Intro
Discover 5 key facts about Metoclopramide, a medication for nausea, vomiting, and gastroparesis, exploring its uses, side effects, and interactions, including dopamine receptor antagonism and gastrointestinal motility regulation.
Metoclopramide is a medication that has been widely used for several decades, primarily for its antiemetic and prokinetic properties. It is known to help manage nausea, vomiting, and conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Despite its effectiveness, metoclopramide has a complex profile, with both benefits and risks that patients and healthcare providers should be aware of. Here are five key facts about metoclopramide that highlight its importance, usage, and considerations.
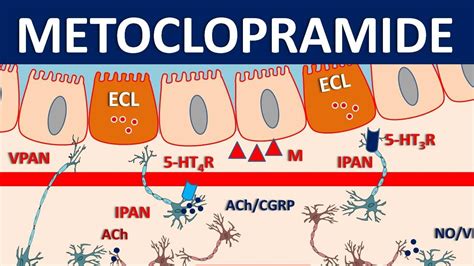
Metoclopramide works by affecting the upper digestive tract to increase the movement of the stomach and intestines, helping to speed up the passage of food through the stomach into the intestines. This action is beneficial for patients suffering from gastroparesis, a condition where the stomach takes too long to empty its contents. The drug also has a central action in the brain, which helps to prevent nausea and vomiting, making it useful for patients undergoing chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or those experiencing postoperative nausea.
The medication is available in various forms, including tablets, oral solutions, and injectable solutions, allowing for flexibility in administration. This versatility is particularly useful in different clinical settings, from outpatient management of GERD to the inpatient management of severe nausea and vomiting. However, the choice of formulation and the dosing regimen should be carefully considered based on the patient's specific condition, age, and other medications they might be taking.
One of the critical aspects of metoclopramide is its side effect profile. While generally well-tolerated, it can cause a range of side effects, from mild drowsiness and fatigue to more severe reactions such as dystonic reactions, particularly in children and young adults. A rare but serious side effect is tardive dyskinesia, a condition characterized by involuntary, repetitive body movements. This risk is higher with long-term use, emphasizing the need for careful consideration and monitoring when prescribing metoclopramide for extended periods.
The use of metoclopramide has evolved over the years, with ongoing research and clinical guidelines influencing its prescription patterns. For instance, its use in pregnancy is approached with caution, particularly in the first trimester, due to the potential risks to the fetus. Similarly, in pediatric patients, the dosage and duration of treatment must be carefully managed to minimize the risk of side effects. These considerations underscore the importance of healthcare providers staying updated on the latest recommendations and guidelines for metoclopramide use.
Introduction to Metoclopramide
Benefits of Metoclopramide

Working Mechanism of Metoclopramide
Steps for Taking Metoclopramide

Practical Examples and Statistical Data

Key Considerations for Metoclopramide Use
When considering metoclopramide for treatment, several key factors must be taken into account. These include the patient's medical history, current medications, and the specific condition being treated. For example, patients with a history of depression or Parkinson's disease may require careful monitoring due to the potential for metoclopramide to exacerbate these conditions. Additionally, the drug's potential for interaction with other medications, such as anticholinergics, should be considered to avoid adverse effects.SEO Optimization for Metoclopramide

Encouraging Engagement

Final Thoughts on Metoclopramide

What is metoclopramide used for?
+Metoclopramide is used to treat nausea, vomiting, and conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and gastroparesis.
How does metoclopramide work?
+Metoclopramide works by affecting the upper digestive tract to increase the movement of the stomach and intestines and by blocking dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone to prevent nausea and vomiting.
What are the common side effects of metoclopramide?
+Common side effects include drowsiness, fatigue, and headache. Serious side effects can include dystonic reactions and tardive dyskinesia, especially with long-term use.
