Intro
Discover 5 uses of Metronidazole, an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication, treating infections, bacterial vaginosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, giardiasis, and amoebiasis, with its antimicrobial properties.
Metronidazole is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication used to treat various infections caused by bacteria and protozoa. It is a versatile drug with a wide range of applications, making it a crucial component in the treatment of numerous diseases. The importance of metronidazole lies in its ability to target and eliminate harmful microorganisms, thereby alleviating symptoms and promoting recovery. As a result, understanding the uses of metronidazole is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The significance of metronidazole can be attributed to its effectiveness in treating infections that are resistant to other antibiotics. Its unique mechanism of action allows it to target anaerobic bacteria, which are bacteria that thrive in environments with low oxygen levels. This makes metronidazole an ideal choice for treating infections in areas with limited oxygen supply, such as the gastrointestinal tract and the female reproductive system. Furthermore, metronidazole is also used to treat protozoal infections, which are caused by single-celled organisms that can infect various parts of the body.
Metronidazole has been widely used for several decades, and its applications continue to expand as new research emerges. The drug is available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and creams, making it easily accessible for patients with different needs. Additionally, metronidazole is often used in combination with other medications to enhance its effectiveness and treat complex infections. The versatility and efficacy of metronidazole have made it a staple in modern medicine, and its uses continue to be explored and expanded upon.
Introduction to Metronidazole

Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of metronidazole involve its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. After oral administration, metronidazole is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within 1-2 hours. The drug is then distributed throughout the body, with high concentrations found in the liver, kidney, and other tissues. Metronidazole is metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine, with a half-life of approximately 8 hours.Uses of Metronidazole

Treatment of Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is a common condition that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina, leading to symptoms such as vaginal discharge, odor, and irritation. Metronidazole is the primary treatment for bacterial vaginosis, with a recommended dose of 500 mg twice daily for 7 days. The drug has been shown to be highly effective in treating bacterial vaginosis, with cure rates exceeding 90%.Benefits and Risks of Metronidazole

Precautions and Contraindications
Metronidazole is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the drug or its components. It is also contraindicated in patients with severe liver disease, as the drug can exacerbate liver damage. Additionally, metronidazole should be used with caution in patients with neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, and in patients with a history of blood dyscrasias.Metronidazole in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Metronidazole in Breastfeeding
Metronidazole is excreted in breast milk, although the amounts are generally considered to be low. However, the drug can cause adverse effects in nursing infants, such as gastrointestinal upset and allergic reactions. As a result, metronidazole should be used with caution in breastfeeding women, and the benefits of treatment should be weighed against the potential risks to the infant.Metronidazole Resistance
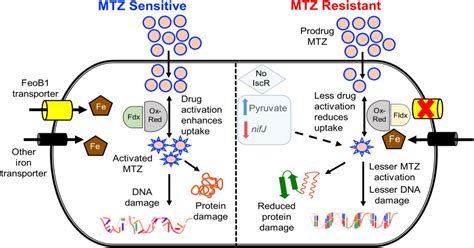
Prevention of Metronidazole Resistance
The prevention of metronidazole resistance requires a multifaceted approach, including: * Responsible use of the drug, with careful consideration of the diagnosis and treatment plan * Use of alternative treatments, such as other antibiotics or non-antibiotic therapies * Development of new antibiotics and treatments that are effective against resistant strains * Education and awareness of the risks of antibiotic resistance and the importance of responsible antibiotic useConclusion and Future Directions

To further explore the topic of metronidazole, we invite readers to comment and share their thoughts and experiences. Additionally, we encourage readers to take specific actions, such as consulting with a healthcare provider before using metronidazole and reporting any adverse effects to the relevant authorities.
What is metronidazole used for?
+Metronidazole is used to treat various infections caused by bacteria and protozoa, including bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis, amoebiasis, giardiasis, and anaerobic bacterial infections.
How does metronidazole work?
+Metronidazole works by interfering with the DNA of microorganisms, ultimately leading to their death.
What are the side effects of metronidazole?
+The side effects of metronidazole include gastrointestinal side effects, neurological side effects, allergic reactions, and interactions with other medications.
Can metronidazole be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Metronidazole can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, although it should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
What is metronidazole resistance?
+Metronidazole resistance refers to the development of resistant strains of bacteria and protozoa that are no longer susceptible to the effects of metronidazole.
