Intro
Learn about normal bilirubin levels in infants, jaundice symptoms, and phototherapy treatments to manage high bilirubin, ensuring healthy liver function and preventing kernicterus.
Bilirubin is a yellow compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in red blood cells. In infants, bilirubin levels are a significant concern as they can be a sign of health issues, particularly in the first few weeks of life. Understanding bilirubin levels in infants is crucial for parents and healthcare professionals to ensure the well-being and proper development of newborns. The importance of monitoring bilirubin levels cannot be overstated, as elevated levels can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the world of bilirubin, exploring its causes, effects, and the measures that can be taken to manage it in infants.
The first few weeks of an infant's life are critical, and monitoring their health is a top priority. Bilirubin levels are a key aspect of this monitoring, as they can indicate the presence of underlying health issues. For instance, high bilirubin levels can cause jaundice, a condition characterized by a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes. Jaundice is common in newborns, but in some cases, it can be a sign of a more serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Parents and healthcare professionals must be aware of the signs and symptoms of high bilirubin levels to provide timely and effective treatment.
As we explore the topic of bilirubin levels in infants, it is essential to understand the factors that contribute to elevated bilirubin levels. These factors can include prematurity, infection, and genetic disorders, among others. By understanding the causes of high bilirubin levels, healthcare professionals can develop effective treatment plans to manage the condition and prevent long-term complications. Moreover, parents can take steps to reduce the risk of elevated bilirubin levels in their infants, such as ensuring proper feeding and hydration. In the following sections, we will discuss the causes, effects, and management of bilirubin levels in infants in greater detail.
Bilirubin and Jaundice in Infants
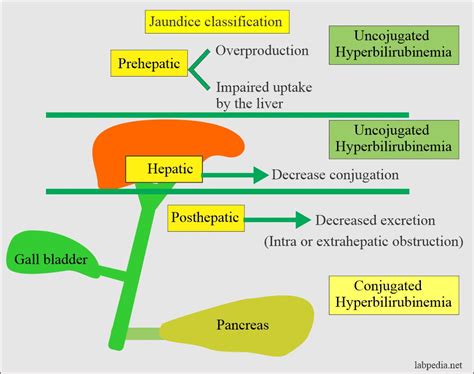
Causes of High Bilirubin Levels
The causes of high bilirubin levels in infants can be diverse and complex. Some of the most common causes include: * Prematurity: Premature infants are more likely to experience high bilirubin levels due to their underdeveloped liver. * Infection: Infections such as sepsis or meningitis can cause high bilirubin levels in infants. * Genetic disorders: Certain genetic disorders, such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, can increase the risk of high bilirubin levels. * Blood type incompatibility: Blood type incompatibility between the mother and infant can cause high bilirubin levels. * Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding can cause high bilirubin levels in some infants, particularly if the mother has a history of breastfeeding difficulties.Diagnosis and Treatment of High Bilirubin Levels
Phototherapy for High Bilirubin Levels
Phototherapy is a common treatment for high bilirubin levels in infants. It involves exposing the infant to a specific wavelength of light that helps break down bilirubin in the blood. Phototherapy is typically used in conjunction with other treatments, such as hydration and monitoring of bilirubin levels. The benefits of phototherapy include: * Reduced risk of kernicterus: Phototherapy can help reduce the risk of kernicterus, a serious condition that can occur when bilirubin levels are extremely high. * Improved outcomes: Phototherapy can improve outcomes for infants with high bilirubin levels, particularly when used in conjunction with other treatments. * Non-invasive: Phototherapy is a non-invasive treatment that does not require surgery or other invasive procedures.Management and Prevention of High Bilirubin Levels

Risk Factors for High Bilirubin Levels
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of high bilirubin levels in infants. These risk factors include: * Prematurity: Premature infants are more likely to experience high bilirubin levels due to their underdeveloped liver. * Low birth weight: Infants with low birth weight are more likely to experience high bilirubin levels. * Infection: Infections such as sepsis or meningitis can increase the risk of high bilirubin levels. * Genetic disorders: Certain genetic disorders, such as G6PD deficiency, can increase the risk of high bilirubin levels. * Blood type incompatibility: Blood type incompatibility between the mother and infant can increase the risk of high bilirubin levels.Long-Term Effects of High Bilirubin Levels

Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of high bilirubin levels are critical to preventing long-term effects and ensuring the best possible outcomes for infants. Some of the reasons why early detection and treatment are important include: * Reduced risk of kernicterus: Early detection and treatment can reduce the risk of kernicterus, a serious condition that can occur when bilirubin levels are extremely high. * Improved outcomes: Early detection and treatment can improve outcomes for infants with high bilirubin levels, particularly when used in conjunction with other treatments. * Prevention of long-term effects: Early detection and treatment can help prevent long-term effects, such as cognitive impairment and hearing loss.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
As we conclude this article, it is essential to remember that high bilirubin levels are a treatable condition, and early detection and treatment can make a significant difference in outcomes for infants. By working together, healthcare professionals, parents, and caregivers can help reduce the risk of high bilirubin levels and ensure the best possible start in life for newborns.What are the symptoms of high bilirubin levels in infants?
+The symptoms of high bilirubin levels in infants can include jaundice, lethargy, and poor feeding. In severe cases, high bilirubin levels can cause kernicterus, a serious condition that can cause brain damage and other neurological problems.
How are high bilirubin levels diagnosed in infants?
+High bilirubin levels in infants are typically diagnosed using a blood test that measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. In some cases, additional tests such as a complete blood count (CBC) or liver function tests may be ordered to rule out underlying health issues.
What are the treatment options for high bilirubin levels in infants?
+The treatment options for high bilirubin levels in infants depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment may include phototherapy, exchange transfusions, and hydration. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help reduce bilirubin levels.
Can high bilirubin levels be prevented in infants?
+While high bilirubin levels cannot be completely prevented, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. These include ensuring proper hydration, monitoring bilirubin levels, and providing breastfeeding support and guidance.
What are the long-term effects of high bilirubin levels in infants?
+The long-term effects of high bilirubin levels in infants can include kernicterus, cognitive impairment, hearing loss, and neurological problems. Early detection and treatment are critical to preventing these long-term effects and ensuring the best possible outcomes for infants.
