Intro
Discover how a CO2 blood test works, measuring carbon dioxide levels to diagnose respiratory issues, acidosis, and kidney function, using arterial blood gas analysis, bicarbonate levels, and pH balance to provide accurate results.
The importance of understanding how the body regulates its internal balance cannot be overstated, and one crucial aspect of this balance is the level of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood. A CO2 blood test is a vital diagnostic tool used to measure the amount of CO2 in the blood, providing valuable insights into the body's acid-base balance. This test is often performed in conjunction with other tests to assess the overall health of an individual. Understanding how a CO2 blood test works and what its results signify can empower individuals to take better control of their health.
The human body is a complex system where the balance of various substances, including gases like CO2, is meticulously maintained. CO2 is a byproduct of metabolism and is transported in the blood back to the lungs, where it is exhaled out. The level of CO2 in the blood can indicate how well the body is ventilating and the effectiveness of the gas exchange process in the lungs. Moreover, it reflects the body's metabolic rate and the balance between the production and elimination of CO2.
A CO2 blood test, also known as a bicarbonate test, measures the level of bicarbonate ions in the blood, which indirectly reflects the level of CO2. Bicarbonate is a crucial component in the body's buffering system, helping to maintain the blood's pH level within a narrow, healthy range. This test can reveal issues related to the respiratory or metabolic systems, guiding healthcare providers in diagnosing conditions such as respiratory diseases, metabolic disorders, or other systemic issues that could affect the body's acid-base balance.
Introduction to CO2 Blood Test

The CO2 blood test is a simple yet informative diagnostic tool. It is usually performed as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) or an electrolyte panel. These panels assess various components of the blood, including electrolytes, sugars, and waste products, to provide a broad view of a person's metabolic health. The test itself involves drawing a blood sample from a vein, typically in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
How CO2 Blood Test Works

The CO2 blood test works by measuring the level of bicarbonate ions in the blood. Bicarbonate serves as a buffer, helping to regulate the blood's pH level. When CO2 levels in the blood increase, it can combine with water to form carbonic acid, which then dissociates into hydrogen ions and bicarbonate ions. The level of bicarbonate ions is directly related to the level of CO2 in the blood because it is the body's way of managing excess CO2 through the buffering system.
Steps Involved in the CO2 Blood Test
The process of conducting a CO2 blood test involves several steps: - **Preparation**: The individual may be required to fast for a certain period before the test to ensure accurate results. - **Blood Draw**: A healthcare professional draws a blood sample from a vein, usually in the arm. - **Analysis**: The blood sample is sent to a laboratory where the level of bicarbonate is measured. - **Interpretation**: The results are interpreted by a healthcare provider, who looks for normal, elevated, or decreased levels of bicarbonate.Benefits of CO2 Blood Test

The CO2 blood test offers several benefits, including:
- Early Detection of Diseases: It can help in the early detection of diseases related to the respiratory and metabolic systems.
- Monitoring of Treatment: For individuals already diagnosed with conditions affecting their acid-base balance, the CO2 blood test can monitor the effectiveness of their treatment.
- Assessment of Overall Health: It provides insights into the body's metabolic rate and the effectiveness of the gas exchange process in the lungs.
Interpreting CO2 Blood Test Results
Interpreting the results of a CO2 blood test involves understanding what the levels of bicarbonate signify: - **Normal Levels**: Typically, the normal range for bicarbonate levels is between 23 and 29 mmol/L, but this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory. - **Elevated Levels**: High bicarbonate levels may indicate metabolic alkalosis, a condition where the blood becomes too alkaline. - **Decreased Levels**: Low bicarbonate levels may suggest metabolic acidosis, where the blood becomes too acidic.Common Conditions Diagnosed with CO2 Blood Test
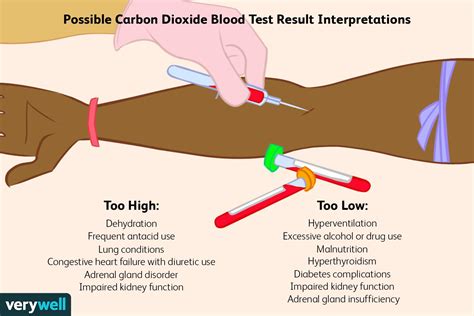
Several conditions can be diagnosed or monitored using the CO2 blood test, including:
- Respiratory Diseases: Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or pneumonia can affect the lungs' ability to exchange gases, leading to abnormal CO2 levels.
- Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes, kidney disease, and other metabolic disorders can affect the body's acid-base balance.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Certain conditions, like severe diarrhea, can lead to the loss of bicarbonate, affecting the blood's pH level.
Limitations and Considerations
While the CO2 blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has its limitations and considerations: - **Variability in Results**: Results can vary slightly between different laboratories. - **Interpretation Requires Context**: The interpretation of the results must be done in the context of the individual's overall health and other diagnostic findings.Preparing for a CO2 Blood Test

Preparing for a CO2 blood test involves:
- Fasting: Individuals may be required to fast for a certain period before the test.
- Avoiding Certain Foods: Some foods can affect the results, so it's advisable to avoid them before the test.
- Informing Healthcare Provider: Informing the healthcare provider about any medications or supplements being taken is crucial.
After the Test
After the CO2 blood test: - **Results Interpretation**: The healthcare provider will interpret the results and discuss them with the individual. - **Follow-Up Tests**: Depending on the results, additional tests may be required for further evaluation. - **Treatment Plan**: If a condition is diagnosed, a treatment plan will be devised based on the individual's specific needs.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, the CO2 blood test is a critical diagnostic tool that offers insights into the body's acid-base balance and can help in the early detection and management of various diseases. As medical science continues to evolve, the role of such tests in preventive medicine and personalized healthcare is likely to expand. Understanding the importance and implications of a CO2 blood test can empower individuals to engage more proactively with their healthcare, fostering a more collaborative approach to maintaining good health.
What does a CO2 blood test measure?
+A CO2 blood test measures the level of bicarbonate ions in the blood, which reflects the body's acid-base balance and indirectly indicates the level of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood.
Why is a CO2 blood test important?
+It is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring conditions related to the respiratory and metabolic systems, helping in the early detection of diseases and guiding treatment plans.
How do I prepare for a CO2 blood test?
+Preparation may include fasting for a certain period and avoiding certain foods or medications that could affect the test results. It's essential to follow the specific instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with CO2 blood tests in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us create more relevant and useful content for our readers.
