Intro
A complete blood count (CBC) with differential is a crucial diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about the different components of blood. It is a commonly ordered test that helps healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood disorders. In this article, we will delve into the world of CBC with differential, exploring its importance, components, and interpretation.
The importance of a CBC with differential cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental test that helps healthcare professionals understand the overall health of a patient. By analyzing the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, healthcare professionals can identify potential health issues and develop effective treatment plans. A CBC with differential is often used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as anemia, leukemia, and infection, as well as to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments.
A CBC with differential typically includes several components, including a white blood cell count, red blood cell count, platelet count, and differential count. The differential count is a critical component of the test, as it provides information about the different types of white blood cells present in the blood. The five main types of white blood cells are neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type of white blood cell plays a unique role in the immune system, and abnormalities in their counts can indicate various health issues.
Cbc Count Components
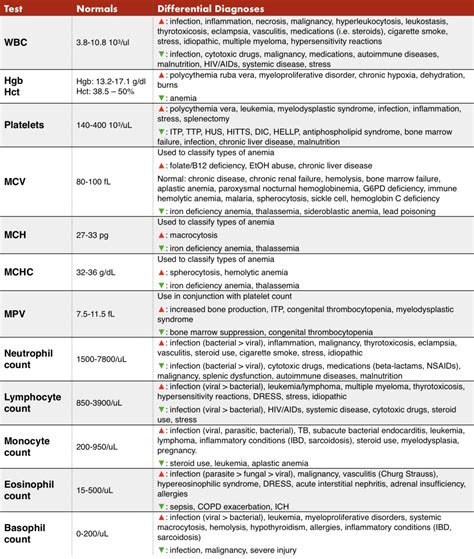
The components of a CBC with differential are crucial in understanding the test results. The white blood cell count, also known as the leukocyte count, measures the total number of white blood cells in the blood. A high white blood cell count can indicate infection, inflammation, or blood disorders, while a low count can indicate a weakened immune system. The red blood cell count, also known as the erythrocyte count, measures the total number of red blood cells in the blood. A high red blood cell count can indicate dehydration, while a low count can indicate anemia.
Cbc Differential Count
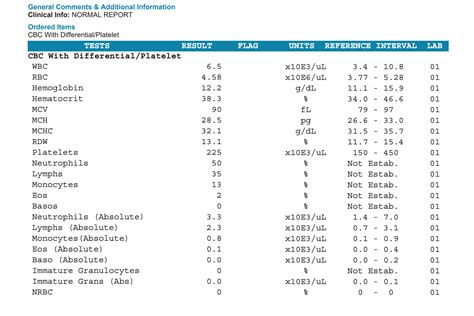
The differential count is a critical component of the CBC with differential. It provides information about the different types of white blood cells present in the blood. The five main types of white blood cells are neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Neutrophils are the most abundant type of white blood cell and play a key role in fighting bacterial infections. Lymphocytes, on the other hand, play a crucial role in the immune system, helping to fight viral infections and other diseases. Monocytes are large white blood cells that mature into macrophages, which help to clean up dead cells and other debris. Eosinophils play a role in fighting parasitic infections, while basophils are involved in the inflammatory response.
Types of White Blood Cells
The different types of white blood cells are: * Neutrophils: 45-75% of total white blood cells * Lymphocytes: 20-40% of total white blood cells * Monocytes: 5-10% of total white blood cells * Eosinophils: 1-4% of total white blood cells * Basophils: <1% of total white blood cellsCbc Count Interpretation
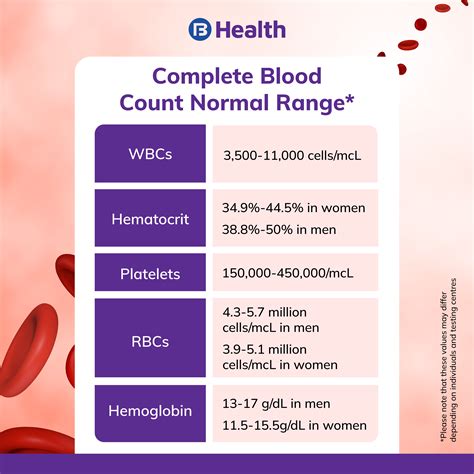
Interpreting the results of a CBC with differential requires a thorough understanding of the different components of the test. A healthcare professional will typically evaluate the results in conjunction with the patient's medical history, physical examination, and other diagnostic tests. Abnormal results can indicate various health issues, including anemia, infection, and blood disorders. For example, a high white blood cell count can indicate a bacterial infection, while a low count can indicate a viral infection.
Abnormal Results
Abnormal results can include: * High white blood cell count: infection, inflammation, or blood disorders * Low white blood cell count: weakened immune system, viral infection, or bone marrow disorder * High red blood cell count: dehydration, polycythemia vera, or other blood disorders * Low red blood cell count: anemia, blood loss, or bone marrow disorderCbc Count with Differential in Disease Diagnosis
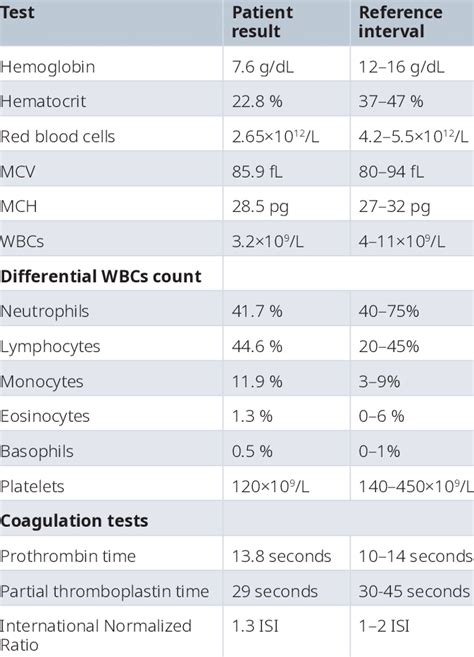
A CBC with differential is a valuable tool in disease diagnosis. It can help healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood disorders. For example, a patient with anemia may have a low red blood cell count, while a patient with a bacterial infection may have a high white blood cell count. A CBC with differential can also help healthcare professionals evaluate the effectiveness of treatments and monitor for potential side effects.
Disease Diagnosis
A CBC with differential can be used to diagnose and monitor various diseases, including: * Anemia: low red blood cell count, low hemoglobin, or low hematocrit * Infection: high white blood cell count, elevated neutrophil count, or elevated lymphocyte count * Blood disorders: abnormal white blood cell count, abnormal red blood cell count, or abnormal platelet countCbc Count with Differential in Monitoring Treatment
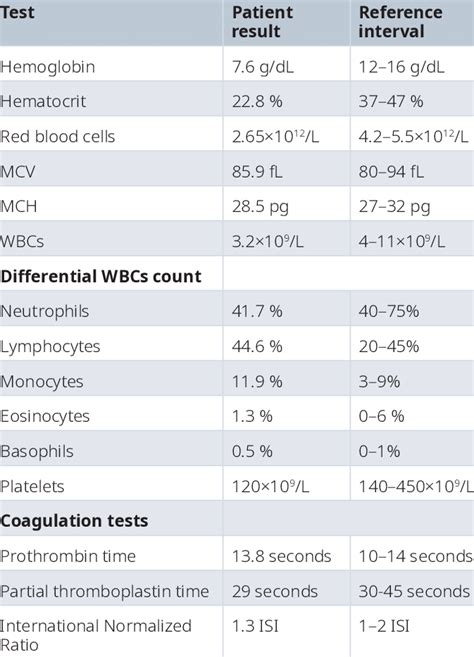
A CBC with differential is also a valuable tool in monitoring treatment. It can help healthcare professionals evaluate the effectiveness of treatments and monitor for potential side effects. For example, a patient undergoing chemotherapy may have a low white blood cell count, indicating a need for dose adjustments or supportive care. A CBC with differential can also help healthcare professionals monitor for potential complications, such as anemia or infection.
Monitoring Treatment
A CBC with differential can be used to monitor treatment, including: * Chemotherapy: monitoring for potential side effects, such as low white blood cell count or anemia * Antibiotics: monitoring for potential side effects, such as elevated liver enzymes or low platelet count * Blood transfusions: monitoring for potential complications, such as transfusion-related reactions or iron overloadCbc Count with Differential in Preventive Care
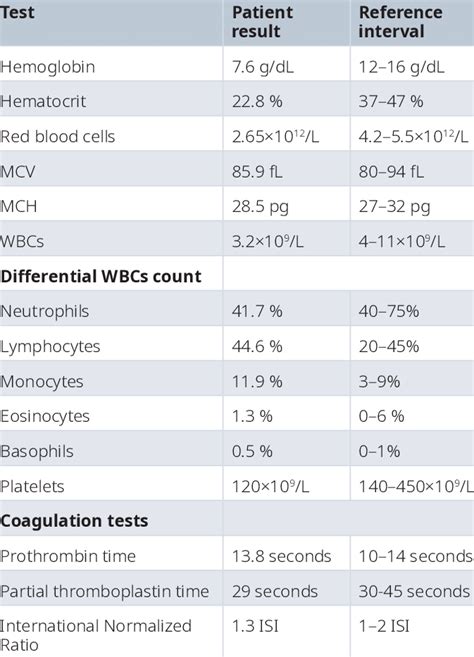
A CBC with differential is also a valuable tool in preventive care. It can help healthcare professionals identify potential health issues before they become serious. For example, a patient with a family history of anemia may have a low red blood cell count, indicating a need for iron supplements or other interventions. A CBC with differential can also help healthcare professionals monitor for potential health issues, such as infection or blood disorders.
Preventive Care
A CBC with differential can be used in preventive care, including: * Routine health screenings: monitoring for potential health issues, such as anemia or infection * Family history: identifying potential health issues, such as anemia or blood disorders * Lifestyle modifications: monitoring for potential health issues, such as iron deficiency or vitamin deficiencyWhat is a CBC with differential?
+A CBC with differential is a blood test that measures the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What is the differential count?
+The differential count is a component of the CBC that provides information about the different types of white blood cells present in the blood.
What are the different types of white blood cells?
+The five main types of white blood cells are neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
In summary, a CBC with differential is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about the different components of blood. It is a commonly ordered test that helps healthcare professionals diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood disorders. By understanding the different components of the test and their interpretation, healthcare professionals can develop effective treatment plans and monitor for potential complications. If you have any questions or concerns about CBC with differential, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others.
