Intro
Discover key facts about Metoprolol, a beta blocker medication, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to better manage hypertension, angina, and heart failure, while minimizing risks and optimizing treatment outcomes.
Metoprolol is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure, chest pain, and heart failure. Despite its common use, there are many aspects of metoprolol that patients and even some healthcare professionals may not be fully aware of. Understanding the facts about metoprolol can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and treatment options. The importance of knowing these facts cannot be overstated, as it empowers patients to manage their conditions more effectively and to communicate more effectively with their healthcare providers.
The role of metoprolol in managing cardiovascular health is multifaceted, and its benefits extend beyond just lowering blood pressure or alleviating symptoms of chest pain. It's a medication that has undergone extensive research, and its effects on the body are well-documented. However, like all medications, metoprolol comes with its own set of potential side effects and considerations that patients should be aware of. By delving into the specifics of how metoprolol works, its benefits, and its potential drawbacks, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of what to expect from this medication and how it fits into their overall treatment plan.
Metoprolol is classified as a beta-blocker, which means it works by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and by slowing the heart rate and reducing its workload. This mechanism of action is crucial in managing conditions where the heart is under strain, such as in hypertension or after a heart attack. The medication's ability to reduce the heart's demand for oxygen can help prevent further damage and improve survival rates in certain cardiac conditions. Given its widespread use and the significant impact it can have on patients' lives, it's essential to explore the key facts about metoprolol in greater detail.
Introduction to Metoprolol

Benefits of Metoprolol
The benefits of metoprolol are numerous and well-documented. It is effective in reducing blood pressure, which can significantly lower the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. Additionally, metoprolol has been shown to improve survival rates in patients who have had a heart attack, making it a critical component of post-myocardial infarction care. Its ability to reduce the frequency of angina attacks and improve exercise tolerance also enhances the quality of life for many patients.How Metoprolol Works
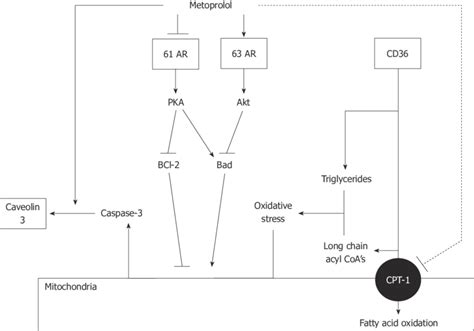
Common Uses of Metoprolol
Metoprolol is used for a variety of conditions, including hypertension, angina pectoris, heart failure, and to improve survival after a heart attack. It may also be used in the management of certain arrhythmias and to control tachycardia (rapid heart rate) in hyperthyroidism. The versatility of metoprolol in treating different cardiovascular conditions makes it a valuable asset in the management of heart health.Potential Side Effects of Metoprolol
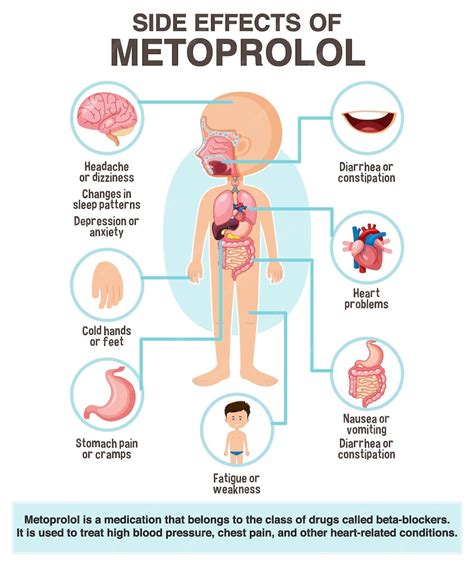
Interactions and Precautions
Metoprolol can interact with a variety of other medications, including other beta-blockers, certain antidepressants, and over-the-counter cough and cold medicines. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all the medications they are taking to avoid potential drug interactions. Additionally, metoprolol should be used with caution in certain patient populations, such as those with diabetes, as it can mask symptoms of hypoglycemia, and in patients with liver disease, as metoprolol is metabolized by the liver.Dosage and Administration
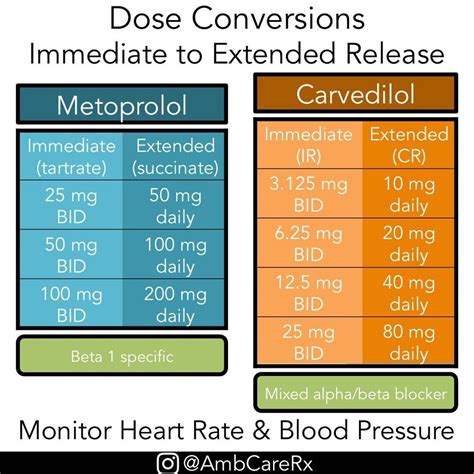
Special Considerations
In certain situations, the use of metoprolol requires special consideration. For example, in patients undergoing surgery, metoprolol should be continued as usual, but the anesthesiologist should be informed. In patients with diabetes, careful monitoring of blood glucose levels is necessary, as metoprolol can affect glucose metabolism. Pregnancy and breastfeeding are other scenarios where the use of metoprolol needs careful evaluation, as the medication can cross the placenta and is excreted in breast milk.Metoprolol in Combination Therapy
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring and follow-up are crucial for patients taking metoprolol. This includes regular check-ups with the healthcare provider, monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate, and adjustments to the treatment plan as necessary. Patients should also be educated on the signs and symptoms of potential side effects and the importance of adherence to their medication regimen.Conclusion and Future Directions

What is metoprolol used for?
+Metoprolol is used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions. It is also used to improve survival after a heart attack.
How does metoprolol work?
+Metoprolol works by blocking the action of certain natural chemicals in your body, such as epinephrine, on the heart and blood vessels. This effect lowers the heart rate, blood pressure, and strain on the heart.
What are the potential side effects of metoprolol?
+Common side effects of metoprolol include dizziness, lightheadedness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Less common but serious side effects can include worsening heart failure and bronchospasm in patients with asthma.
We hope this comprehensive overview of metoprolol has provided you with valuable insights into its uses, benefits, and considerations. Whether you're a patient, a healthcare provider, or simply someone interested in cardiovascular health, understanding metoprolol can help you make more informed decisions about treatment options and management strategies. If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences with metoprolol, please don't hesitate to comment below. Sharing knowledge and personal stories can help create a supportive community and foster better health outcomes for everyone involved.
