Intro
Discover 7 ways Patch Works enhances productivity, streamlining workflows with automated patching, vulnerability management, and compliance scanning, ensuring robust cybersecurity and IT efficiency.
The concept of patching has been around for decades, and its importance cannot be overstated. In various industries, including technology, healthcare, and manufacturing, patching plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation of systems, products, and services. Despite its significance, many individuals are not aware of the intricacies of patching and how it works. In this article, we will delve into the world of patching, exploring its benefits, mechanisms, and applications.
Patching is a process that involves creating and applying patches to fix issues, update software, or modify systems. These patches can be used to address security vulnerabilities, improve performance, or add new features to existing products. The patching process is crucial in maintaining the integrity and functionality of systems, and its importance extends to various aspects of our lives. From securing our personal data to ensuring the reliability of critical infrastructure, patching is an essential component of modern technology.
The significance of patching cannot be overstated, and its applications are diverse. In the technology sector, patching is used to update software, fix bugs, and address security vulnerabilities. In healthcare, patching is used to update medical devices, ensuring they remain safe and effective. In manufacturing, patching is used to improve the performance and efficiency of production lines. With the increasing reliance on technology, the importance of patching will only continue to grow, making it essential to understand the mechanisms and benefits of this process.
Introduction to Patching
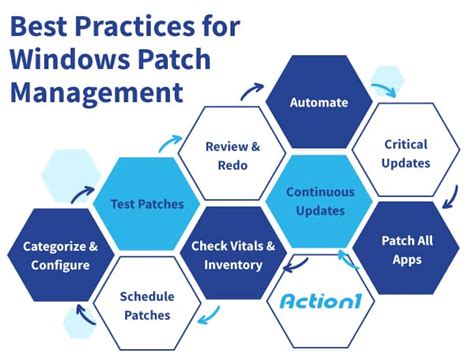
Patching is a complex process that involves several steps, from identifying issues to applying patches. The process begins with the identification of a problem or vulnerability, which is then reported to the relevant authorities. Once the issue is confirmed, a patch is created to address the problem. The patch is then tested to ensure its effectiveness and safety, before being released to the public. The patching process is critical in maintaining the integrity of systems, and its importance extends to various aspects of our lives.
Benefits of Patching
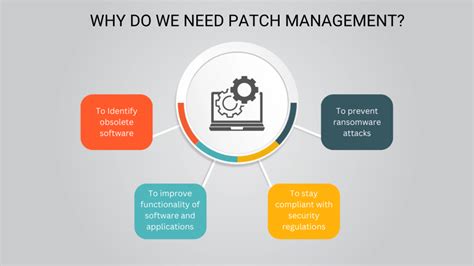
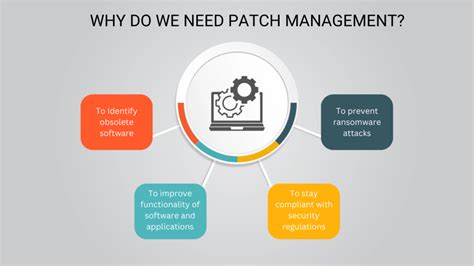
The benefits of patching are numerous, and they extend to various aspects of our lives. Some of the most significant benefits of patching include:
- Improved security: Patching helps to address security vulnerabilities, ensuring the safety and integrity of systems.
- Enhanced performance: Patching can improve the performance of systems, making them more efficient and reliable.
- New features: Patching can add new features to existing products, improving their functionality and usability.
- Compliance: Patching can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
How Patching Works

The patching process is complex, involving several steps and stakeholders. The process begins with the identification of a problem or vulnerability, which is then reported to the relevant authorities. Once the issue is confirmed, a patch is created to address the problem. The patch is then tested to ensure its effectiveness and safety, before being released to the public. The patching process is critical in maintaining the integrity of systems, and its importance extends to various aspects of our lives.
Types of Patches

There are several types of patches, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some of the most common types of patches include:
- Security patches: These patches are designed to address security vulnerabilities, ensuring the safety and integrity of systems.
- Feature patches: These patches add new features to existing products, improving their functionality and usability.
- Performance patches: These patches improve the performance of systems, making them more efficient and reliable.
- Compliance patches: These patches help organizations comply with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
Applications of Patching

The applications of patching are diverse, extending to various industries and aspects of our lives. Some of the most significant applications of patching include:
- Technology: Patching is used to update software, fix bugs, and address security vulnerabilities.
- Healthcare: Patching is used to update medical devices, ensuring they remain safe and effective.
- Manufacturing: Patching is used to improve the performance and efficiency of production lines.
- Finance: Patching is used to ensure the security and integrity of financial systems, protecting sensitive data and preventing fraud.
Best Practices for Patching

To ensure the effectiveness of patching, it is essential to follow best practices. Some of the most significant best practices for patching include:
- Regularly updating systems and software to ensure they remain secure and efficient.
- Testing patches before applying them to ensure their effectiveness and safety.
- Implementing a patch management process to ensure the timely and effective application of patches.
- Providing training and support to users to ensure they understand the importance of patching and how to apply patches effectively.
Common Challenges in Patching

Despite the importance of patching, there are several challenges that organizations and individuals face. Some of the most common challenges in patching include:
- Limited resources: Patching can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process, requiring significant investment in terms of time, money, and personnel.
- Complexity: Patching can be a complex process, requiring specialized knowledge and skills.
- Risk of errors: Patching can introduce new errors or vulnerabilities, if not done correctly.
- Resistance to change: Some users may resist changes introduced by patches, requiring significant effort to educate and train them.
Future of Patching
The future of patching is uncertain, but one thing is clear - the importance of patching will only continue to grow. As technology continues to evolve, the need for patching will become more pressing, requiring organizations and individuals to invest in patch management processes and technologies. Some of the most significant trends that will shape the future of patching include:
- Increased use of automation: Automation will play a critical role in patching, reducing the risk of errors and improving the efficiency of the patching process.
- Greater emphasis on security: Security will become an even greater priority in patching, as organizations and individuals seek to protect themselves from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
- More emphasis on user education: User education will become more important, as organizations and individuals seek to educate users about the importance of patching and how to apply patches effectively.
What is patching?
+Patching is the process of creating and applying patches to fix issues, update software, or modify systems.
Why is patching important?
+Patching is important because it helps to address security vulnerabilities, improve performance, and add new features to existing products.
What are the benefits of patching?
+The benefits of patching include improved security, enhanced performance, new features, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
As we conclude, it is essential to remember that patching is a critical component of modern technology. By understanding the benefits, mechanisms, and applications of patching, organizations and individuals can ensure the integrity and functionality of their systems. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with patching, and to continue the conversation on the importance of this process. Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or just starting to learn about patching, we encourage you to join the discussion and explore the many resources available on this topic. Together, we can work to ensure the smooth operation of systems and the security of our data, by embracing the power of patching.
