Intro
Discover causes and symptoms of low body temperature below normal, including hypothyroidism, anemia, and poor circulation, and learn how to diagnose and treat abnormally low body temps with natural remedies and medical interventions.
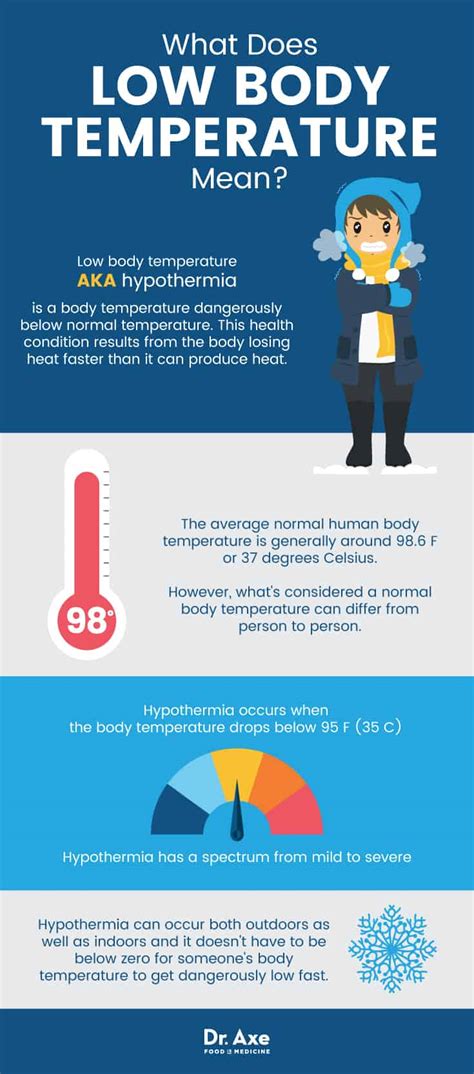
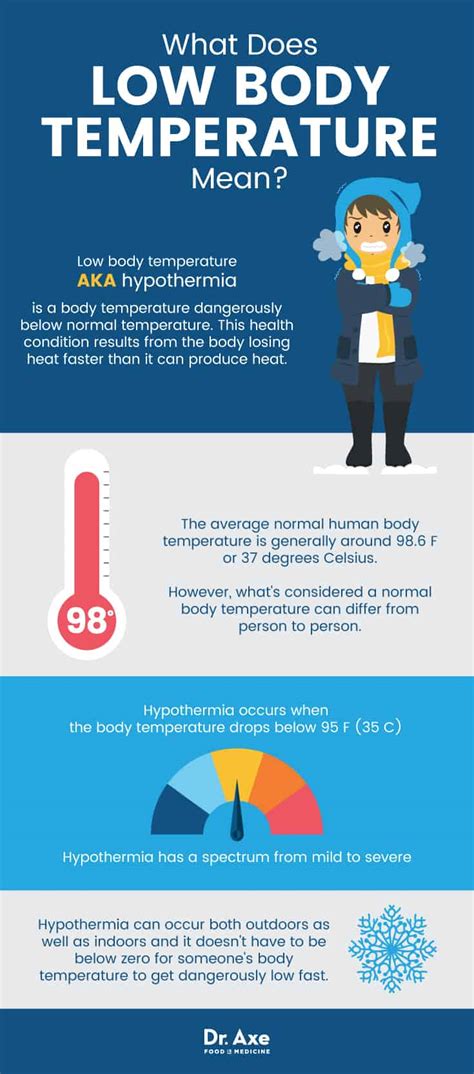
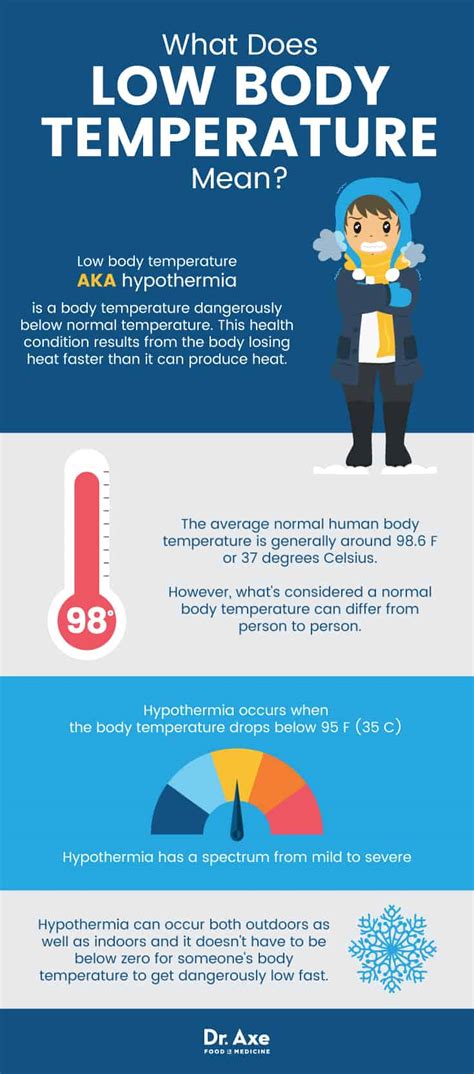
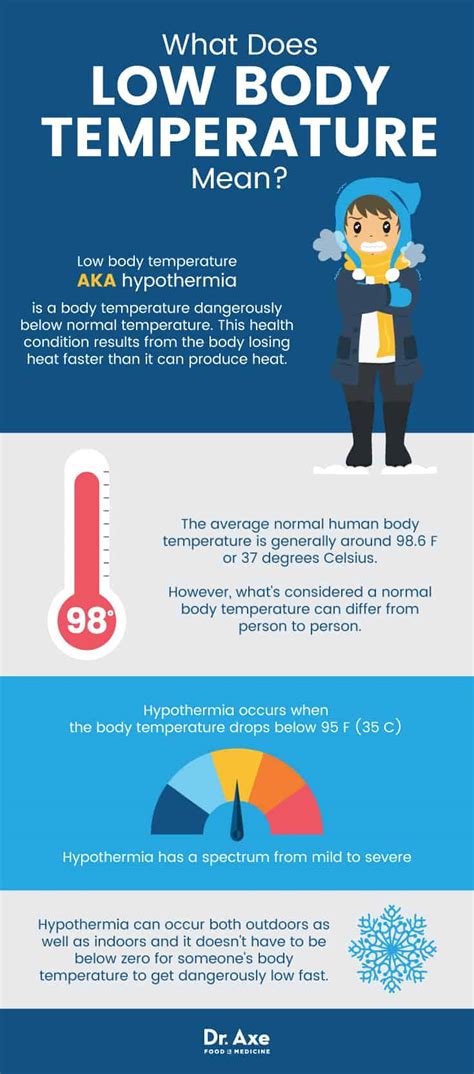
Having a low body temperature, also known as hypothermia, can be a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. Normal body temperature is around 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary slightly from person to person. A body temperature below 95°F (35°C) is considered low and can be a sign of an underlying health issue. In this article, we will explore the importance of maintaining a normal body temperature, the causes and symptoms of low body temperature, and the steps you can take to prevent and treat it.
Low body temperature can be caused by a variety of factors, including exposure to cold temperatures, certain medical conditions, and the use of certain medications. For example, people who work or spend a lot of time outdoors in cold weather may be at risk of developing hypothermia. Additionally, certain medical conditions such as hypothyroidism, diabetes, and anemia can increase the risk of developing low body temperature. It is essential to be aware of the causes and symptoms of low body temperature to take preventive measures and seek medical attention if necessary.
Maintaining a normal body temperature is crucial for overall health and well-being. The body's temperature regulation system helps to maintain a stable internal temperature, despite changes in external temperature. This is important for many bodily functions, including metabolism, nerve function, and immune function. When the body temperature drops, these functions can be impaired, leading to a range of symptoms and potentially serious health complications. In severe cases, low body temperature can be life-threatening, making it essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Causes of Low Body Temperature
Symptoms of Low Body Temperature

Prevention of Low Body Temperature
Treatment of Low Body Temperature
Complications of Low Body Temperature
Risk Factors for Low Body Temperature

Age-Related Risk Factors
Age is a significant risk factor for low body temperature. Older adults and young children are at increased risk of developing hypothermia due to a range of factors, including: * Impaired temperature regulation: Older adults and young children may have impaired temperature regulation, making it more difficult for the body to maintain a stable internal temperature. * Reduced mobility: Older adults and young children may have reduced mobility, making it more difficult to get out of the cold or seek medical attention. * Chronic medical conditions: Older adults and young children may have chronic medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or diabetes, that can increase the risk of developing low body temperature.Medical Condition-Related Risk Factors
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of developing low body temperature. These include: * Hypothyroidism: This medical condition occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, which can affect the body's temperature regulation system. * Diabetes: People with diabetes may be at risk of developing low body temperature due to nerve damage or poor blood circulation. * Anemia: This medical condition occurs when the body does not have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin, which can affect the body's ability to regulate temperature.What is the normal body temperature range?
+Normal body temperature is around 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary slightly from person to person.
What are the symptoms of low body temperature?
+The symptoms of low body temperature include shivering, confusion, drowsiness, weakness, and slurred speech.
How can I prevent low body temperature?
+There are several steps you can take to prevent low body temperature, including dressing warmly, staying dry, staying active, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding certain medications.
In conclusion, low body temperature is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention. It is essential to be aware of the causes and symptoms of low body temperature to take preventive measures and seek medical attention if necessary. By understanding the risk factors and taking steps to prevent low body temperature, you can help to maintain a healthy and stable body temperature. If you have any concerns about low body temperature or would like to learn more, please comment below or share this article with others.
