Intro
Learn about the normal blood glucose range, including target levels, glucose monitoring, and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels to prevent diabetes and related complications.
Maintaining a normal blood glucose range is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the body's primary source of energy. The body regulates blood glucose levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and other organs. Understanding the importance of normal blood glucose levels can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain their health and prevent potential complications.
The importance of maintaining a normal blood glucose range cannot be overstated. When blood glucose levels are within a healthy range, the body can function properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease is reduced. On the other hand, high or low blood glucose levels can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can even be life-threatening if left untreated. Therefore, it is essential to understand what constitutes a normal blood glucose range and how to maintain it.
Blood glucose levels can fluctuate throughout the day, depending on various factors such as diet, physical activity, and sleep patterns. Normal blood glucose levels typically range from 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for individuals without diabetes. However, these levels can vary slightly depending on the individual and the time of day. For example, blood glucose levels tend to be higher after eating and lower after fasting or exercise. Understanding these fluctuations can help individuals better manage their blood glucose levels and maintain a healthy range.
Understanding Blood Glucose Levels
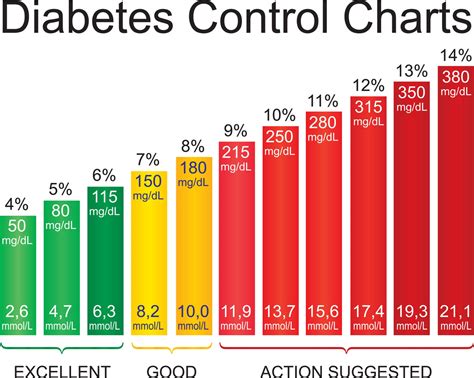
Understanding blood glucose levels is crucial for maintaining a healthy range. Blood glucose levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and can be affected by various factors such as diet, physical activity, and sleep patterns. Normal blood glucose levels typically range from 70 to 140 mg/dL for individuals without diabetes. However, these levels can vary slightly depending on the individual and the time of day. For example, blood glucose levels tend to be higher after eating and lower after fasting or exercise.
Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect blood glucose levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can raise blood glucose levels, while eating protein-rich or high-fiber foods can help lower them. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood glucose levels, while a sedentary lifestyle can raise them. * Sleep patterns: Poor sleep quality or duration can disrupt blood glucose regulation, leading to higher levels. * Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood glucose levels, while relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga can help lower them. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids or certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood glucose levels.Maintaining a Normal Blood Glucose Range

Maintaining a normal blood glucose range requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits and, if necessary, medical treatment. Here are some tips for maintaining a healthy blood glucose range:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood glucose levels.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood glucose levels.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring is an essential tool for maintaining a normal blood glucose range. There are several ways to monitor blood glucose levels, including: * Fasting blood glucose test: Measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast. * Postprandial blood glucose test: Measures blood glucose levels after eating. * Random blood glucose test: Measures blood glucose levels at any time of day. * Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): Uses a small device to track blood glucose levels throughout the day.Normal Blood Glucose Range for Different Age Groups

Normal blood glucose ranges can vary slightly depending on age. Here are some general guidelines for normal blood glucose ranges for different age groups:
- Newborns (0-1 month): 54-145 mg/dL
- Infants (1-12 months): 60-140 mg/dL
- Toddlers (1-2 years): 65-135 mg/dL
- Children (6-12 years): 70-130 mg/dL
- Adolescents (13-18 years): 70-140 mg/dL
- Adults (19-65 years): 70-140 mg/dL
- Older adults (66 years and older): 80-150 mg/dL
Implications of Abnormal Blood Glucose Levels
Abnormal blood glucose levels can have serious implications for overall health. High blood glucose levels can lead to: * Diabetes: A chronic condition characterized by high blood glucose levels. * Heart disease: High blood glucose levels can increase the risk of heart disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure. * Kidney disease: High blood glucose levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney disease. * Nerve damage: High blood glucose levels can damage nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain. * Blindness: High blood glucose levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blindness.Diagnosing and Treating Abnormal Blood Glucose Levels
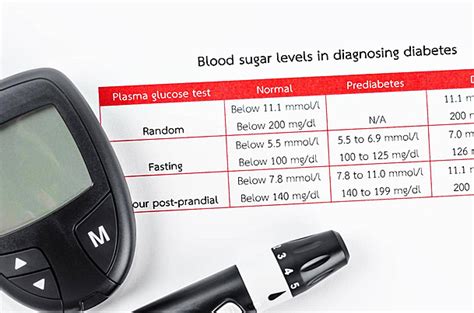
Diagnosing and treating abnormal blood glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach. Here are some steps for diagnosing and treating abnormal blood glucose levels:
- Get tested: If you are experiencing symptoms of abnormal blood glucose levels, such as increased thirst or urination, blurred vision, or slow healing of cuts and wounds, get tested.
- Consult a healthcare provider: If your test results indicate abnormal blood glucose levels, consult a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
- Develop a treatment plan: Work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that may include lifestyle changes, medication, or insulin therapy.
- Monitor blood glucose levels: Regularly monitor blood glucose levels to ensure that treatment is effective and to make adjustments as needed.
Preventing Abnormal Blood Glucose Levels
Preventing abnormal blood glucose levels requires a proactive approach. Here are some tips for preventing abnormal blood glucose levels: * Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood glucose levels. * Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. * Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood glucose levels. * Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining a normal blood glucose range is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that affect blood glucose levels and taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy range, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease. If you are concerned about your blood glucose levels or are experiencing symptoms of abnormal blood glucose levels, consult a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with maintaining a normal blood glucose range. What strategies have you found to be most effective? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? Share your story in the comments below, and let's work together to promote healthy blood glucose levels and overall well-being.
What is a normal blood glucose range?
+A normal blood glucose range typically ranges from 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for individuals without diabetes.
What factors can affect blood glucose levels?
+Several factors can affect blood glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, sleep patterns, stress, and certain medications.
How can I maintain a normal blood glucose range?
+To maintain a normal blood glucose range, focus on eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and managing stress.
What are the implications of abnormal blood glucose levels?
+Abnormal blood glucose levels can lead to serious health complications, including diabetes, heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness.
How can I diagnose and treat abnormal blood glucose levels?
+Diagnosing and treating abnormal blood glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach, including getting tested, consulting a healthcare provider, developing a treatment plan, and monitoring blood glucose levels.
