Intro
Discover prolactin hormone functions, a vital regulator of lactation, growth, and reproductive processes, influencing breast milk production, fertility, and immune response, with effects on thyroid and adrenal glands, and overall endocrine system balance.
The human body is a complex system made up of numerous hormones, each playing a unique role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. Among these hormones, prolactin is one of the most fascinating, with a wide range of functions that impact various aspects of our lives. From lactation and reproduction to immune response and stress management, prolactin's influence is multifaceted and far-reaching. In this article, we will delve into the world of prolactin, exploring its functions, mechanisms, and significance in human health.
Prolactin is often associated with lactation and breastfeeding, and for good reason. During pregnancy and childbirth, prolactin levels surge, stimulating the growth of milk-producing cells in the breasts and facilitating the production of milk. This process is essential for the nourishment and development of newborns, making prolactin a vital hormone for mothers and their babies. However, prolactin's role extends beyond lactation, influencing other physiological processes such as reproductive health, bone density, and immune function.
The prolactin hormone is produced by the pituitary gland, a small endocrine gland located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland is often referred to as the "master gland" due to its role in regulating the production of other hormones in the body. Prolactin is secreted in response to various stimuli, including stress, sleep, and nipple stimulation. Its levels can fluctuate throughout the day, with peak production typically occurring during sleep and decreasing upon waking.
Prolactin and Reproductive Health
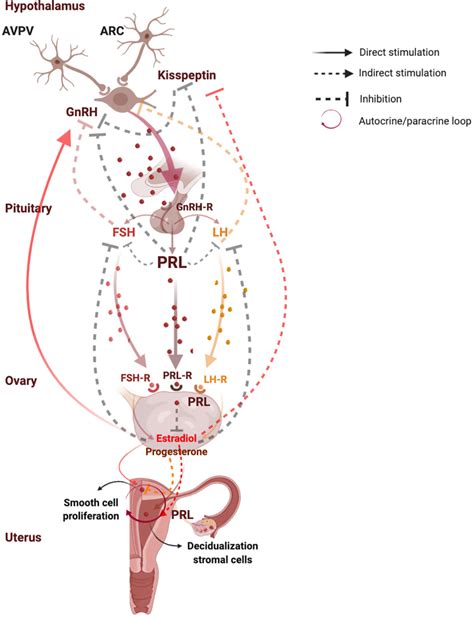
Prolactin plays a significant role in reproductive health, particularly in women. During pregnancy, prolactin levels increase, supporting the growth of the fetus and preparing the breasts for lactation. After childbirth, prolactin helps to stimulate milk production, ensuring that newborns receive the nutrients they need for growth and development. In addition to its role in lactation, prolactin also influences menstrual cycles and fertility. Elevated prolactin levels can disrupt menstrual cycles, leading to irregular periods or infertility. Therefore, it is essential to maintain healthy prolactin levels to support reproductive health.
How Prolactin Affects Menstrual Cycles
Prolactin's impact on menstrual cycles is complex and multifaceted. High prolactin levels can suppress the production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), leading to decreased estrogen and progesterone levels. This can cause menstrual irregularities, including oligomenorrhea (infrequent periods) or amenorrhea (absence of periods). Furthermore, prolactin can also affect the release of eggs from the ovaries, leading to anovulatory cycles and infertility.Prolactin and Bone Health
Prolactin has also been shown to play a role in bone health, particularly in women. Research suggests that prolactin can stimulate the production of osteoblasts, cells responsible for building bone tissue. This can lead to increased bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Additionally, prolactin may also influence the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone tissue, further supporting bone health.
The Relationship Between Prolactin and Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. Prolactin's role in bone health may help to prevent or manage osteoporosis. Studies have shown that women with hyperprolactinemia (elevated prolactin levels) may have increased bone density, reducing their risk of osteoporosis. However, more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between prolactin and osteoporosis.Prolactin and Immune Function
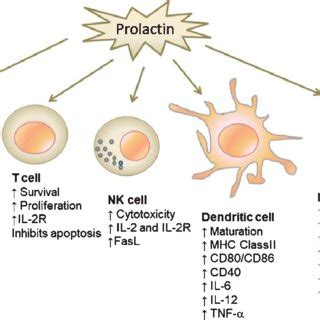
Prolactin has immunomodulatory effects, influencing the activity of immune cells and the production of cytokines. Research suggests that prolactin can stimulate the production of antibodies, activating immune cells such as macrophages and natural killer cells. This can help to protect against infections and diseases, supporting overall immune function.
Prolactin's Role in Inflammation
Prolactin may also play a role in inflammation, a complex process involving the activation of immune cells and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Elevated prolactin levels have been associated with increased inflammation, which can contribute to various diseases, including autoimmune disorders and cardiovascular disease. However, prolactin's anti-inflammatory effects may help to mitigate this response, reducing the risk of chronic diseases.Prolactin and Stress Management
Prolactin is often referred to as a "stress hormone" due to its release in response to stress and other stimuli. During periods of stress, prolactin levels can surge, helping to activate the body's stress response. This can lead to increased alertness, energy, and focus, supporting the body's ability to cope with stress. However, chronically elevated prolactin levels can have negative effects, contributing to anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders.
The Impact of Stress on Prolactin Levels
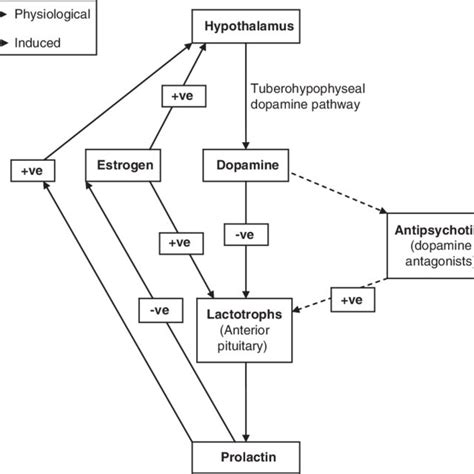
Stress can significantly impact prolactin levels, leading to increased production and release. This can be attributed to the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a complex neuroendocrine system that regulates the body's stress response. Chronic stress can lead to hyperprolactinemia, which can have negative effects on reproductive health, bone density, and immune function.Prolactin and Mental Health

Prolactin's influence on mental health is complex and multifaceted. Elevated prolactin levels have been associated with various mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and psychosis. However, prolactin may also have antidepressant effects, reducing symptoms of depression and improving mood.
Prolactin's Role in Psychosis
Prolactin's role in psychosis is not fully understood, but research suggests that elevated prolactin levels may contribute to the development of psychotic symptoms. This may be attributed to prolactin's effects on dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation and cognitive function. Further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between prolactin and psychosis.Prolactin and Sleep

Prolactin's release is closely tied to sleep, with peak production occurring during the night. This can help to regulate sleep-wake cycles, supporting overall sleep quality. Additionally, prolactin may also influence the release of other hormones involved in sleep regulation, such as melatonin and growth hormone.
The Relationship Between Prolactin and Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders, such as insomnia and sleep apnea, can significantly impact prolactin levels. Research suggests that individuals with sleep disorders may have altered prolactin release, leading to changes in sleep quality and overall health. Further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between prolactin and sleep disorders.Prolactin and Nutrition

Prolactin's influence on nutrition is complex, with effects on appetite, metabolism, and weight regulation. Elevated prolactin levels can suppress appetite, leading to weight loss, while decreased prolactin levels can increase appetite, contributing to weight gain.
Prolactin's Role in Weight Regulation
Prolactin may play a role in weight regulation, influencing the balance between energy intake and expenditure. Research suggests that prolactin can affect the activity of hormones involved in appetite regulation, such as leptin and ghrelin. Further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between prolactin and weight regulation.Prolactin and Exercise
Prolactin's release is influenced by exercise, with increased production and release during physical activity. This can help to regulate exercise-induced stress, supporting overall exercise performance and recovery.
Prolactin's Role in Exercise-Induced Stress
Exercise can induce stress, activating the body's stress response and leading to increased prolactin release. This can help to regulate exercise-induced stress, supporting overall exercise performance and recovery. However, chronically elevated prolactin levels can have negative effects, contributing to overtraining and decreased exercise performance.What is prolactin and what does it do?
+Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that plays a significant role in lactation, reproductive health, bone density, and immune function.
What are the symptoms of hyperprolactinemia?
+Hyperprolactinemia can cause a range of symptoms, including galactorrhea (spontaneous milk production), amenorrhea (absence of periods), and infertility.
How can I manage my prolactin levels?
+Managing prolactin levels can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes, including stress management, regular exercise, and a balanced diet.
What are the risks associated with elevated prolactin levels?
+Elevated prolactin levels can increase the risk of osteoporosis, infertility, and mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
Can prolactin levels be affected by medication?
+Yes, certain medications, such as antipsychotics and antidepressants, can affect prolactin levels, leading to hyperprolactinemia or hypoprolactinemia.
In conclusion, prolactin is a multifaceted hormone that plays a significant role in various physiological processes, including lactation, reproductive health, bone density, and immune function. Understanding prolactin's functions and mechanisms can help individuals take control of their health, making informed decisions about lifestyle changes and medical treatments. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with prolactin, and to explore the many resources available for managing prolactin levels and promoting overall health and well-being.
