Management
Adults with autism can benefit from developing self-care and stress management strategies, such as: * Engaging in regular exercise or physical activity to reduce stress and anxiety * Practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation * Developing a daily routine and structure to improve executive function and organization * Seeking support from friends, family, or mental health professionals to manage emotions and behaviorsConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with autism diagnosis in adults. Have you or a loved one received an autism diagnosis? What challenges and benefits have you encountered? Share your story in the comments below, and let's work together to promote awareness, acceptance, and inclusion for adults with autism.
What are the common symptoms of autism in adults?
+Common symptoms of autism in adults include difficulties with social interaction and communication, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities. Adults with autism may also experience anxiety, depression, and other co-occurring mental health conditions.
How is autism diagnosed in adults?
+Autism diagnosis in adults typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a team of professionals, including psychologists, psychiatrists, and speech therapists. This may include cognitive and behavioral tests, as well as a thorough medical and psychological history.
What support and services are available for adults with autism?
+Adults with autism may be eligible for a range of support and services, including counseling, therapy, and accommodations in the workplace or educational setting. They may also benefit from self-care and stress management strategies, such as exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques.
Can adults with autism lead successful and independent lives?
+Yes, many adults with autism are able to lead successful and independent lives, with the right support and accommodations. By developing strategies to manage their symptoms and challenges, adults with autism can achieve their goals, form meaningful relationships, and contribute to their communities.
How can I support a loved one with autism?
+Supporting a loved one with autism can involve educating yourself about autism, being patient and understanding, and advocating for their needs and rights. You can also encourage them to access support and services, such as counseling and therapy, and offer emotional support and encouragement.
