Intro
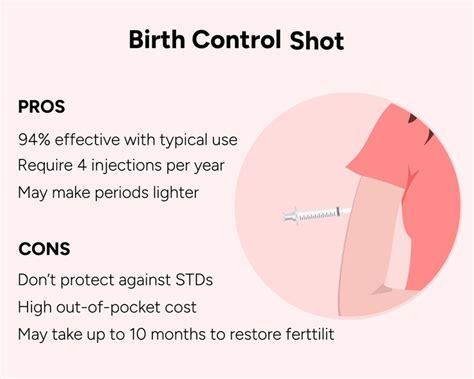
The use of birth control shots, also known as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA), has become increasingly popular among women seeking a convenient and effective method of contraception. Birth control shots are a type of injectable contraceptive that contains a synthetic form of the hormone progesterone. This hormone plays a crucial role in regulating the menstrual cycle and preventing pregnancy. In this article, we will delve into the world of birth control shots, exploring their benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects.
Birth control shots have been shown to be highly effective in preventing pregnancy, with a success rate of over 99%. This is due to the fact that the hormone progesterone works to thicken the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. Additionally, progesterone prevents ovulation, which means that even if sperm were able to reach the egg, there would be no egg to fertilize. The convenience and effectiveness of birth control shots have made them a popular choice among women, particularly those with busy lifestyles or those who have difficulty remembering to take daily birth control pills.
The use of birth control shots has also been linked to several non-contraceptive benefits, including a reduced risk of endometrial and ovarian cancer. The hormone progesterone has been shown to have a protective effect on the lining of the uterus, reducing the risk of abnormal cell growth. Furthermore, birth control shots have been shown to reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease, a condition that can cause infertility and chronic pain. With so many benefits, it's no wonder that birth control shots have become a staple in the world of contraception.
How Birth Control Shots Work
- Prevent ovulation: By suppressing the release of eggs from the ovaries, birth control shots ensure that there is no egg available for fertilization.
- Thicken cervical mucus: The progesterone in birth control shots causes the cervical mucus to thicken, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg.
- Thin the uterine lining: The hormone progesterone causes the uterine lining to thin, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant.
Benefits of Birth Control Shots
The benefits of birth control shots are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of using birth control shots include:- Convenience: Birth control shots are administered every three months, making them a convenient option for women with busy lifestyles.
- Effectiveness: Birth control shots have a success rate of over 99%, making them one of the most effective forms of contraception available.
- Reduced risk of cancer: The hormone progesterone in birth control shots has been shown to have a protective effect on the lining of the uterus, reducing the risk of endometrial and ovarian cancer.
- Reduced risk of pelvic inflammatory disease: Birth control shots have been shown to reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease, a condition that can cause infertility and chronic pain.
Types of Birth Control Shots
- Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA): This is the most common type of birth control shot, containing a synthetic form of the hormone progesterone.
- Norethindrone enanthate: This type of birth control shot contains a synthetic form of the hormone norethindrone, which is similar to progesterone.
- Estradiol cypionate: This type of birth control shot contains a synthetic form of the hormone estrogen, which is often used in combination with progesterone.
Side Effects of Birth Control Shots
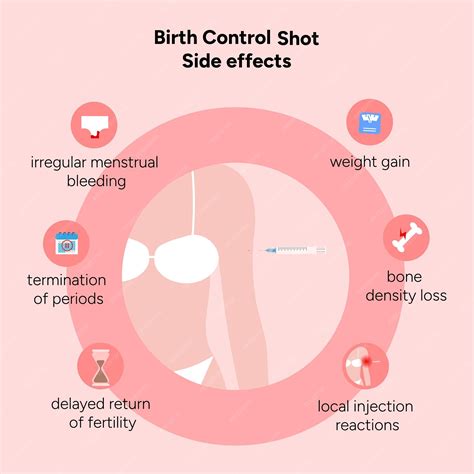
While birth control shots are generally well-tolerated, they can cause some side effects in some women. Some of the most common side effects of birth control shots include:- Weight gain: Some women may experience weight gain while using birth control shots, although this is not always the case.
- Mood changes: The hormone progesterone in birth control shots can cause mood changes, including depression and anxiety.
- Breast tenderness: Some women may experience breast tenderness or swelling while using birth control shots.
- Irregular periods: Birth control shots can cause irregular periods or spotting, especially during the first few months of use.
Who Can Use Birth Control Shots
- Age: Birth control shots are suitable for women of all ages, although they may not be recommended for women under the age of 16.
- Medical conditions: Women with certain medical conditions, such as breast cancer or liver disease, may not be able to use birth control shots.
- Breastfeeding: Birth control shots are not recommended for women who are breastfeeding, as they can affect milk production.
How to Get Birth Control Shots
Getting birth control shots is a relatively straightforward process that involves visiting a healthcare provider. Some of the steps involved in getting birth control shots include:- Scheduling an appointment: Women who are interested in getting birth control shots should schedule an appointment with their healthcare provider.
- Medical history: The healthcare provider will take a medical history to determine whether birth control shots are suitable.
- Injection: The birth control shot is administered via injection, usually in the arm or buttock.
Effectiveness of Birth Control Shots
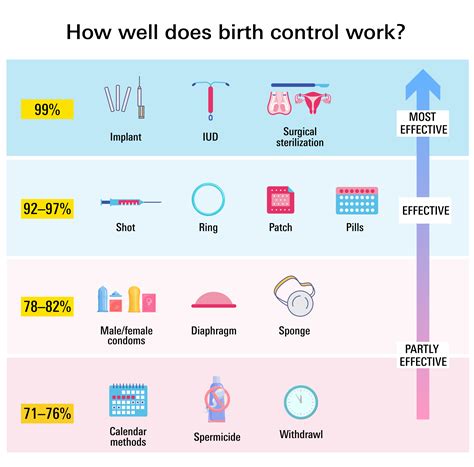
- Timing: Birth control shots should be administered every three months to ensure continuous protection against pregnancy.
- Dose: The dose of progesterone in birth control shots can affect their effectiveness, with higher doses providing greater protection.
- Individual factors: Individual factors, such as weight and medical history, can affect the effectiveness of birth control shots.
Common Myths About Birth Control Shots
There are several common myths about birth control shots that can make it difficult for women to make informed decisions about their contraception. Some of the most common myths include:- Birth control shots cause weight gain: While some women may experience weight gain while using birth control shots, this is not always the case.
- Birth control shots are only for young women: Birth control shots are suitable for women of all ages, although they may not be recommended for women under the age of 16.
- Birth control shots are expensive: Birth control shots are a cost-effective form of contraception, especially when compared to other forms of birth control.
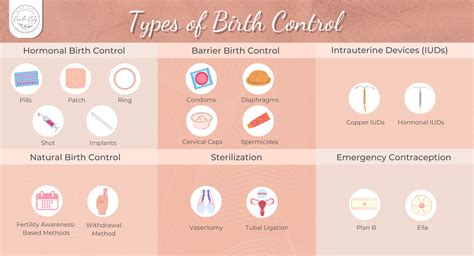
Comparison with Other Forms of Contraception
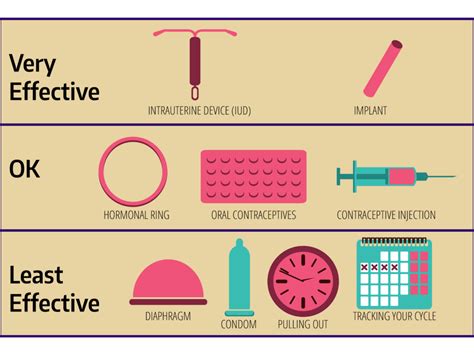
- Birth control pills: Birth control pills are a daily form of contraception that contain a combination of estrogen and progesterone.
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs): IUDs are a long-term form of contraception that are inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
- Condoms: Condoms are a barrier form of contraception that are used to prevent pregnancy and protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, birth control shots are a highly effective and convenient form of contraception that can provide continuous protection against pregnancy for up to three months. While they may not be suitable for all women, they are a versatile option that can be used by women of all ages. If you are considering using birth control shots, it's essential to speak with your healthcare provider to determine whether they are right for you. With their high success rate and numerous benefits, birth control shots are an excellent option for women who want to take control of their reproductive health.We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with birth control shots in the comments section below. Have you used birth control shots in the past? What were your experiences like? Do you have any questions or concerns about using birth control shots? Share your story and help others make informed decisions about their contraception.
What are birth control shots?
+Birth control shots are a type of injectable contraceptive that contains a synthetic form of the hormone progesterone.
How effective are birth control shots?
+Birth control shots have a success rate of over 99%, making them one of the most effective forms of contraception available.
What are the benefits of using birth control shots?
+The benefits of using birth control shots include convenience, effectiveness, and a reduced risk of certain medical conditions, such as endometrial and ovarian cancer.
