Intro
Discover Z Pack dosing guidelines, including dosage instructions, treatment duration, and medication interactions, to ensure safe and effective use of azithromycin for bacterial infections, respiratory issues, and other conditions, following FDA-approved protocols.
The importance of understanding Z Pack dosing guidelines cannot be overstated, as this medication has become a staple in the treatment of various bacterial infections. Zithromax, commonly referred to as a Z Pack, is an antibiotic that belongs to the macrolide class, which works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. Its widespread use is due to its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of bacterial infections, including respiratory, skin, and sexually transmitted infections. However, like all medications, its efficacy and safety depend on proper dosing, making it crucial for both healthcare providers and patients to be well-versed in Z Pack dosing guidelines.
The Z Pack's popularity stems from its convenience, typically provided in a 5-day or 3-day dosing regimen, which enhances patient compliance. This dosing regimen is a significant factor in the medication's success, as it simplifies the treatment process for patients, potentially leading to better outcomes due to increased adherence to the prescribed treatment plan. Despite its convenience and effectiveness, the Z Pack, like all antibiotics, must be used judiciously to combat the growing issue of antibiotic resistance. This requires a thorough understanding of when to prescribe the Z Pack, the appropriate dosing for different infections, and the potential side effects that may necessitate alternative treatments.
Understanding the dosing guidelines for a Z Pack involves recognizing the different types of infections it treats and the specific dosing recommendations for each. The medication is available in various forms, including tablets and oral suspension, which allows for a range of dosing options suitable for different patient populations, including children and adults. The flexibility in dosing, combined with its generally well-tolerated side effect profile, makes the Z Pack a preferred choice for many healthcare providers. However, with the rise of antibiotic resistance, it's essential to use this medication responsibly, following established guidelines to ensure its continued efficacy.
Z Pack Administration and Dosage
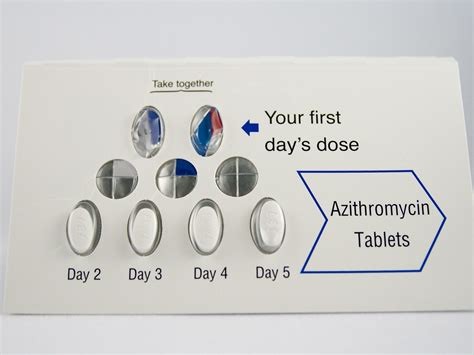
The administration and dosage of a Z Pack are critical components of its effective use. The standard adult dose of azithromycin for most infections is 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg once daily for the next 4 days. However, dosing can vary based on the specific infection being treated. For example, in the case of uncomplicated chlamydia, the recommended dose is often a single 1 gram dose. Understanding these variations is essential for healthcare providers to ensure that patients receive the most effective treatment for their particular condition.
Factors Influencing Z Pack Dosage

Several factors can influence the dosage of a Z Pack, including the type and severity of the infection, patient age, weight, and renal function. For pediatric patients, the dose is often calculated based on the child's weight, emphasizing the need for accurate dosing to ensure efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. In patients with renal impairment, dose adjustments may be necessary to prevent accumulation of the drug, which could lead to adverse effects. These considerations highlight the importance of individualizing treatment plans when prescribing a Z Pack.
Common Infections Treated with Z Pack
The Z Pack is effective against a variety of bacterial infections, including community-acquired pneumonia, acute bacterial sinusitis, and uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections. Its use in treating sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia, is also well-documented. The breadth of its antimicrobial activity, combined with its favorable pharmacokinetic profile, which allows for once-daily dosing and high tissue penetration, makes the Z Pack a valuable option for these conditions.
Benefits of Z Pack in Treating Infections

The benefits of using a Z Pack to treat bacterial infections are numerous. Its broad-spectrum activity means it can be used against a wide range of pathogens, and its convenience enhances patient compliance. Additionally, the Z Pack has been shown to have a low incidence of side effects, particularly when compared to other antibiotics, making it a favorable choice for many patients. The medication's ability to achieve high concentrations in tissues also contributes to its efficacy, ensuring that the infection site is adequately exposed to the antibiotic.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions

Like all medications, the Z Pack can cause side effects, although they are generally mild and transient. Common side effects include gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. Less frequently, patients may experience more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions or effects on the cardiac conduction system, such as QT interval prolongation. It's also important to consider potential drug interactions when prescribing a Z Pack, as it can interact with other medications, including antacids, which can decrease its absorption, and certain antiarrhythmic drugs, which may increase the risk of QT interval prolongation.
Precautions and Contraindications

There are several precautions and contraindications to consider when prescribing a Z Pack. Patients with a known hypersensitivity to azithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics should not receive a Z Pack. Additionally, caution is advised in patients with certain cardiac conditions, given the potential for QT interval prolongation. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should only be treated with a Z Pack when the benefits outweigh the risks, as there is limited data on its use in these populations.
Responsible Use of Z Pack to Combat Antibiotic Resistance

The responsible use of antibiotics like the Z Pack is crucial in the fight against antibiotic resistance. This involves only prescribing antibiotics when they are truly necessary, choosing the most appropriate antibiotic for the specific infection, and ensuring that patients complete the full course of treatment as prescribed. By using antibiotics judiciously, we can help preserve their efficacy for future generations.
Future Directions in Antibiotic Therapy
As antibiotic resistance continues to pose a significant threat to public health, research into new antibiotic therapies and alternative treatments is ongoing. This includes the development of new classes of antibiotics, as well as strategies to enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics. Additionally, there is a growing interest in non-antibiotic approaches to treating infections, such as the use of bacteriophage therapy and antimicrobial peptides.
What is the standard dosing regimen for a Z Pack?
+The standard adult dose for most infections is 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg once daily for the next 4 days.
Can the Z Pack be used to treat viral infections?
+No, the Z Pack is an antibiotic and is only effective against bacterial infections. It should not be used to treat viral infections.
Are there any potential interactions between the Z Pack and other medications?
+Yes, the Z Pack can interact with other medications, including antacids and certain antiarrhythmic drugs. It's essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking.
In conclusion, the Z Pack is a valuable antibiotic for the treatment of various bacterial infections, offering a convenient dosing regimen and a generally favorable side effect profile. However, its use must be guided by a thorough understanding of its dosing guidelines, potential side effects, and interactions. By using the Z Pack responsibly and adhering to established treatment guidelines, we can help ensure its continued efficacy in treating bacterial infections. We invite readers to share their thoughts on the importance of responsible antibiotic use and the role of the Z Pack in modern medicine. Your input can help foster a deeper understanding of this critical topic and encourage more informed discussions about antibiotic therapy.
