Intro
Discover how Liver Function Blood Tests diagnose liver health, assessing ALT, AST, and bilirubin levels to detect damage, disease, or dysfunction, and understand the importance of liver function tests in monitoring overall well-being.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health. It is responsible for filtering toxins, regulating blood sugar levels, and producing essential proteins. However, liver damage or disease can occur due to various factors, such as viral infections, excessive alcohol consumption, or genetic disorders. Liver function blood tests are a crucial diagnostic tool used to assess the liver's health and detect any potential problems. These tests can help identify liver damage or disease at an early stage, allowing for prompt treatment and preventing further complications.
Liver function blood tests are commonly used to evaluate the liver's ability to perform its normal functions. These tests measure the levels of various enzymes, proteins, and other substances in the blood that are produced or cleared by the liver. Abnormal results can indicate liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer. Additionally, liver function blood tests can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track the progression of liver disease over time.
The importance of liver function blood tests cannot be overstated. Liver disease can be asymptomatic in its early stages, and if left untreated, it can lead to severe complications, such as liver failure or even death. By detecting liver damage or disease early on, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent further damage. Furthermore, liver function blood tests can help identify individuals who are at risk of developing liver disease, allowing for early intervention and prevention.
Liver Function Tests: An Overview
Liver function tests are a group of blood tests that measure the levels of various enzymes, proteins, and other substances in the blood. These tests can be used to evaluate the liver's ability to perform its normal functions, such as filtering toxins, regulating blood sugar levels, and producing essential proteins. The most common liver function tests include:
- Alanine transaminase (ALT)
- Aspartate transaminase (AST)
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT)
- Bilirubin
- Albumin
- Prothrombin time (PT)
Each of these tests provides valuable information about the liver's health and can help diagnose liver damage or disease.
Alanine Transaminase (ALT)
ALT is an enzyme found primarily in the liver, but also in smaller amounts in the kidneys, heart, and muscles. Elevated ALT levels in the blood can indicate liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis. ALT is a sensitive indicator of liver health and is often used as a screening test for liver disease.Aspartate Transaminase (AST)
AST is another enzyme found in the liver, as well as in the heart, muscles, and kidneys. Like ALT, elevated AST levels in the blood can indicate liver damage or disease. However, AST is not as specific to the liver as ALT and can be elevated in other conditions, such as heart disease or muscle damage.Interpreting Liver Function Test Results

Interpreting liver function test results requires careful consideration of the individual's medical history, physical examination, and other diagnostic tests. Abnormal results can indicate liver damage or disease, but can also be influenced by other factors, such as medication use or underlying medical conditions.
- Elevated ALT and AST levels can indicate liver damage or disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Elevated ALP levels can indicate bone or liver disease, such as osteomalacia or cholestasis.
- Elevated GGT levels can indicate liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, as well as other conditions, such as pancreatitis or kidney disease.
- Elevated bilirubin levels can indicate liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, as well as other conditions, such as hemolytic anemia.
- Low albumin levels can indicate liver disease, such as cirrhosis, as well as other conditions, such as nephrotic syndrome or malnutrition.
- Prolonged PT can indicate liver disease, such as cirrhosis, as well as other conditions, such as bleeding disorders or vitamin K deficiency.
Liver Function Tests in Clinical Practice
Liver function tests are widely used in clinical practice to diagnose and monitor liver disease. These tests can help identify individuals who are at risk of developing liver disease, allowing for early intervention and prevention. Additionally, liver function tests can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track the progression of liver disease over time.Liver Disease: Causes and Risk Factors
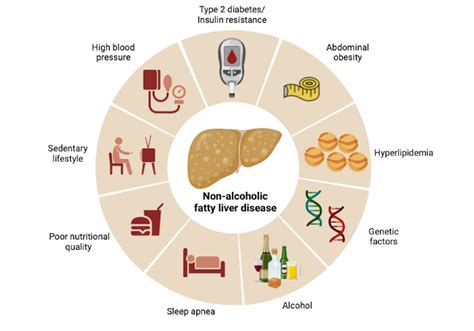
Liver disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Viral infections, such as hepatitis B and C
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Genetic disorders, such as hemochromatosis or Wilson's disease
- Obesity and metabolic syndrome
- Certain medications, such as acetaminophen or statins
- Environmental toxins, such as pesticides or heavy metals
Individuals who are at risk of developing liver disease include:
- Those with a family history of liver disease
- Those who are overweight or obese
- Those who have a history of excessive alcohol consumption
- Those who have been exposed to viral infections, such as hepatitis B or C
- Those who have been exposed to environmental toxins, such as pesticides or heavy metals
Prevention and Management of Liver Disease
Prevention and management of liver disease require a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical treatment, and regular monitoring. Lifestyle modifications include:- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Avoiding exposure to environmental toxins
- Practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of viral infections
- Getting vaccinated against hepatitis A and B
Medical treatment for liver disease depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Antiviral medications for hepatitis B and C
- Corticosteroids for autoimmune hepatitis
- Medications to reduce inflammation and scarring in the liver
- Surgery or liver transplantation in severe cases
Regular monitoring of liver function tests can help track the progression of liver disease and adjust treatment as needed.
Liver Transplantation: A Treatment Option for End-Stage Liver Disease
Liver transplantation is a treatment option for individuals with end-stage liver disease. This procedure involves replacing the damaged liver with a healthy liver from a donor. Liver transplantation can be a life-saving procedure for individuals with severe liver disease, but it is a complex and risky procedure that requires careful consideration and preparation.
The criteria for liver transplantation include:
- End-stage liver disease, such as cirrhosis or liver cancer
- Severe liver dysfunction, such as jaundice or coagulopathy
- Failure of medical treatment to manage liver disease
- Presence of complications, such as variceal bleeding or hepatic encephalopathy
The liver transplantation procedure involves:
- Removing the damaged liver
- Implanting the healthy donor liver
- Connecting the blood vessels and bile ducts to the new liver
After liver transplantation, individuals require lifelong immunosuppression to prevent rejection of the transplanted liver. Regular monitoring of liver function tests and adjustment of immunosuppressive medications can help prevent complications and ensure the long-term success of the transplant.
Future Directions in Liver Disease Diagnosis and Treatment
Future directions in liver disease diagnosis and treatment include the development of new biomarkers and imaging techniques to detect liver disease at an early stage. Additionally, research is ongoing to develop new treatments for liver disease, such as gene therapy and stem cell transplantation.New biomarkers, such as microRNAs and circulating tumor DNA, may offer improved sensitivity and specificity for detecting liver disease. Imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound, may provide more accurate and detailed information about liver morphology and function.
Gene therapy and stem cell transplantation may offer new treatment options for liver disease, particularly for genetic disorders or severe liver damage. These emerging technologies hold promise for improving the diagnosis and treatment of liver disease, but further research is needed to fully realize their potential.
Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, liver function blood tests are a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing liver health and detecting liver damage or disease. These tests can help identify individuals who are at risk of developing liver disease, allowing for early intervention and prevention. Additionally, liver function tests can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and track the progression of liver disease over time.
Recommendations for individuals at risk of liver disease include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Avoiding exposure to environmental toxins
- Practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of viral infections
- Getting vaccinated against hepatitis A and B
- Regular monitoring of liver function tests
By following these recommendations and staying informed about liver disease diagnosis and treatment, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their liver health and prevent liver disease.
What are liver function tests?
+Liver function tests are a group of blood tests that measure the levels of various enzymes, proteins, and other substances in the blood to evaluate the liver's health and detect any potential problems.
What are the most common causes of liver disease?
+The most common causes of liver disease include viral infections, such as hepatitis B and C, excessive alcohol consumption, genetic disorders, obesity and metabolic syndrome, and certain medications.
What are the symptoms of liver disease?
+The symptoms of liver disease can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the disease, but may include jaundice, fatigue, abdominal swelling, and dark urine.
How is liver disease diagnosed?
+Liver disease is diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, liver function tests, imaging studies, and biopsy.
What are the treatment options for liver disease?
+The treatment options for liver disease depend on the underlying cause and severity of the disease, but may include medication, lifestyle modifications, and surgery or liver transplantation in severe cases.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of liver function blood tests and their importance in diagnosing and managing liver disease. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
