Intro
Discover 5 ways to fight C Diff, a bacterial infection, using natural remedies, probiotics, and antibiotics, while managing symptoms and preventing recurrence, to promote gut health and overall wellness.
The rise of Clostridioides difficile, commonly referred to as C. diff, has become a significant concern in the healthcare sector. This bacterium can cause a range of symptoms, from mild diarrhea to life-threatening colon inflammation. The importance of understanding and combating C. diff cannot be overstated, as it affects hundreds of thousands of people each year, particularly those with weakened immune systems or individuals who have undergone antibiotic treatments. The fight against C. diff requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating preventive measures, diagnostic advancements, and effective treatment strategies. As we delve into the world of C. diff, it becomes clear that awareness and proactive steps are crucial in managing and reducing the incidence of this infection.
The impact of C. diff on public health is profound, with significant economic and social implications. The economic burden stems from prolonged hospital stays, repeated treatments, and the necessity for stringent infection control measures. Moreover, the social impact on patients and their families can be devastating, leading to isolation and a diminished quality of life. Therefore, it is essential to explore and implement effective strategies to combat C. diff, focusing on prevention, early detection, and innovative treatments. By understanding the mechanisms of C. diff infection and transmission, we can develop targeted interventions that address the root causes of the disease, ultimately reducing its prevalence and mitigating its effects on individuals and communities.
The complexity of C. diff infections necessitates a comprehensive approach, involving healthcare providers, researchers, and the public. Education plays a vital role in this endeavor, as it empowers individuals to take preventive measures and recognize the early signs of infection. Furthermore, advances in medical research are continually uncovering new insights into the nature of C. diff, paving the way for more effective treatments and management strategies. As we navigate the challenges posed by C. diff, it is crucial to remain informed, adapt to new findings, and support efforts aimed at combating this resilient bacterium.
Understanding C. Diff Infections
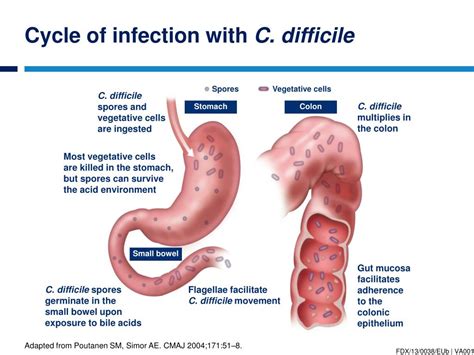
Transmission and Risk Factors
The transmission of C. diff often occurs in healthcare settings, where the bacteria can spread through contaminated surfaces, medical equipment, or the hands of healthcare workers. However, community-acquired cases are also on the rise, highlighting the need for broader preventive measures. Key risk factors for C. diff infection include recent antibiotic use, hospitalization, advanced age, and underlying health conditions. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for developing targeted prevention and intervention strategies.Prevention Strategies

Vaccination and Probiotics
Research into vaccines against C. diff is ongoing, with several candidates showing promise in clinical trials. Additionally, the use of probiotics, which are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for health, is being explored as a potential preventive measure. Probiotics can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which may reduce the risk of C. diff infection. However, more studies are needed to fully understand the effectiveness of these approaches.Treatment Options
Recurrent Infections
Recurrent C. diff infections pose a significant challenge, as they can be difficult to treat and may require repeated courses of antibiotics or other interventions. Strategies for managing recurrent infections include prolonged treatment courses, the use of probiotics, and, in some cases, FMT. Ongoing research is focused on developing more effective treatments for recurrent C. diff, including new antibiotics and immunotherapy approaches.Diagnostic Advances
Molecular Testing
Molecular testing, including PCR, has become a cornerstone in the diagnosis of C. diff. These tests can rapidly detect the genetic material of the bacteria, allowing for timely initiation of treatment. Furthermore, molecular epidemiology can help trace the source of outbreaks, facilitating targeted infection control measures. The continued development and refinement of diagnostic tools will be essential in the fight against C. diff, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions and improve patient outcomes.Public Awareness and Education

Community Engagement
Engaging the community in the fight against C. diff involves fostering partnerships between healthcare providers, public health organizations, and local communities. This collaborative approach can facilitate the dissemination of accurate information, promote best practices in infection control, and support research initiatives. By working together, we can enhance our collective response to C. diff, ultimately reducing its incidence and impact on public health.Future Directions

Research and Development
Continued investment in research and development is essential for advancing our understanding of C. diff and for discovering effective countermeasures. This includes basic science research into the pathogenesis of C. diff, as well as clinical trials evaluating new treatments and preventive measures. Collaboration between academia, industry, and healthcare institutions will be crucial in driving innovation and translating research findings into clinical practice.What are the primary symptoms of a C. diff infection?
+The primary symptoms of a C. diff infection include diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and loss of appetite. In severe cases, symptoms can escalate to include bloody stools, severe abdominal cramping, and signs of dehydration.
How is C. diff typically treated?
+C. diff is typically treated with antibiotics that are effective against the bacteria, such as vancomycin or fidaxomicin. In some cases, particularly for recurrent infections, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) may be recommended.
Can C. diff infections be prevented?
+Yes, C. diff infections can be prevented through good hygiene practices, such as frequent hand washing, proper cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, and responsible use of antibiotics. Vaccines and probiotics are also being explored as potential preventive measures.
As we continue to navigate the complexities of C. diff, it is clear that a multifaceted approach is necessary to combat this resilient bacterium. By combining advances in medical research, public awareness, and community engagement, we can work towards reducing the incidence and impact of C. diff infections. We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and engage in discussions about C. diff, contributing to a broader understanding and collective effort to fight this infection. Together, we can make a difference and improve outcomes for those affected by C. diff.
