Intro
Unlock BNP acronym medical meaning, exploring its role in diagnosing heart failure, cardiac conditions, and biomarker testing, with related terms like natriuretic peptides and cardiovascular health.
The medical field is filled with acronyms and abbreviations that can be confusing for those who are not familiar with them. One such acronym is BNP, which stands for Brain Natriuretic Peptide. In the medical field, BNP is a hormone produced by the heart and plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing heart failure. The importance of understanding BNP cannot be overstated, as it has become a vital tool in the diagnosis and treatment of heart-related conditions.
The discovery of BNP has revolutionized the way doctors diagnose and manage heart failure. Before the discovery of BNP, doctors relied on symptoms and other tests to diagnose heart failure. However, these methods were not always accurate, and heart failure was often diagnosed at an advanced stage. With the discovery of BNP, doctors can now diagnose heart failure earlier and more accurately, allowing for timely treatment and improved patient outcomes.
BNP is produced by the ventricles of the heart in response to excessive stretching of heart muscle cells. This stretching can occur due to various conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart valve problems, or heart failure. When BNP is released into the bloodstream, it helps to relax and dilate blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and improving heart function. Elevated levels of BNP in the blood can indicate heart failure, making it a valuable diagnostic tool.
What is BNP
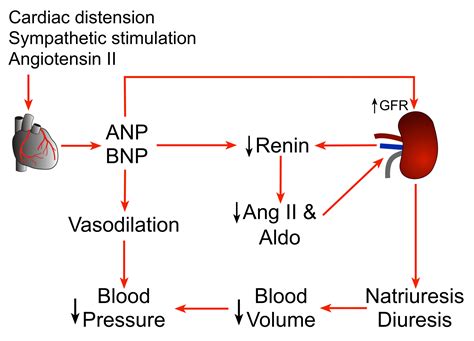
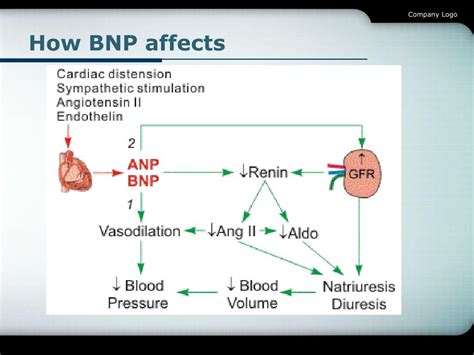
How BNP Works
BNP works by binding to specific receptors in the body, called natriuretic peptide receptors. These receptors are found in various tissues, including blood vessels, kidneys, and adrenal glands. When BNP binds to these receptors, it triggers a series of signaling pathways that lead to the relaxation and dilation of blood vessels, increased sodium excretion, and increased urine production.BNP Test
The BNP test is a valuable diagnostic tool because it can help doctors diagnose heart failure earlier and more accurately. Elevated levels of BNP in the blood can indicate heart failure, even in patients who do not have symptoms. The test can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to adjust medication as needed.
Interpretation of BNP Results
The interpretation of BNP results depends on the level of BNP in the blood. Normal levels of BNP are typically below 100 pg/mL. Elevated levels of BNP can indicate heart failure, and the severity of the condition can be assessed based on the level of BNP.- BNP levels below 100 pg/mL: Normal
- BNP levels between 100-300 pg/mL: Mild heart failure
- BNP levels between 300-600 pg/mL: Moderate heart failure
- BNP levels above 600 pg/mL: Severe heart failure
Benefits of BNP Test
- Early diagnosis of heart failure: The BNP test can help doctors diagnose heart failure earlier and more accurately, allowing for timely treatment and improved patient outcomes.
- Monitoring of treatment: The test can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to adjust medication as needed.
- Assessment of severity: The test can be used to assess the severity of heart failure, allowing doctors to tailor treatment to the individual needs of the patient.
- Reduced hospitalization: The test can help reduce hospitalization rates by allowing doctors to diagnose and treat heart failure earlier and more effectively.
Limitations of BNP Test
While the BNP test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations. These include:- False positives: Elevated levels of BNP can be caused by conditions other than heart failure, such as pulmonary embolism or sepsis.
- False negatives: Normal levels of BNP do not necessarily rule out heart failure, as some patients with heart failure may have normal levels of BNP.
- Variability: BNP levels can vary depending on the laboratory and the assay used, making it essential to use a standardized assay and to interpret results in the context of clinical symptoms and other diagnostic tests.
BNP and Heart Failure
Heart failure is a chronic condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It can be caused by various conditions, such as high blood pressure, heart valve problems, or coronary artery disease.
The symptoms of heart failure can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but they may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs and feet
- Coughing up pink, frothy mucus
- Chest pain or discomfort
Treatment of Heart Failure
The treatment of heart failure depends on the underlying cause of the condition and the severity of symptoms. It may include:- Medications: Such as ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and diuretics to reduce symptoms and slow disease progression.
- Lifestyle modifications: Such as dietary changes, exercise, and stress reduction to improve overall health and reduce symptoms.
- Devices: Such as pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators to improve heart function and reduce symptoms.
- Surgery: Such as heart transplantation or valve repair to treat underlying conditions and improve heart function.
BNP and Other Conditions
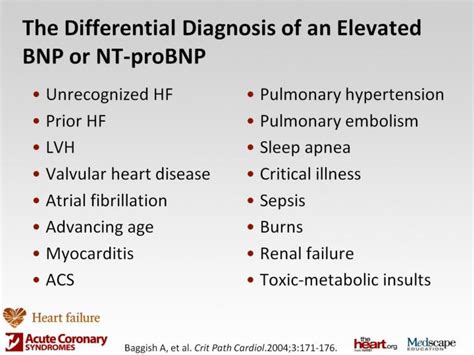
- Pulmonary embolism: A blockage of an artery in the lungs that can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood.
- Sepsis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when the body's response to an infection becomes uncontrolled and causes widespread inflammation.
- Coronary artery disease: A condition in which the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked, causing chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms that can cause symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
BNP and Kidney Disease
BNP can also be elevated in patients with kidney disease, particularly those with end-stage renal disease. This is because the kidneys play a crucial role in removing BNP from the bloodstream, and impaired kidney function can lead to elevated levels of BNP.In patients with kidney disease, BNP can be used to diagnose and manage heart failure, but it is essential to interpret results in the context of clinical symptoms and other diagnostic tests.
Conclusion and Future Directions
Future directions for BNP research include the development of new assays and the exploration of its role in other conditions, such as pulmonary embolism and sepsis. Additionally, the use of BNP in combination with other biomarkers and diagnostic tests may improve the accuracy and effectiveness of heart failure diagnosis and treatment.
As research continues to uncover the complexities of BNP and its role in various conditions, it is essential for healthcare professionals to stay up-to-date on the latest developments and to use BNP in a clinically relevant and evidence-based manner.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with BNP in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one been diagnosed with heart failure using the BNP test? What were your experiences with the test, and how did it impact your treatment and management of the condition?
What is BNP and what does it measure?
+BNP, or Brain Natriuretic Peptide, is a hormone produced by the heart that measures the level of strain on the heart. Elevated levels of BNP can indicate heart failure.
How is the BNP test performed?
+The BNP test is a blood test that measures the level of BNP in the blood. It is usually performed in a laboratory, and the results are available within a few hours.
What are the benefits of the BNP test?
+The BNP test has several benefits, including early diagnosis of heart failure, monitoring of treatment, assessment of severity, and reduced hospitalization rates.
