Intro
Learn about normal blood glucose levels range, monitoring, and control. Understand target levels, glucose testing, and managing blood sugar to prevent diabetes complications, including hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The body regulates blood glucose levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and small intestine. When blood glucose levels are within the normal range, the body functions optimally, and the risk of developing chronic diseases is reduced. However, when blood glucose levels are consistently high or low, it can lead to serious health complications. In this article, we will delve into the importance of maintaining normal blood glucose levels, the factors that affect blood glucose levels, and the steps that can be taken to manage blood glucose levels effectively.
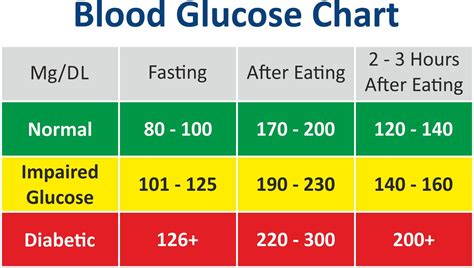
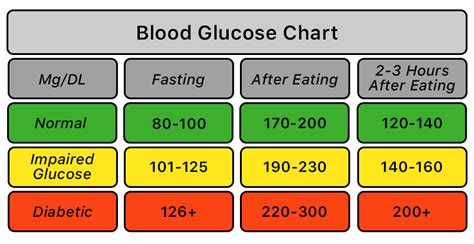
The normal range for blood glucose levels varies depending on the time of day, the last meal consumed, and individual factors such as age and physical activity level. Generally, a normal fasting blood glucose level is between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). After eating, blood glucose levels typically rise, but they should not exceed 140 mg/dL. It is essential to monitor blood glucose levels regularly to ensure they are within the normal range. This is particularly important for individuals with diabetes or those who are at risk of developing the condition.
Understanding blood glucose levels and their impact on overall health is vital for making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and lifestyle. By maintaining normal blood glucose levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Furthermore, managing blood glucose levels effectively can improve energy levels, cognitive function, and overall quality of life. In the following sections, we will explore the factors that affect blood glucose levels, the benefits of maintaining normal blood glucose levels, and the steps that can be taken to manage blood glucose levels effectively.
Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Levels
Physical activity level is another critical factor that affects blood glucose levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can help improve insulin sensitivity, which enables glucose to enter cells more efficiently. Stress and sleep patterns can also impact blood glucose levels. Chronic stress can cause the body to produce more cortisol, a hormone that raises blood glucose levels. Similarly, poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt the body's natural glucose regulation processes.
How Diet Affects Blood Glucose Levels
The type and quantity of food consumed can significantly impact blood glucose levels. Foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, can cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels. On the other hand, foods that are high in protein and healthy fats, such as lean meats and nuts, can help regulate blood glucose levels. The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood glucose levels. Foods with a high GI, such as white rice and white bread, can cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels, while foods with a low GI, such as whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, can help regulate blood glucose levels.Benefits of Maintaining Normal Blood Glucose Levels
Regular physical activity and a balanced diet are essential for maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can help improve insulin sensitivity, which enables glucose to enter cells more efficiently. A balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources can help regulate blood glucose levels and provide the body with the necessary nutrients for optimal function.
Importance of Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining normal blood glucose levels. Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, which enables glucose to enter cells more efficiently. Additionally, physical activity can help reduce stress and anxiety, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall quality of life. The American Diabetes Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, such as running, per week.Steps to Manage Blood Glucose Levels

By following these steps, individuals can manage their blood glucose levels effectively and reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for managing blood glucose levels.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring is essential for managing blood glucose levels effectively. Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly can help individuals identify patterns and trends, make informed decisions about their diet and exercise routine, and adjust their treatment plan as needed. The frequency of monitoring depends on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, the treatment plan, and the individual's lifestyle.Common Complications of High Blood Glucose Levels
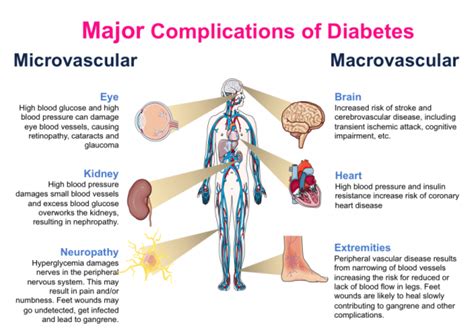
Kidney disease is another common complication of high blood glucose levels. High blood glucose levels can damage the kidneys' filters, leading to kidney failure. Nerve damage, also known as neuropathy, is a common complication of high blood glucose levels. High blood glucose levels can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet. Vision problems, such as blindness, can also occur due to high blood glucose levels.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment are essential for preventing complications of high blood glucose levels. Regular monitoring and screening can help identify individuals who are at risk of developing complications. Early treatment, such as lifestyle changes and medication, can help manage blood glucose levels and prevent complications.Role of Nutrition in Managing Blood Glucose Levels
By incorporating these nutrients into their diet, individuals can help manage their blood glucose levels and reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases.
Importance of Meal Planning
Meal planning is essential for managing blood glucose levels. A well-planned meal can help regulate blood glucose levels, provide sustained energy, and support overall health. The following tips can help individuals plan their meals effectively: * Eat regular meals: Eating regular meals can help regulate blood glucose levels and provide sustained energy. * Choose whole, unprocessed foods: Whole, unprocessed foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. * Include a source of protein: Lean protein sources, such as lean meats, fish, and legumes, can help regulate blood glucose levels. * Limit added sugars: Added sugars, found in foods such as sugary snacks and sweetened beverages, can cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels.By following these tips, individuals can plan their meals effectively and manage their blood glucose levels.
Conclusion and Next Steps

What is the normal range for blood glucose levels?
+The normal range for blood glucose levels varies depending on the time of day, the last meal consumed, and individual factors such as age and physical activity level. Generally, a normal fasting blood glucose level is between 70 and 99 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). After eating, blood glucose levels typically rise, but they should not exceed 140 mg/dL.
What are the benefits of maintaining normal blood glucose levels?
+Maintaining normal blood glucose levels has numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases, improving energy levels, and enhancing cognitive function. When blood glucose levels are within the normal range, the body functions optimally, and the risk of developing conditions such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage is reduced.
How can I manage my blood glucose levels effectively?
+Managing blood glucose levels effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular monitoring, a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management. The following steps can help individuals manage their blood glucose levels effectively: monitor blood glucose levels regularly, eat a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, practice stress-reducing techniques, and get enough sleep each night.
