Intro
Lower blood sugar naturally with 5 expert tips, managing diabetes through healthy diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes, improving insulin sensitivity and glucose control.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts energy levels, weight management, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. With the increasing prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes, understanding how to manage blood sugar has become more important than ever. By adopting a few simple yet effective strategies, individuals can significantly improve their blood sugar control and reduce the risk of related health issues. This article aims to provide readers with actionable tips and insights to help them achieve and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
The importance of managing blood sugar cannot be overstated, as uncontrolled levels can lead to a range of complications, from mild symptoms like fatigue and blurred vision to severe conditions such as kidney damage, nerve damage, and even blindness. Moreover, the impact of blood sugar on mental health should not be overlooked, as fluctuations in blood glucose levels can affect mood, cognitive function, and overall quality of life. By taking proactive steps to manage blood sugar, individuals can mitigate these risks and enjoy better health and well-being.
For those looking to improve their blood sugar control, it's essential to understand that small, consistent changes can add up over time. Whether it's adjusting dietary habits, increasing physical activity, or exploring stress management techniques, every effort counts. This article will delve into practical strategies for managing blood sugar, providing readers with a comprehensive guide to achieving and maintaining healthy levels. From the benefits of regular exercise and balanced nutrition to the importance of monitoring and stress reduction, we'll cover it all.
Understanding Blood Sugar

Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, typically peaking after meals and decreasing during fasting periods. For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are usually between 70 and 140 mg/dL after eating and below 100 mg/dL when fasting. Understanding these ranges is crucial for identifying potential issues and taking corrective action. For those with diabetes, the goal is to keep blood sugar levels as close to the normal range as possible to prevent complications.Tip 1: Monitor Your Blood Sugar Regularly
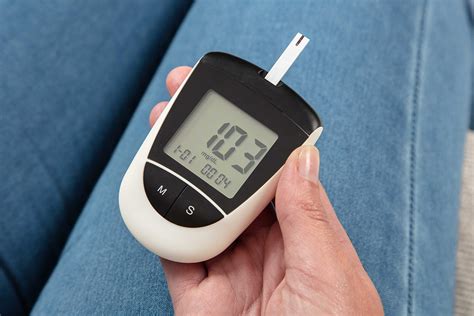
How to Monitor Blood Sugar
Monitoring blood sugar involves using a glucose meter to measure the concentration of glucose in the blood. This is typically done by pricking the finger with a lancet to obtain a small blood sample, which is then placed on a test strip and inserted into the meter. The process is relatively painless and provides immediate results. The frequency of monitoring depends on the individual's health status and treatment plan but usually involves checking levels before meals, after meals, and at bedtime.Tip 2: Adopt a Balanced Diet
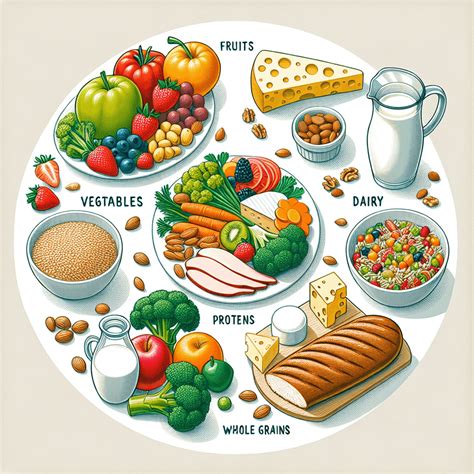

Nutritional Tips for Blood Sugar Control
- **Choose Complex Carbohydrates**: Foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are rich in fiber, which slows down the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing sudden spikes. - **Incorporate Lean Proteins**: Proteins like poultry, fish, and legumes can help regulate blood sugar levels and provide a feeling of fullness. - **Healthy Fats Are Essential**: Foods rich in healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.Tip 3: Stay Hydrated

Benefits of Hydration
- **Regulates Blood Sugar**: Helps in flushing out excess glucose. - **Boosts Energy**: Even mild dehydration can cause fatigue; staying hydrated ensures better energy levels. - **Supports Overall Health**: Essential for the proper functioning of all bodily systems.Tip 4: Engage in Regular Physical Activity

Exercise Tips for Blood Sugar Control
- **Start Slow**: Begin with short sessions and gradually increase duration and intensity. - **Find an Activity You Enjoy**: This will make it easier to stick to a regular exercise routine. - **Incorporate Both Aerobic and Strength Training**: Both types of exercise offer unique benefits for blood sugar management and overall health.Tip 5: Manage Stress

Stress Reduction Techniques
- **Meditation and Mindfulness**: Help in reducing stress and improving mental health. - **Yoga**: Combines physical movement with deep breathing and meditation techniques. - **Deep Breathing Exercises**: Simple and effective way to reduce stress and improve oxygen flow.In conclusion, managing blood sugar levels is a multifaceted process that involves regular monitoring, dietary adjustments, hydration, physical activity, and stress management. By incorporating these strategies into daily life, individuals can significantly improve their blood sugar control, reducing the risk of diabetes and related health complications. It's essential to remember that small changes can add up over time, and seeking support from healthcare providers and loved ones can make the journey to better health more manageable and successful.
We invite you to share your experiences and tips for managing blood sugar in the comments below. Your insights can help others on their journey to better health. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from these tips.
What are normal blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL after eating and below 100 mg/dL when fasting for individuals without diabetes.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar?
+The frequency of monitoring blood sugar depends on your health status and treatment plan, but it usually involves checking levels before meals, after meals, and at bedtime.
What foods are best for managing blood sugar?
+Foods that are rich in fiber and nutrients, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, are best for managing blood sugar.
