Intro
Discover the meaning of blood in phlegm, a symptom of respiratory issues, including coughing up blood, bronchitis, and lung infections, understanding its causes and implications for overall health.
The presence of blood in phlegm can be a concerning and unsettling symptom for many individuals. Phlegm, a thick and sticky substance produced by the mucous membranes in the respiratory tract, is a natural response to irritants, infections, or inflammation in the lungs and airways. However, when blood appears in phlegm, it can indicate an underlying condition that requires medical attention. In this article, we will delve into the possible causes, symptoms, and implications of blood in phlegm, as well as provide guidance on when to seek medical help.
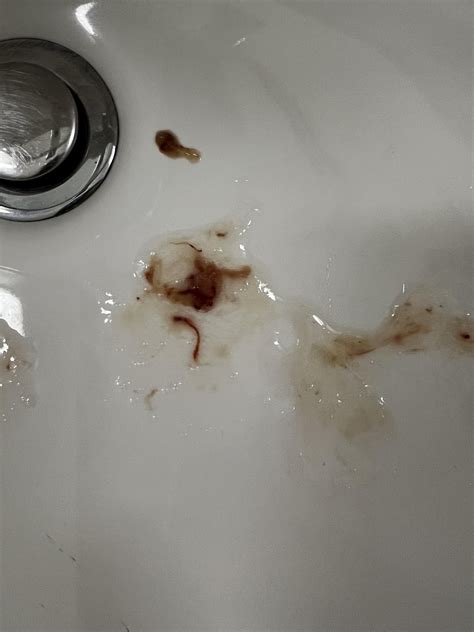
The appearance of blood in phlegm can range from a small streak of red or pink to a more significant amount of bright red or dark brown blood. The color and consistency of the blood can provide valuable clues about the underlying cause. For instance, a small amount of bright red blood may indicate a minor injury or irritation, while a larger amount of dark brown blood could suggest a more serious condition, such as a lung infection or cancer.
Causes of Blood in Phlegm
Respiratory Tract Infections
Respiratory tract infections, such as bronchitis or pneumonia, are common causes of blood in phlegm. These infections can cause inflammation and bleeding in the airways, leading to the production of blood-tinged phlegm. In most cases, the bleeding is minor and resolves on its own with treatment of the underlying infection. However, in some cases, the bleeding can be more significant, and medical attention may be necessary.Chronic Conditions
Chronic conditions, such as COPD or cystic fibrosis, can also cause blood in phlegm. These conditions can lead to chronic inflammation and scarring in the lungs, which can cause bleeding and the production of blood-tinged phlegm. In some cases, the bleeding can be a sign of a more serious complication, such as a lung infection or a pulmonary embolism.Symptoms and Implications

Some common symptoms associated with blood in phlegm include:
- Coughing up blood or blood-tinged phlegm
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Fatigue or weakness
- Fever or chills
Coughing Up Blood
Coughing up blood or blood-tinged phlegm is the most common symptom of blood in phlegm. The amount and color of the blood can provide valuable clues about the underlying cause. For instance, a small amount of bright red blood may indicate a minor injury or irritation, while a larger amount of dark brown blood could suggest a more serious condition.Chest Pain or Discomfort
Chest pain or discomfort is another common symptom associated with blood in phlegm. The pain can range from a mild discomfort to a sharp, stabbing pain, and can be exacerbated by deep breathing, coughing, or movement.Diagnosis and Treatment
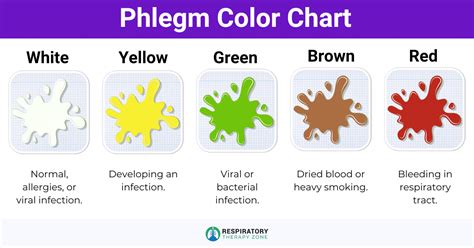
Treatment for blood in phlegm typically involves addressing the underlying cause. For instance, if the bleeding is caused by a respiratory tract infection, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed to treat the infection. In other cases, medication or surgery may be necessary to treat the underlying condition.
Some common treatments for blood in phlegm include:
- Antibiotics or antiviral medications to treat respiratory tract infections
- Bronchodilators or corticosteroids to treat chronic conditions like COPD or asthma
- Pain medication to relieve chest pain or discomfort
- Surgery to treat underlying conditions like lung cancer or a pulmonary embolism
Antibiotics or Antiviral Medications
Antibiotics or antiviral medications are commonly used to treat respiratory tract infections that cause blood in phlegm. These medications can help to reduce the severity of symptoms, prevent complications, and promote recovery.Bronchodilators or Corticosteroids
Bronchodilators or corticosteroids are commonly used to treat chronic conditions like COPD or asthma. These medications can help to reduce inflammation, prevent bronchospasm, and improve lung function.Prevention and Management
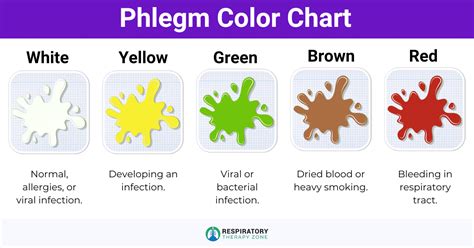
Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to prevent and manage blood in phlegm. Smoking can irritate the lungs and airways, leading to inflammation and bleeding. Quitting smoking can help to reduce the risk of complications and promote recovery.Avoiding Exposure to Pollutants
Avoiding exposure to pollutants or irritants is another important strategy for preventing and managing blood in phlegm. Pollutants, such as dust, chemicals, or secondhand smoke, can irritate the lungs and airways, leading to inflammation and bleeding.What are the common causes of blood in phlegm?
+Blood in phlegm can be caused by respiratory tract infections, chronic conditions like COPD or cystic fibrosis, or lung cancer.
How is blood in phlegm diagnosed?
+Blood in phlegm is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as a chest X-ray or blood tests.
What are the symptoms of blood in phlegm?
+The symptoms of blood in phlegm can include coughing up blood or blood-tinged phlegm, chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, or fever.
In conclusion, blood in phlegm is a concerning symptom that requires medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and implications of blood in phlegm, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage the condition. If you are experiencing blood in phlegm, it is essential to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive proper treatment. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with blood in phlegm in the comments section below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may be experiencing similar symptoms.
