Intro
Discover the importance of Thyroid Blood Work Tests, including TSH, Free T4, and T3 tests, to diagnose and manage thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Thyroid disorders are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. The thyroid gland, located in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall hormonal balance. When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, weight gain or loss, mood changes, and hair loss. To diagnose and monitor thyroid disorders, healthcare professionals rely on thyroid blood work tests. These tests are essential for determining the proper course of treatment and ensuring that patients receive the necessary care to manage their condition.
Thyroid blood work tests are used to evaluate the levels of various hormones and substances in the blood that are related to thyroid function. The most common tests include thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), free triiodothyronine (FT3), and thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb). These tests help healthcare professionals diagnose conditions such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroiditis. By analyzing the results of these tests, healthcare professionals can determine the underlying cause of thyroid dysfunction and develop an effective treatment plan.
The importance of thyroid blood work tests cannot be overstated. These tests provide valuable insights into thyroid function, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage thyroid disorders effectively. Without these tests, it would be challenging to determine the proper course of treatment, and patients may experience prolonged symptoms, decreased quality of life, and increased risk of complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of thyroid blood work tests, exploring the different types of tests, their purposes, and how they are used to diagnose and manage thyroid disorders.
Understanding Thyroid Function
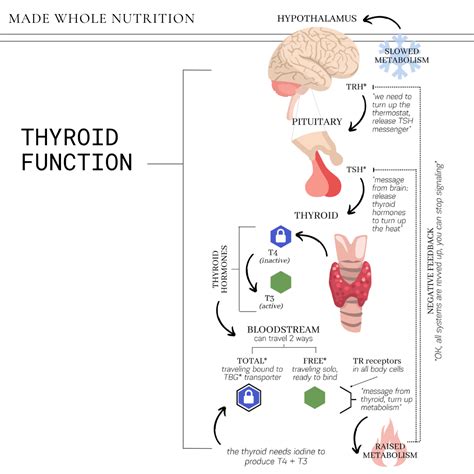
The thyroid gland produces two primary hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and overall hormonal balance. The hypothalamus, a region in the brain, produces thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH, in turn, stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T4 and T3. The levels of T4 and T3 in the blood are tightly regulated by a feedback mechanism, ensuring that the thyroid gland produces the necessary amounts of these hormones to maintain optimal function.
Thyroid Hormone Production
The production of thyroid hormones involves a complex interplay between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. The process begins with the release of TRH from the hypothalamus, which stimulates the pituitary gland to release TSH. TSH then binds to receptors on the surface of thyroid cells, stimulating the production of T4 and T3. The thyroid gland also produces other hormones, including thyroglobulin and calcitonin, which play important roles in regulating calcium levels and maintaining bone health.Types of Thyroid Blood Work Tests

There are several types of thyroid blood work tests, each with its own specific purpose. The most common tests include:
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test: This test measures the level of TSH in the blood, which helps healthcare professionals evaluate thyroid function and diagnose conditions such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
- Free thyroxine (FT4) test: This test measures the level of FT4 in the blood, which helps healthcare professionals evaluate the production of thyroid hormones and diagnose conditions such as hypothyroidism.
- Free triiodothyronine (FT3) test: This test measures the level of FT3 in the blood, which helps healthcare professionals evaluate the production of thyroid hormones and diagnose conditions such as hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb) test: This test measures the level of TPOAb in the blood, which helps healthcare professionals diagnose autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Interpreting Thyroid Blood Work Test Results
Interpreting the results of thyroid blood work tests requires careful consideration of several factors, including the patient's medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. Healthcare professionals use the results of these tests to diagnose and manage thyroid disorders, and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. The following are some general guidelines for interpreting thyroid blood work test results:- TSH: A high TSH level may indicate hypothyroidism, while a low TSH level may indicate hyperthyroidism.
- FT4: A low FT4 level may indicate hypothyroidism, while a high FT4 level may indicate hyperthyroidism.
- FT3: A low FT3 level may indicate hypothyroidism, while a high FT3 level may indicate hyperthyroidism.
- TPOAb: A high TPOAb level may indicate an autoimmune thyroid disorder such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Diagnosing Thyroid Disorders
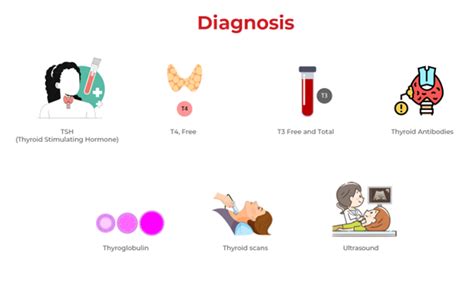
Thyroid blood work tests are essential for diagnosing thyroid disorders. By analyzing the results of these tests, healthcare professionals can determine the underlying cause of thyroid dysfunction and develop an effective treatment plan. The following are some common thyroid disorders that can be diagnosed using thyroid blood work tests:
- Hypothyroidism: A condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, resulting in decreased production of thyroid hormones.
- Hyperthyroidism: A condition characterized by an overactive thyroid gland, resulting in increased production of thyroid hormones.
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis: An autoimmune thyroid disorder characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland and decreased production of thyroid hormones.
- Graves' disease: An autoimmune thyroid disorder characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland and increased production of thyroid hormones.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Disorders
Treatment options for thyroid disorders depend on the underlying cause of thyroid dysfunction and the severity of symptoms. The following are some common treatment options for thyroid disorders:- Hypothyroidism: Treatment typically involves synthetic thyroid hormone replacement medication, such as levothyroxine (T4) or liothyronine (T3).
- Hyperthyroidism: Treatment typically involves antithyroid medication, such as methimazole or propylthiouracil, to reduce the production of thyroid hormones.
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis: Treatment typically involves synthetic thyroid hormone replacement medication, such as levothyroxine (T4) or liothyronine (T3).
- Graves' disease: Treatment typically involves antithyroid medication, such as methimazole or propylthiouracil, to reduce the production of thyroid hormones.
Monitoring Thyroid Function

Monitoring thyroid function is essential for ensuring that patients receive the necessary care to manage their condition. Thyroid blood work tests are used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to adjust medication dosages as needed. The following are some tips for monitoring thyroid function:
- Regular blood tests: Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor thyroid function and to adjust medication dosages as needed.
- Symptom monitoring: Patients should monitor their symptoms and report any changes to their healthcare professional.
- Medication adherence: Patients should take their medication as directed and report any side effects to their healthcare professional.
Importance of Patient Education
Patient education is essential for ensuring that patients understand their condition and the importance of monitoring thyroid function. Healthcare professionals should educate patients on the following topics:- Thyroid function and the importance of monitoring
- Treatment options and medication management
- Symptom monitoring and reporting
- Lifestyle changes to manage thyroid function, such as dietary changes and stress management
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, thyroid blood work tests are essential for diagnosing and managing thyroid disorders. By understanding the different types of tests, their purposes, and how they are used to diagnose and manage thyroid disorders, patients can take an active role in their healthcare. Healthcare professionals should educate patients on the importance of monitoring thyroid function and provide guidance on treatment options and medication management. By working together, patients and healthcare professionals can ensure that thyroid disorders are properly diagnosed and managed, resulting in improved health outcomes and quality of life.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about thyroid blood work tests in the comments section below. If you have any personal experiences with thyroid disorders, we encourage you to share your story to help others understand the importance of monitoring thyroid function. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns about thyroid blood work tests, please do not hesitate to ask.
What is the purpose of thyroid blood work tests?
+Thyroid blood work tests are used to evaluate the levels of various hormones and substances in the blood that are related to thyroid function. These tests help healthcare professionals diagnose conditions such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroiditis.
What are the different types of thyroid blood work tests?
+The most common types of thyroid blood work tests include thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), free triiodothyronine (FT3), and thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb) tests.
How are thyroid blood work test results interpreted?
+Interpreting thyroid blood work test results requires careful consideration of several factors, including the patient's medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. Healthcare professionals use the results of these tests to diagnose and manage thyroid disorders, and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
