Intro
Understand FSH blood test results, including normal ranges, high and low levels, and implications for fertility, menopause, and hormone balance, with expert insights on follicle-stimulating hormone.
The FSH blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to evaluate the reproductive health of both men and women. FSH, or follicle-stimulating hormone, plays a vital role in the development and maturation of reproductive cells, and abnormal levels can indicate a range of issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of FSH blood test results, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and what implications they may have for fertility and overall health.
As we navigate the complex landscape of reproductive health, it becomes increasingly clear that FSH blood tests are a vital component of diagnostic care. By examining FSH levels, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into the functioning of the reproductive system, identifying potential problems and guiding treatment decisions. Whether you are trying to conceive, experiencing symptoms of infertility, or simply seeking to understand your reproductive health, a comprehensive understanding of FSH blood test results is essential.
The importance of FSH blood tests cannot be overstated, as they offer a unique window into the inner workings of the reproductive system. By analyzing FSH levels, healthcare providers can assess the health of the ovaries, testes, and pituitary gland, identifying issues that may be impacting fertility or overall health. As we explore the intricacies of FSH blood test results, we will examine the various factors that influence FSH levels, the different ranges and what they signify, and the potential implications for fertility and reproductive health.
Understanding FSH Blood Test Results

To grasp the significance of FSH blood test results, it is essential to understand the role of FSH in the reproductive system. In women, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovaries, which contain eggs. In men, FSH promotes the production of sperm in the testes. Abnormal FSH levels can indicate a range of issues, including infertility, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and pituitary gland disorders.
FSH blood test results are typically reported in units of milli-international units per milliliter (mIU/mL). The normal range for FSH levels varies depending on age, sex, and the laboratory conducting the test. In general, FSH levels are considered normal when they fall within the following ranges:
- Women:
- Follicular phase (days 1-14 of the menstrual cycle): 2.0-10.0 mIU/mL
- Ovulatory phase (days 14-17 of the menstrual cycle): 5.0-20.0 mIU/mL
- Luteal phase (days 17-28 of the menstrual cycle): 1.0-10.0 mIU/mL
- Men: 1.0-10.0 mIU/mL
Interpreting FSH Blood Test Results
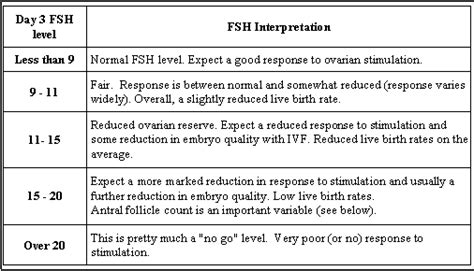
Interpreting FSH blood test results requires a nuanced understanding of the complex interactions between FSH, the reproductive system, and overall health. Elevated FSH levels can indicate a range of issues, including:
- Premature ovarian failure (POF)
- Menopause
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Pituitary gland disorders
- Testicular dysfunction
On the other hand, low FSH levels can suggest:
- Hypogonadism (reduced gonad function)
- Pituitary gland disorders
- Thyroid disorders
- Adrenal gland disorders
It is essential to note that FSH blood test results should be interpreted in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound, pelvic exam, and hormone level assessments. A comprehensive evaluation of reproductive health requires a multifaceted approach, taking into account the complex interplay between hormones, reproductive organs, and overall health.
Factors Influencing FSH Levels
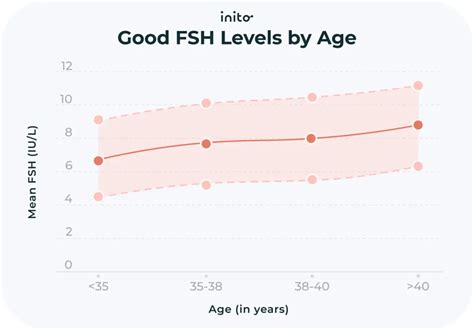
Several factors can influence FSH levels, including:
- Age: FSH levels naturally increase with age, particularly in women.
- Menstrual cycle phase: FSH levels vary throughout the menstrual cycle, with higher levels during the follicular phase.
- Pregnancy: FSH levels decrease during pregnancy.
- Thyroid disorders: Certain thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism, can impact FSH levels.
- Adrenal gland disorders: Adrenal gland disorders, such as Cushing's syndrome, can influence FSH levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy, can affect FSH levels.
Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately interpreting FSH blood test results and developing effective treatment plans.
Implications for Fertility

FSH blood test results have significant implications for fertility, particularly in women. Elevated FSH levels can indicate reduced ovarian reserve, making it more challenging to conceive. On the other hand, low FSH levels can suggest hypogonadism, which can also impact fertility.
In men, FSH blood test results can help diagnose testicular dysfunction, which can affect sperm production and fertility. Abnormal FSH levels can also indicate pituitary gland disorders, which can impact fertility.
For individuals struggling with infertility, FSH blood tests can provide valuable insights into the underlying causes of their fertility issues. By analyzing FSH levels, healthcare providers can develop targeted treatment plans, such as fertility medications, intrauterine insemination (IUI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Treatment Options

Treatment options for abnormal FSH levels depend on the underlying cause and individual circumstances. For women with elevated FSH levels, treatment may involve:
- Fertility medications to stimulate ovulation
- IUI or IVF to enhance fertility
- Hormone replacement therapy to regulate menstrual cycles
- Lifestyle modifications, such as weight management and stress reduction
For men with abnormal FSH levels, treatment may involve:
- Fertility medications to stimulate sperm production
- Hormone replacement therapy to regulate testosterone levels
- Lifestyle modifications, such as weight management and stress reduction
- Assisted reproductive technologies, such as IUI or IVF
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to address underlying issues, such as pituitary gland tumors or testicular dysfunction.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, FSH blood test results offer a valuable window into reproductive health, providing insights into the complex interactions between hormones, reproductive organs, and overall health. By understanding the factors that influence FSH levels and the implications for fertility, individuals can take proactive steps to address reproductive health concerns.
If you have questions or concerns about your FSH blood test results, we encourage you to consult with a healthcare provider. They can help you interpret your results, develop a personalized treatment plan, and navigate the complex landscape of reproductive health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with FSH blood tests in the comments below. Your insights can help others better understand the importance of reproductive health and the role of FSH blood tests in maintaining optimal well-being.
What is the normal range for FSH levels in women?
+The normal range for FSH levels in women varies depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle. During the follicular phase, FSH levels typically range from 2.0-10.0 mIU/mL, while during the ovulatory phase, levels range from 5.0-20.0 mIU/mL.
Can FSH blood tests diagnose infertility?
+FSH blood tests can provide valuable insights into reproductive health, but they cannot diagnose infertility on their own. A comprehensive evaluation of reproductive health, including medical history, physical exam, and diagnostic testing, is necessary to determine the underlying causes of infertility.
How often should I get an FSH blood test?
+The frequency of FSH blood tests depends on individual circumstances and reproductive health concerns. Women experiencing symptoms of infertility or menstrual irregularities may require more frequent testing, while men with testicular dysfunction may need regular monitoring.
