Intro
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) in the brain are a complex and fascinating topic that has garnered significant attention in the medical community. An AVM is a tangle of blood vessels in the brain that can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. In this article, we will delve into the world of brain AVMs, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and more.
The importance of understanding brain AVMs cannot be overstated. These abnormal connections between arteries and veins can lead to serious complications, including bleeding, seizures, and even stroke. Moreover, brain AVMs can affect anyone, regardless of age or background, making it essential to raise awareness about this condition. By learning more about brain AVMs, we can better appreciate the intricacies of the human brain and the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms persist.
As we navigate the complexities of brain AVMs, it is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of an AVM. These can include headaches, seizures, weakness or numbness in the face or limbs, and vision problems. While some people may not experience any symptoms at all, others may suffer from debilitating effects that impact their daily lives. By understanding the symptoms and risks associated with brain AVMs, we can take the first step towards seeking medical help and preventing potential complications.
What is an Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)?
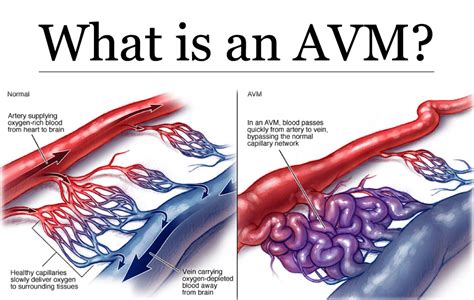
Types of Brain AVMs
There are several types of brain AVMs, each with distinct characteristics and risks. These include: * **Pial AVMs**: These are the most common type of AVM and occur in the pial surface of the brain. * **Dural AVMs**: These occur in the dura mater, a protective layer that covers the brain and spinal cord. * **Brainstem AVMs**: These occur in the brainstem, which connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord.Causes and Risk Factors of Brain AVMs

Genetic Mutations
Genetic mutations can play a significant role in the development of brain AVMs. Certain genetic disorders, such as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, can increase the risk of developing an AVM.Symptoms of Brain AVMs
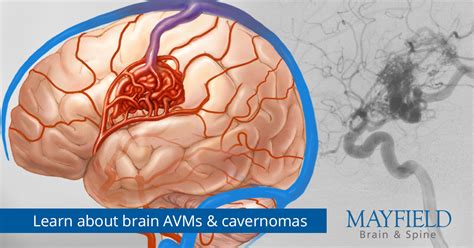
Diagnosis of Brain AVMs
Diagnosing brain AVMs typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, and angiography. These tests can help doctors visualize the AVM and determine its size, location, and severity.Treatment Options for Brain AVMs
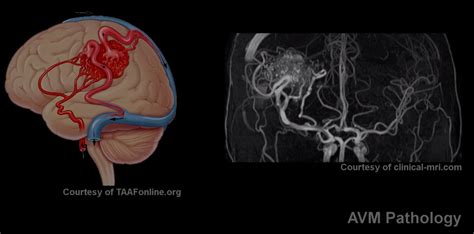
Complications of Brain AVMs
Untreated brain AVMs can lead to serious complications, including bleeding, seizures, and stroke. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.Living with a Brain AVM
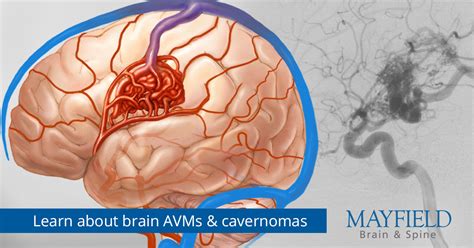
Coping with Symptoms
Coping with the symptoms of a brain AVM requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes. This can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.Current Research and Future Directions

Advances in Treatment
Advances in treatment options are continually being made, including the development of new medications and therapies. These advances offer hope for improved treatment outcomes and quality of life for individuals with brain AVMs.What is the main cause of brain AVMs?
+The main cause of brain AVMs is still not fully understood, but research suggests that they may be related to genetic mutations, trauma, or infections.
What are the symptoms of brain AVMs?
+The symptoms of brain AVMs can include headaches, seizures, weakness or numbness in the face or limbs, and vision problems.
How are brain AVMs diagnosed?
+Diagnosing brain AVMs typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, and angiography.
What are the treatment options for brain AVMs?
+Treatment options for brain AVMs depend on the size, location, and severity of the AVM and can include surgery, embolization, and radiation therapy.
Can brain AVMs be prevented?
+While brain AVMs cannot be prevented, seeking medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time can help prevent complications.
In conclusion, brain AVMs are complex and fascinating conditions that require a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for brain AVMs, we can better appreciate the intricacies of the human brain and the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms persist. If you or someone you know is living with a brain AVM, we encourage you to share your story, ask questions, and seek support from medical professionals and support groups. Together, we can work towards improving our understanding of brain AVMs and developing new treatments to improve the lives of those affected.
