Intro
Learn key stroke risk factors, including high blood pressure, diabetes, and family history, to understand your likelihood of stroke and take preventative measures with lifestyle changes and medical interventions.
Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. It occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either due to a blockage or a rupture of the blood vessels, leading to damage or death of brain cells. Understanding the risk factors for stroke is crucial in preventing and managing this condition. In this article, we will delve into the various stroke risk factors, their causes, and what you can do to reduce your risk.
The importance of knowing stroke risk factors cannot be overstated. By being aware of the factors that increase your risk, you can take proactive steps to mitigate them, thereby reducing your likelihood of experiencing a stroke. Moreover, early recognition of stroke symptoms and prompt medical attention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term damage. As we explore the various stroke risk factors, it is essential to remember that many of these factors are modifiable, meaning that you have the power to change them and reduce your risk.
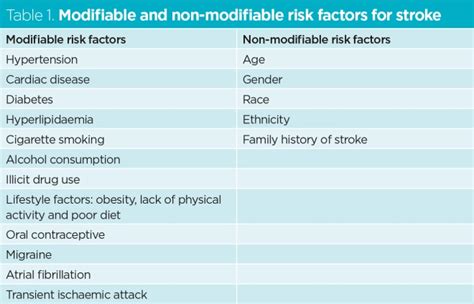
Stroke risk factors can be broadly categorized into two groups: non-modifiable and modifiable risk factors. Non-modifiable risk factors are those that you cannot change, such as your age, family history, and genetics. Modifiable risk factors, on the other hand, are those that you can change through lifestyle modifications, medical treatment, or other interventions. Understanding the difference between these two categories is vital in developing an effective strategy for reducing your stroke risk.
Non-Modifiable Stroke Risk Factors
Age and Family History
Age is a significant non-modifiable risk factor for stroke. As you get older, your blood vessels become more susceptible to damage, and your risk of developing conditions like high blood pressure and atherosclerosis increases. Family history also plays a crucial role, as certain genetic conditions can increase your risk of stroke. If you have a family history of stroke, it is essential to discuss your risk with your doctor and develop a plan to reduce your risk.Genetics and Medical Conditions
Certain genetic conditions, such as sickle cell disease, can increase your risk of stroke. Additionally, medical conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol can also increase your risk. These conditions can damage your blood vessels and increase your risk of stroke. It is essential to manage these conditions through lifestyle modifications and medical treatment to reduce your risk.Modifiable Stroke Risk Factors
High Blood Pressure and High Cholesterol
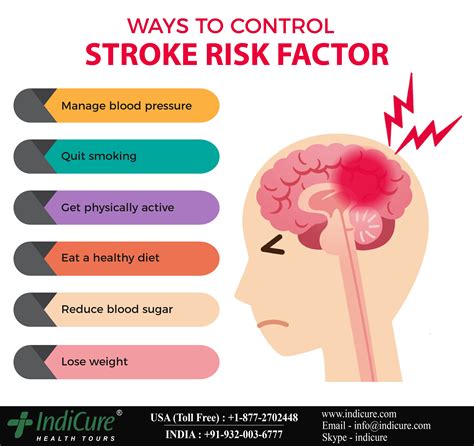
High blood pressure and high cholesterol are two of the most significant modifiable risk factors for stroke. High blood pressure can damage your blood vessels, making them more susceptible to blockage or rupture. High cholesterol can also increase your risk of stroke by contributing to the buildup of plaque in your arteries. Managing these conditions through lifestyle modifications and medical treatment can significantly reduce your risk.Smoking and Obesity
Smoking and obesity are also significant modifiable risk factors for stroke. Smoking can damage your blood vessels and increase your risk of stroke, while obesity can increase your risk of developing conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes. Quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce your risk of stroke.Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Stroke Risk
Healthy Diet and Regular Physical Activity
A healthy diet and regular physical activity are essential in reducing your risk of stroke. A diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help manage conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol. Regular physical activity can also help manage these conditions and reduce your risk of stroke. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per day.Stress Management and Sleep
Stress management and sleep are also crucial in reducing your risk of stroke. Chronic stress can increase your risk of stroke by contributing to the development of conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes. Getting enough sleep is also essential, as sleep deprivation can increase your risk of stroke. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night and engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga.Medical Treatment and Intervention
Medication and Surgery
Medication and surgery can be effective in reducing your risk of stroke. If you have a condition like high blood pressure or high cholesterol, your doctor may prescribe medication to manage it. Additionally, if you have a history of stroke or are at high risk of stroke, your doctor may recommend procedures like carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty to reduce your risk.Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation and recovery are also crucial in reducing your risk of stroke. If you have experienced a stroke, it is essential to work with a rehabilitation team to regain your strength and mobility. This can include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Additionally, making lifestyle modifications and managing your risk factors can help reduce your risk of another stroke.What are the symptoms of a stroke?
+The symptoms of a stroke include sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding speech, sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes, sudden severe headache with no known cause, and sudden trouble walking, dizziness, or loss of balance.
How can I reduce my risk of stroke?
+You can reduce your risk of stroke by making lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress. Additionally, managing conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol through medication and lifestyle modifications can also reduce your risk.
What should I do if I experience symptoms of a stroke?
+If you experience symptoms of a stroke, call emergency services immediately. Prompt medical attention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term damage.
In
Final Thoughts

