Intro
Discover how Beta Blockers medications work, their types, and uses in managing hypertension, angina, and heart failure, with related treatments like calcium channel blockers and diuretics.
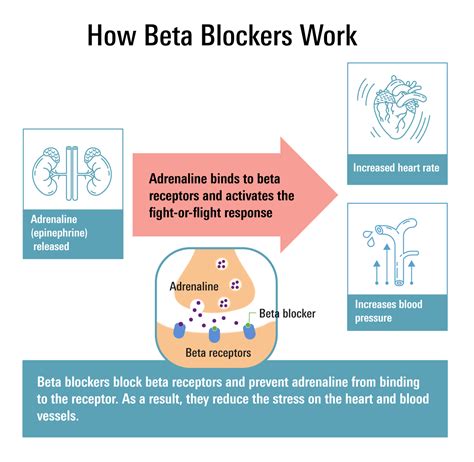
The use of beta blockers medications has become a crucial aspect of managing various health conditions, particularly those related to the cardiovascular system. Beta blockers, also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, are a class of medications that work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and by slowing the heart rate and reducing its workload. This, in turn, lowers blood pressure and increases oxygen supply to the heart. With the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, the importance of beta blockers cannot be overstated. In this article, we will delve into the world of beta blockers, exploring their benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects.
The significance of beta blockers lies in their ability to manage a range of health conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias. By reducing the heart rate and the force of contraction, beta blockers help to decrease the oxygen demand of the heart, thereby reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Furthermore, beta blockers have been shown to improve survival rates in patients with heart failure, making them an essential component of treatment plans. With the rising burden of cardiovascular diseases, the role of beta blockers in maintaining heart health cannot be emphasized enough.
The use of beta blockers is not limited to cardiovascular diseases alone. They are also used to manage conditions such as glaucoma, migraines, and performance anxiety. In the case of glaucoma, beta blockers reduce the production of fluid in the eye, thereby decreasing pressure and preventing damage to the optic nerve. Similarly, beta blockers have been shown to be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of migraines. By understanding the diverse applications of beta blockers, we can appreciate their importance in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Beta Blockers Mechanism of Action
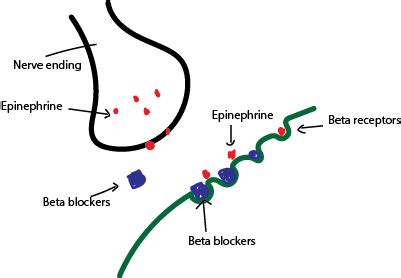
Types of Beta Blockers
There are several types of beta blockers, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most commonly used beta blockers include: * Propranolol: a non-selective beta blocker used to manage high blood pressure, angina, and arrhythmias * Metoprolol: a selective beta-1 blocker used to manage high blood pressure, angina, and heart failure * Atenolol: a selective beta-1 blocker used to manage high blood pressure and angina * Bisoprolol: a selective beta-1 blocker used to manage heart failure * Carvedilol: a non-selective beta blocker with alpha-1 blocking activity, used to manage high blood pressure and heart failureBeta Blockers Benefits
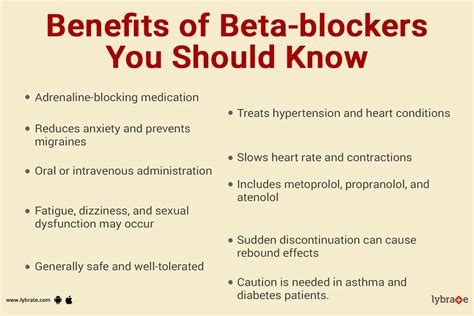
Potential Side Effects
While beta blockers are generally well-tolerated, they can cause a range of side effects, including: * Fatigue and drowsiness * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Shortness of breath * Cold hands and feet * Nausea and vomiting * Diarrhea or constipationBeta Blockers and Exercise
Interactions with Other Medications
Beta blockers can interact with a range of other medications, including: * Calcium channel blockers: can increase the risk of hypotension and bradycardia * Anti-arrhythmic medications: can increase the risk of arrhythmias * Anti-depressant medications: can increase the risk of hypotension and bradycardia * Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): can increase the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular eventsBeta Blockers and Pregnancy
Monitoring and Follow-up
Patients taking beta blockers require regular monitoring and follow-up to ensure that the medication is working effectively and to minimize the risk of side effects. This includes: * Regular blood pressure checks * Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring * Blood tests to monitor kidney and liver function * Regular review of medication and dosage adjustments as neededBeta Blockers and Breastfeeding

Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, beta blockers are a vital component of managing various health conditions, particularly those related to the cardiovascular system. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects of beta blockers, patients and healthcare providers can work together to develop effective treatment plans. As research continues to evolve, we can expect to see new and innovative applications of beta blockers, further solidifying their importance in maintaining heart health and overall well-being.We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with beta blockers in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one been prescribed beta blockers? What benefits or side effects have you experienced? Your input can help others better understand the importance of beta blockers and their role in maintaining heart health.
What are beta blockers used for?
+Beta blockers are used to manage a range of health conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
How do beta blockers work?
+Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, leading to a decrease in heart rate, blood pressure, and cardiac output.
What are the potential side effects of beta blockers?
+Potential side effects of beta blockers include fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, cold hands and feet, nausea, and vomiting.
Can I exercise while taking beta blockers?
+Yes, you can exercise while taking beta blockers, but it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best exercise plan and to monitor progress.
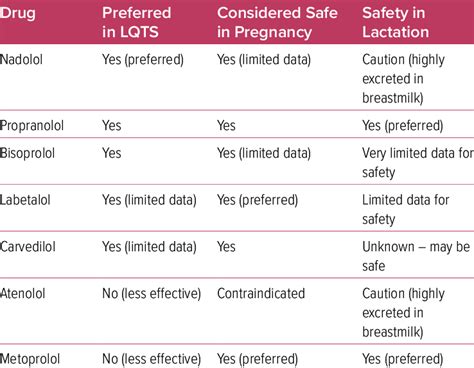
Can I take beta blockers during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
+The use of beta blockers during pregnancy or breastfeeding requires careful consideration and monitoring by a healthcare provider to minimize the risk of side effects to the fetus or infant.
