Intro
Discover B12 Deficiency Anemia Symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, and pale skin, and learn about diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of this condition, also known as vitamin B12 deficiency anemia or megaloblastic anemia.
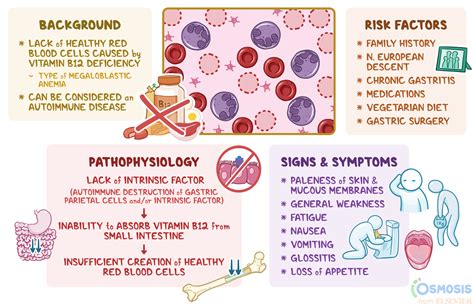
B12 deficiency anemia is a condition that occurs when the body does not have enough vitamin B12 to produce adequate red blood cells. Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. In this article, we will delve into the importance of vitamin B12, the causes of B12 deficiency anemia, and the various symptoms that can occur.
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that is found in animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy products. It is also available in supplement form, which can be beneficial for individuals who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet. The body requires vitamin B12 to produce red blood cells, and a deficiency can lead to anemia. Anemia is a condition characterized by a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood, which can cause a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
B12 deficiency anemia can be caused by a variety of factors, including a lack of vitamin B12 in the diet, malabsorption of vitamin B12, or certain medical conditions. Individuals who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet are at a higher risk of developing B12 deficiency anemia, as they do not consume animal products that are rich in vitamin B12. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease or Crohn's disease, can lead to malabsorption of vitamin B12. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term complications.
Causes of B12 Deficiency Anemia

Medical Conditions that Cause B12 Deficiency Anemia
Certain medical conditions can lead to B12 deficiency anemia, including celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and gastric bypass surgery. Celiac disease is a condition that causes the immune system to react to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. This can lead to damage to the small intestine, which can cause malabsorption of vitamin B12. Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that can cause damage to the small intestine, leading to malabsorption of vitamin B12. Gastric bypass surgery can also lead to malabsorption of vitamin B12, as it can reduce the size of the stomach and alter the digestive process.Symptoms of B12 Deficiency Anemia

Mild Symptoms of B12 Deficiency Anemia
Mild symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia may include: * Fatigue and weakness * Shortness of breath * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Headaches and migraines * Pale skin and yellowing of the skin and eyesSevere Symptoms of B12 Deficiency Anemia
Severe symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia may include: * Diarrhea and constipation * Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet * Muscle weakness and wasting * Vision problems and blurred vision * Mood changes, such as depression and anxietyDiagnosis and Treatment of B12 Deficiency Anemia
Vitamin B12 Supplements
Vitamin B12 supplements are available in various forms, including oral tablets, injections, and nasal sprays. Oral tablets are the most common form of vitamin B12 supplement, and they can be taken daily to help treat B12 deficiency anemia. Injections of vitamin B12 are typically given monthly, and they can be more effective than oral tablets for individuals with severe B12 deficiency anemia. Nasal sprays are a relatively new form of vitamin B12 supplement, and they can be taken daily to help treat B12 deficiency anemia.Prevention of B12 Deficiency Anemia

Dietary Changes to Prevent B12 Deficiency Anemia
Dietary changes can help prevent B12 deficiency anemia, including: * Eating animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy products * Taking vitamin B12 supplements * Avoiding certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease * Eating fortified foods, such as cereals and plant-based milkComplications of B12 Deficiency Anemia

Nerve Damage Complications
Nerve damage complications can include: * Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet * Vision problems and blurred vision * Muscle weakness and wasting * Mood changes, such as depression and anxietyConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with B12 deficiency anemia in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to ask. You can also share this article with friends and family who may be interested in learning more about B12 deficiency anemia.
What are the symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia?
+The symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia can include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. More severe symptoms can include pale skin, diarrhea, and numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
How is B12 deficiency anemia diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of B12 deficiency anemia typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A blood test can measure the levels of vitamin B12 in the blood, and a bone marrow test can help diagnose anemia.
How is B12 deficiency anemia treated?
+Treatment of B12 deficiency anemia typically involves vitamin B12 supplements, which can be taken orally or injected into the muscle. In some cases, iron supplements may also be prescribed to help treat anemia.
Can B12 deficiency anemia be prevented?
+Prevention of B12 deficiency anemia can be achieved through a balanced diet that includes animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy products. Individuals who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet can take vitamin B12 supplements to help prevent B12 deficiency anemia.
What are the complications of B12 deficiency anemia?
+Complications of B12 deficiency anemia can be severe and long-term, including nerve damage, heart problems, and increased risk of infections. Nerve damage can cause numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and it can also lead to vision problems and blurred vision.
