Intro
Discover 5 ways to treat stenosis, a narrowing condition, using spinal decompression, physical therapy, and more, to alleviate symptoms and improve mobility, addressing cervical, lumbar, and spinal stenosis effectively.
Stenosis, a condition characterized by the narrowing of passages or openings in the body, can lead to a variety of health issues depending on its location and severity. The most common forms of stenosis affect the spine, heart valves, and arteries, leading to conditions such as spinal stenosis, aortic stenosis, and carotid artery stenosis. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for stenosis is crucial for managing the condition effectively. In this article, we will delve into the importance of addressing stenosis, its impact on health, and most importantly, explore five ways to treat stenosis, emphasizing the latest medical advancements and holistic approaches.
The importance of treating stenosis cannot be overstated. If left untreated, stenosis can lead to severe complications, including paralysis in the case of spinal stenosis, heart failure in the case of aortic stenosis, and stroke in the case of carotid artery stenosis. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing these outcomes and improving the quality of life for individuals with stenosis. The approach to treatment varies widely depending on the location and severity of the stenosis, as well as the patient's overall health. From lifestyle modifications and physical therapy to surgical interventions and medication, the options are diverse and continually evolving.
Stenosis affects not only the physical well-being of an individual but also has a significant impact on their mental and emotional health. The chronic pain and limited mobility associated with spinal stenosis, for example, can lead to depression and anxiety. Similarly, the knowledge of having a potentially life-threatening condition like aortic stenosis can cause considerable stress. Therefore, any treatment plan for stenosis must consider the whole person, addressing physical symptoms while also providing support for mental and emotional well-being. With advancements in medical science and technology, there are now more effective and less invasive treatment options available than ever before, offering hope to those affected by stenosis.
Understanding Stenosis
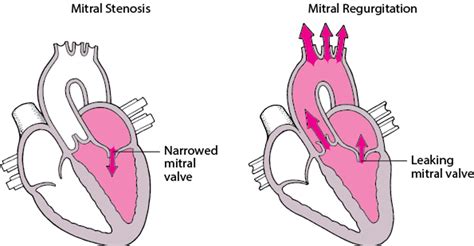
Diagnosis of Stenosis

Treatment Options for Stenosis
-
Lifestyle Modifications and Physical Therapy: For mild cases of stenosis, particularly spinal stenosis, lifestyle modifications such as losing weight, exercising regularly, and improving posture can help alleviate symptoms. Physical therapy can also be beneficial, helping to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
-
Medication: Medications can be used to manage symptoms of stenosis. For example, pain relievers and muscle relaxants may be prescribed for spinal stenosis, while medications to lower cholesterol and blood pressure may be recommended for aortic or carotid artery stenosis to prevent further narrowing of the arteries.
-
Surgical Interventions: For more severe cases of stenosis, surgical intervention may be necessary. This can include laminectomy for spinal stenosis, where part of the vertebra (lamina) is removed to create more space in the spinal canal. For aortic stenosis, surgical options include valve replacement, where the diseased valve is replaced with an artificial one. Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure used to treat carotid artery stenosis, involving the removal of plaque buildup in the carotid arteries.
-
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Advances in medical technology have led to the development of minimally invasive procedures for treating stenosis. For instance, angioplasty and stenting can be used for aortic and carotid artery stenosis, where a small balloon is inflated to widen the artery, and a stent is placed to keep it open. Similarly, minimally invasive spinal procedures can offer alternatives to traditional open surgery for spinal stenosis.
-
Alternative Therapies: Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy may also be considered for managing the symptoms of stenosis, particularly for spinal stenosis. These therapies can help in reducing pain and improving mobility, though their effectiveness can vary from person to person.
Benefits and Risks of Treatment Options
Each treatment option for stenosis comes with its own set of benefits and risks. For example, surgical interventions can provide significant relief from symptoms but also carry risks such as infection, bleeding, and reaction to anesthesia. Minimally invasive procedures generally have fewer risks but may not be suitable for all patients. Lifestyle modifications and physical therapy are beneficial for overall health but may not provide immediate relief for severe stenosis. Understanding these benefits and risks is crucial for making informed decisions about treatment.Living with Stenosis
Future Directions in Stenosis Treatment

Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your experiences and questions about stenosis in the comments below. Your insights can help others understand the condition better and find support in their journey. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards raising awareness about stenosis and promoting better health outcomes for all.
What are the most common types of stenosis?
+The most common types of stenosis include spinal stenosis, aortic stenosis, and carotid artery stenosis, each affecting different parts of the body and requiring distinct treatment approaches.
How is stenosis diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of stenosis involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as MRI, CT scans, echocardiograms, angiograms, or Doppler ultrasounds, depending on the type of stenosis suspected.
What are the risks of untreated stenosis?
+Untreated stenosis can lead to severe complications, including paralysis, heart failure, and stroke, depending on the location and severity of the condition. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to preventing these outcomes.
