Intro
Discover the significance of Blood Sugar 90 Levels, normal blood glucose ranges, and managing diabetes with healthy habits, diet, and monitoring blood sugar levels to maintain optimal glucose control and prevent complications.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, and understanding what blood sugar 90 levels mean can help individuals take control of their health. Blood sugar levels refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood, and normal levels typically range from 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). A blood sugar level of 90 mg/dL is considered within the normal range, but it's essential to understand the context and factors that influence blood sugar levels.
For individuals with diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of managing the condition. Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by high blood sugar levels, which can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage if left unmanaged. The American Diabetes Association recommends that individuals with diabetes aim for a blood sugar level of less than 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals. A blood sugar level of 90 mg/dL is well within these guidelines, indicating good blood sugar control.
However, for individuals without diabetes, a blood sugar level of 90 mg/dL may not be as significant, as it's essential to consider the timing and context of the reading. For example, a blood sugar level of 90 mg/dL after an overnight fast may be considered normal, but the same reading after a meal may indicate impaired glucose tolerance. Understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels, such as diet, physical activity, and stress, can help individuals make informed decisions about their health.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels

Blood sugar levels are influenced by various factors, including diet, physical activity, and hormonal changes. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating glucose uptake in cells. In individuals with diabetes, the pancreas either doesn't produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes) or is unable to effectively use insulin (type 2 diabetes), leading to high blood sugar levels.
Factors That Influence Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate foods or drinks can cause a spike in blood sugar levels. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. * Stress: Stress can raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels.Managing Blood Sugar Levels

Managing blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, medication (if necessary), and regular monitoring. For individuals with diabetes, working with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan is essential. This may involve:
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly to track progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Following a healthy diet that is rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Taking medication as prescribed, such as metformin or insulin, to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Good Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining good blood sugar control can have numerous benefits, including: * Reduced risk of complications: Good blood sugar control can help prevent or delay the onset of complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. * Improved energy levels: Regulating blood sugar levels can help improve energy levels and reduce fatigue. * Enhanced cognitive function: Good blood sugar control may help improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of dementia. * Better overall health: Managing blood sugar levels can help individuals maintain a healthy weight, improve sleep quality, and reduce stress levels.Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
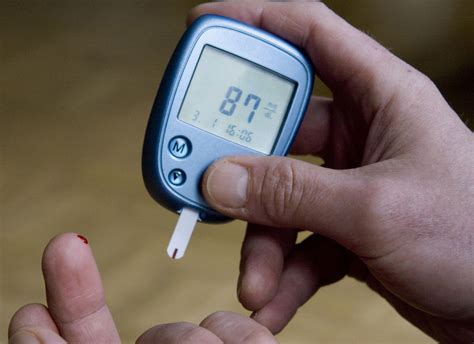
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of managing diabetes. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including:
- Fasting blood sugar tests: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
- Postprandial blood sugar tests: This test measures blood sugar levels after a meal.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): This involves wearing a small device that tracks blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) tests: This test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
Interpreting Blood Sugar Results
Interpreting blood sugar results requires understanding the context and timing of the reading. For example: * A fasting blood sugar level of 90 mg/dL may be considered normal, but a postprandial level of 90 mg/dL may indicate impaired glucose tolerance. * A CGM reading of 90 mg/dL may indicate good blood sugar control, but a reading of 180 mg/dL after a meal may indicate a need for adjustments to the treatment plan.Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels

Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels requires a long-term commitment to lifestyle changes and regular monitoring. Individuals can take several steps to maintain healthy blood sugar levels, including:
- Eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods and low in added sugars and refined carbohydrates.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or cycling, to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Getting enough sleep and practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga.
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Individuals with diabetes or prediabetes should avoid several common mistakes, including: * Skipping meals or snacks, which can lead to low blood sugar levels. * Consuming high-carbohydrate foods or drinks, which can cause a spike in blood sugar levels. * Not monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, which can make it difficult to track progress and make adjustments to the treatment plan. * Not taking medication as prescribed, which can lead to poor blood sugar control and increased risk of complications.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Individuals with diabetes or prediabetes should work with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that incorporates lifestyle changes, medication (if necessary), and regular monitoring. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels and taking steps to maintain good blood sugar control, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing blood sugar levels in the comments below. If you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns about blood sugar levels or diabetes management, please don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance.
What is a normal blood sugar level?
+A normal blood sugar level typically ranges from 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). However, this can vary depending on the individual and the timing of the reading.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on the individual and their treatment plan. Generally, individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels at least once a day, but this can vary depending on their specific needs and goals.
What are the risks of high blood sugar levels?
+High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. It's essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan to manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Can I manage my blood sugar levels through diet and exercise alone?
+For some individuals, diet and exercise may be enough to manage blood sugar levels. However, for others, medication may be necessary to achieve good blood sugar control. It's essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment.
How can I prevent low blood sugar levels?
+Preventing low blood sugar levels requires careful planning and monitoring. Individuals with diabetes should eat regular meals, avoid skipping meals or snacks, and monitor their blood sugar levels regularly to track progress and make adjustments to their treatment plan as needed.
