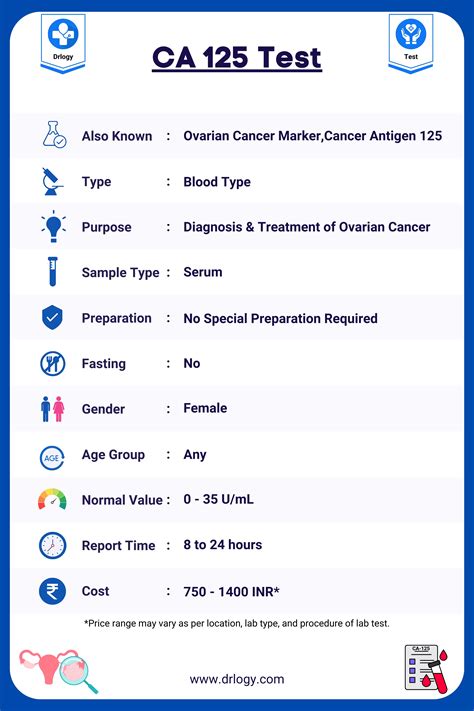
Intro
Discover 5 crucial CA 125 facts, including its role in ovarian cancer diagnosis, tumor marker significance, and blood test interpretations, to understand its implications on womens health and cancer screenings.
The CA 125 test is a widely used diagnostic tool for detecting and monitoring ovarian cancer. Understanding the facts about CA 125 is essential for individuals, especially women, to make informed decisions about their health. In this article, we will delve into the world of CA 125, exploring its significance, uses, and implications.
Ovarian cancer is a leading cause of death among gynecological cancers, and early detection is crucial for effective treatment. The CA 125 test has been a cornerstone in the diagnosis and management of ovarian cancer for decades. However, its role extends beyond ovarian cancer, and it is essential to understand the intricacies of this test. Whether you are a patient, a caregiver, or simply interested in learning more about women's health, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of CA 125 facts.
The importance of understanding CA 125 cannot be overstated. With the increasing awareness of women's health issues, it is vital to empower individuals with knowledge about diagnostic tools and their implications. By exploring the world of CA 125, we can better navigate the complex landscape of ovarian cancer diagnosis and treatment. In the following sections, we will delve into the specifics of CA 125, including its definition, uses, and limitations.
What is CA 125?

How is CA 125 used in diagnosis?
The CA 125 test is commonly used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, such as ultrasound and biopsy, to diagnose ovarian cancer. A high CA 125 level can indicate the presence of ovarian cancer, but it is not definitive. Further testing is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. The CA 125 test can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect potential recurrence.CA 125 and Ovarian Cancer

Stages of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is typically staged using the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) system, which ranges from stage I to stage IV. The CA 125 test can be used to monitor the progression of the disease and detect potential recurrence. Elevated CA 125 levels can indicate the presence of cancer cells, even if they are not visible on imaging tests.CA 125 and Other Conditions
- Endometriosis: A condition in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus.
- Uterine fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease: An infection of the female reproductive organs.
- Pregnancy: CA 125 levels can be elevated during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester.
Interpreting CA 125 Results
Interpreting CA 125 results requires careful consideration of the individual's medical history and other diagnostic tests. A high CA 125 level can indicate the presence of ovarian cancer, but it is not definitive. Further testing, such as ultrasound and biopsy, is necessary to confirm the diagnosis.Limitations of CA 125
- False positives: Elevated CA 125 levels can be caused by non-cancerous conditions, leading to false positives.
- False negatives: Some ovarian cancers may not produce high levels of CA 125, leading to false negatives.
- Limited sensitivity: The CA 125 test is not sensitive enough to detect all cases of ovarian cancer.
Future Directions
Research is ongoing to develop more sensitive and specific diagnostic tests for ovarian cancer. These include:- Biomarker panels: Combining multiple biomarkers, including CA 125, to improve diagnostic accuracy.
- Imaging tests: Developing more sensitive imaging tests, such as ultrasound and MRI, to detect ovarian cancer.
Practical Applications of CA 125

- Monitoring treatment response: CA 125 levels can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect potential recurrence.
- Screening high-risk individuals: CA 125 testing can be used to screen individuals at high risk of ovarian cancer, such as those with a family history of the disease.
Real-World Examples
The CA 125 test has been used in several real-world scenarios, including:- A 45-year-old woman with a family history of ovarian cancer undergoes CA 125 testing as part of her annual health checkup. Her results show elevated levels of CA 125, leading to further testing and diagnosis of ovarian cancer.
- A 60-year-old woman with ovarian cancer undergoes CA 125 testing to monitor her treatment response. Her results show decreasing levels of CA 125, indicating a positive response to treatment.
Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with CA 125 testing in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of ovarian cancer and the role of CA 125 in its diagnosis and management.
What is the normal range for CA 125 levels?
+The normal range for CA 125 levels is typically considered to be below 35 units per milliliter (U/mL). However, this range can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's medical history.
Can CA 125 be used to screen for ovarian cancer in asymptomatic women?
+The CA 125 test is not recommended as a screening tool for asymptomatic women due to its limited sensitivity and specificity. However, it may be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as ultrasound, to screen high-risk individuals.
How often should CA 125 levels be monitored in women with ovarian cancer?
+CA 125 levels should be monitored regularly in women with ovarian cancer to track treatment response and detect potential recurrence. The frequency of monitoring will depend on the individual's medical history and treatment plan.
