Intro
Discover 5 key BNP facts, including its role in heart failure, natriuretic peptide function, and diagnostic biomarker significance, shedding light on cardiovascular health and disease management through BNP testing and analysis.
The importance of understanding BNP (B-type natriuretic peptide) facts cannot be overstated, especially for individuals concerned about their heart health. BNP is a hormone produced by the heart, and its levels can provide critical insights into the functioning of this vital organ. Elevated BNP levels are often associated with heart failure, a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. This association makes BNP a valuable marker for diagnosing and managing heart failure.
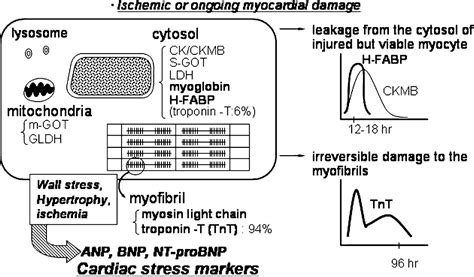
BNP testing has become a crucial tool in cardiology, helping healthcare providers assess the severity of heart failure and monitor the effectiveness of treatments. The peptide is secreted by the ventricles in response to excessive stretching of heart muscle cells, which can occur in heart failure. By measuring BNP levels, healthcare providers can differentiate between heart failure and other conditions that may cause similar symptoms, such as shortness of breath or fatigue. This differentiation is essential for initiating the appropriate treatment plan.
The role of BNP in diagnosing and managing heart conditions underscores the need for a comprehensive understanding of this hormone. From its production and function to its clinical applications, exploring BNP facts can empower individuals to take a more active role in their heart health. Whether you're a healthcare professional seeking to deepen your knowledge or an individual looking to understand your test results better, delving into the world of BNP can provide valuable insights. This article aims to explore the multifaceted aspects of BNP, from its biological basis to its clinical utility, and to discuss how understanding BNP can lead to better heart health outcomes.
Introduction to BNP
Production and Regulation of BNP
The production of BNP is closely tied to the mechanical stress experienced by the heart, particularly the ventricles. When the ventricles are stretched or under increased pressure, as in the case of heart failure, the production of BNP is upregulated. This increase in BNP levels serves as a compensatory mechanism to reduce the workload on the heart by promoting the excretion of sodium and water, thereby reducing blood volume and pressure. The regulation of BNP production is complex and involves various signaling pathways and feedback mechanisms that ensure its levels are appropriately adjusted in response to changes in cardiac load.Clinical Applications of BNP
BNP Testing and Interpretation
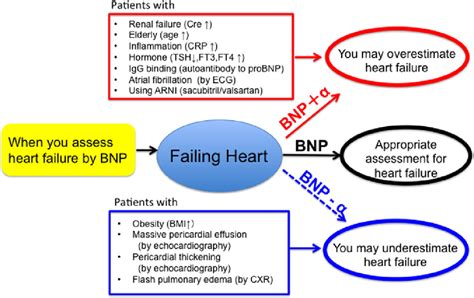
BNP testing involves measuring the levels of BNP in the blood. The test is relatively simple and can be performed on a blood sample. Interpretation of BNP levels must take into account the clinical context, as elevated levels can also be seen in other conditions such as pulmonary embolism or severe sepsis. Generally, higher BNP levels are associated with more severe heart failure. The use of BNP testing in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, such as echocardiography and clinical evaluation, enhances its utility in managing heart failure.Benefits and Limitations of BNP Testing

Factors Influencing BNP Levels
Several factors can influence BNP levels, including age, with levels naturally increasing as one gets older; sex, as women tend to have higher levels than men; and renal function, as impaired kidney function can lead to elevated BNP levels due to reduced clearance. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately interpreting BNP test results and making informed clinical decisions.BNP in Heart Failure Management
Future Directions in BNP Research
Research into BNP and its role in heart health is ongoing. Future studies aim to further elucidate the mechanisms underlying BNP production and action, as well as to explore new clinical applications for BNP testing. This includes investigating the potential of BNP as a therapeutic target for treating heart failure, rather than just a diagnostic marker.Conclusion and Next Steps

Call to Action
If you or someone you know is concerned about heart health, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider. Discussing BNP testing and its implications can provide valuable insights into heart function and guide appropriate care. By staying informed and engaged in heart health, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy heart and mitigating the risks associated with heart failure.What is BNP, and how is it related to heart health?
+BNP, or B-type natriuretic peptide, is a hormone produced by the heart. Its levels are used as a marker for heart failure, a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
How is BNP testing used in clinical practice?
+BNP testing is used to diagnose heart failure, differentiate it from other conditions causing similar symptoms, and monitor the effectiveness of heart failure treatments.
What factors can influence BNP levels?
+BNP levels can be influenced by age, sex, renal function, and the presence of certain medical conditions. These factors must be considered when interpreting BNP test results.
