Intro
Understand the 5 diabetes levels, from prediabetes to type 2, and learn about blood sugar management, insulin resistance, and glucose control to prevent complications and promote healthy living with diabetes diagnosis and treatment options.
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and understanding the different levels of diabetes is crucial for effective management and treatment. The condition is characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to a range of complications if left unchecked. In this article, we will delve into the world of diabetes, exploring the different levels of the condition, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Diabetes is a complex condition that can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. It is essential to understand the different levels of diabetes to develop an effective treatment plan. The levels of diabetes are typically categorized based on the severity of the condition, with each level requiring a unique approach to management. By understanding the different levels of diabetes, individuals can take control of their condition and make informed decisions about their health.
The importance of understanding diabetes levels cannot be overstated. Diabetes is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, and it is essential to take a proactive approach to managing the condition. By recognizing the different levels of diabetes, individuals can identify the early warning signs of the condition and take steps to prevent its progression. In this article, we will explore the different levels of diabetes, including the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for each level.
Understanding Diabetes Levels
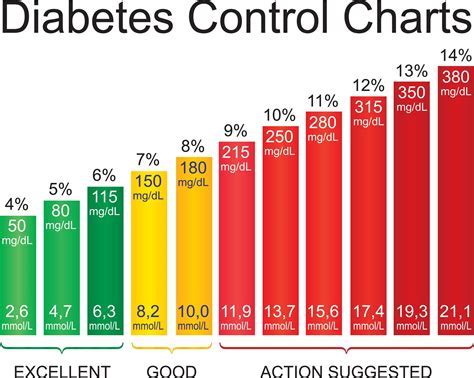
Diabetes levels are typically categorized into five distinct levels, each with its unique characteristics and treatment requirements. The five levels of diabetes are:
- Normal blood sugar levels
- Prediabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes
- Gestational diabetes
Each level of diabetes requires a unique approach to management, and understanding the different levels is essential for effective treatment.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels are typically defined as a fasting blood glucose level of less than 100 mg/dL. Individuals with normal blood sugar levels are not at risk of developing diabetes, and they do not require any special treatment or management. However, it is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to prevent the development of insulin resistance and diabetes.Prediabetes
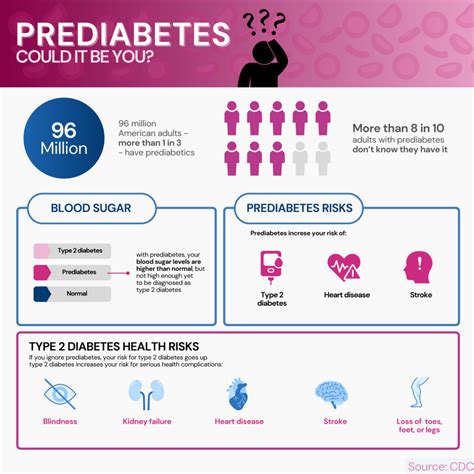
Prediabetes is a condition where the blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. Individuals with prediabetes are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and they require lifestyle changes and medical treatment to prevent the progression of the condition. Prediabetes is often asymptomatic, and it can only be detected through a blood test.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all diabetes cases. It is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body is unable to effectively use insulin, and impaired insulin secretion. Type 2 diabetes can be managed through lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, and medical treatment, including oral medications and insulin therapy.Type 1 Diabetes

Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. It is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, although it can also occur in adults. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin therapy to manage blood sugar levels, and individuals with the condition must carefully monitor their blood sugar levels and adjust their insulin doses accordingly.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester. It is caused by hormonal changes and insulin resistance, and it can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Gestational diabetes requires careful management, including lifestyle changes and medical treatment, to prevent complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy.Causes and Risk Factors

The causes and risk factors for diabetes vary depending on the type of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is caused by an autoimmune response, while type 2 diabetes is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, including obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet. Gestational diabetes is caused by hormonal changes and insulin resistance during pregnancy.
Some common risk factors for diabetes include:
- Family history of diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Unhealthy diet
- Age
- Ethnicity
Understanding the causes and risk factors for diabetes is essential for preventing the condition and developing effective treatment plans.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms of diabetes include: * Increased thirst and urination * Fatigue * Blurred vision * Slow healing of cuts and wounds * Tingling or numbness in the hands and feetDiabetes can be diagnosed through a blood test, which measures the level of glucose in the blood. The diagnosis of diabetes is typically based on the following criteria:
- Fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) of 200 mg/dL or higher
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level of 6.5% or higher
Treatment and Management

The treatment and management of diabetes depend on the type and severity of the condition. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin therapy, while type 2 diabetes can be managed through lifestyle changes and medical treatment. Gestational diabetes requires careful management, including lifestyle changes and medical treatment, to prevent complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Some common treatment options for diabetes include:
- Insulin therapy
- Oral medications
- Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise
- Monitoring of blood sugar levels
It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan and manage the condition.
Complications and Prevention
Diabetes can increase the risk of complications, including: * Heart disease * Kidney disease * Nerve damage * Blindness * AmputationsPreventing complications requires careful management of the condition, including lifestyle changes and medical treatment. Some ways to prevent complications include:
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
- Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider
Living with Diabetes

Living with diabetes requires a proactive approach to managing the condition. Individuals with diabetes must carefully monitor their blood sugar levels, adjust their insulin doses, and make lifestyle changes to prevent complications. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan and manage the condition.
Some tips for living with diabetes include:
- Staying informed about the condition and its management
- Building a support network of family and friends
- Setting realistic goals and expectations
- Prioritizing self-care and stress management
By taking a proactive approach to managing diabetes, individuals can live a long and healthy life.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding the different levels of diabetes is essential for effective management and treatment. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for each level of diabetes, individuals can take control of their condition and make informed decisions about their health. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan and manage the condition.We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with diabetes in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. By working together, we can promote awareness and understanding of diabetes and improve the lives of individuals living with the condition.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
+The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
How is diabetes diagnosed?
+Diabetes can be diagnosed through a blood test, which measures the level of glucose in the blood. The diagnosis of diabetes is typically based on the following criteria: fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher, oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) of 200 mg/dL or higher, and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level of 6.5% or higher.
What are the treatment options for diabetes?
+The treatment options for diabetes depend on the type and severity of the condition. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin therapy, while type 2 diabetes can be managed through lifestyle changes and medical treatment. Gestational diabetes requires careful management, including lifestyle changes and medical treatment, to prevent complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
