Intro
Monitor your blood sugar levels after meals with our chart, tracking glucose spikes and dips to manage diabetes, insulin resistance, and metabolic health, optimizing your diet and lifestyle for stable blood glucose control.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. The body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels is a complex process, involving various organs and hormones. After a meal, blood sugar levels can fluctuate significantly, and understanding these changes is essential for managing diabetes and preventing related complications.
The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels cannot be overstated, as it helps individuals with diabetes to adjust their diet, exercise, and medication to maintain optimal glucose levels. A blood sugar levels after meal chart can be a valuable tool in this regard, providing a visual representation of how different foods and activities affect blood glucose levels. By analyzing this data, individuals can make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment plan, ultimately reducing the risk of long-term health problems.
For individuals without diabetes, understanding how blood sugar levels work can also be beneficial, as it can help prevent the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. A healthy diet and regular physical activity are key components of blood sugar management, and being aware of how different factors influence glucose levels can encourage individuals to make positive lifestyle changes. Furthermore, a blood sugar levels after meal chart can serve as a motivational tool, helping individuals to track their progress and stay committed to their health goals.
Blood Sugar Levels After Meal Chart: Understanding the Basics
To create an effective blood sugar levels after meal chart, it is essential to understand the factors that influence blood glucose levels. The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels, with high-GI foods causing a more rapid increase. Carbohydrates, in particular, have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, as they are broken down into glucose during digestion. The type and amount of carbohydrates consumed, as well as the presence of fiber, protein, and healthy fats, can all affect the glycemic response.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
The following factors can influence blood sugar levels after a meal: * Type and amount of carbohydrates consumed * Presence of fiber, protein, and healthy fats * Glycemic index of foods * Physical activity levels * Medication and insulin therapy (for individuals with diabetes) * Hormonal changes and stress levelsCreating a Blood Sugar Levels After Meal Chart

To create a blood sugar levels after meal chart, individuals can follow these steps:
- Monitor blood glucose levels: Use a glucometer to track blood sugar levels at different times of the day, including before and after meals.
- Record food intake: Keep a food diary to track the types and amounts of foods consumed, including carbohydrates, protein, and fat.
- Note physical activity: Record physical activity levels, including duration and intensity.
- Track medication and insulin: For individuals with diabetes, note the type and dosage of medication or insulin taken.
- Analyze data: Review the data to identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels, and adjust the diet and treatment plan accordingly.
Interpreting the Chart
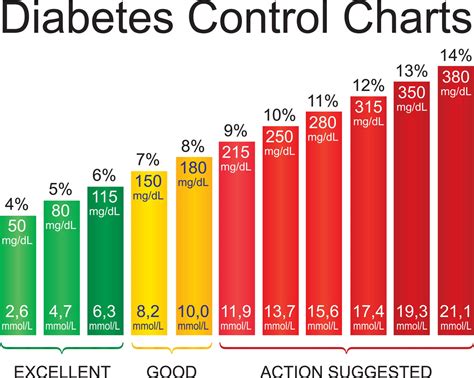
When interpreting the blood sugar levels after meal chart, consider the following: * **Target range**: Aim for a blood sugar level between 70-180 mg/dL after meals. * **Peak and trough**: Identify the peak and trough blood sugar levels after meals, and adjust the diet and treatment plan to minimize extreme fluctuations. * **Patterns and trends**: Look for patterns and trends in blood sugar levels, such as increased levels after consuming certain foods or at specific times of the day.Managing Blood Sugar Levels After Meals

To manage blood sugar levels after meals, consider the following strategies:
- Choose low-GI foods: Select foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Include protein and healthy fats: Add protein and healthy fats to meals to slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and reduce the glycemic response.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent dehydration.
- Be physically active: Engage in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Managing Blood Sugar Levels
The benefits of managing blood sugar levels include: * **Reduced risk of complications**: Lowering the risk of long-term health problems, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. * **Improved energy levels**: Maintaining stable energy levels and reducing fatigue. * **Enhanced mental clarity**: Improving cognitive function and reducing the risk of dementia. * **Better overall health**: Promoting overall health and well-being, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.Common Mistakes to Avoid

When creating and using a blood sugar levels after meal chart, avoid the following common mistakes:
- Inconsistent monitoring: Failing to monitor blood glucose levels regularly, or not tracking food intake and physical activity.
- Inaccurate data: Recording inaccurate or incomplete data, which can lead to incorrect conclusions and adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Not adjusting the treatment plan: Failing to adjust the diet, medication, or insulin therapy based on the data, which can lead to poor blood sugar control.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Creating and using a blood sugar levels after meal chart can be a powerful tool for managing diabetes and promoting overall health. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels, tracking data, and making informed decisions, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Remember to stay consistent, accurate, and proactive in managing blood sugar levels, and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.What is the ideal blood sugar level after a meal?
+The ideal blood sugar level after a meal is between 70-180 mg/dL. However, this range may vary depending on individual factors, such as the type and amount of food consumed, physical activity levels, and medication or insulin therapy.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood sugar levels depends on individual factors, such as the type and severity of diabetes, medication or insulin therapy, and physical activity levels. Generally, it is recommended to monitor blood sugar levels at least 4-6 times a day, including before and after meals.
What are the benefits of using a blood sugar levels after meal chart?
+The benefits of using a blood sugar levels after meal chart include improved blood sugar control, reduced risk of complications, and enhanced overall health and well-being. By tracking and analyzing data, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, medication, and lifestyle, and take control of their health.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and information on managing blood sugar levels after meals. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can promote healthy living and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
