Intro
Discover the Cbc medical abbreviation meaning, including Complete Blood Count, and related terms like Hematology, Blood Tests, and Medical Diagnosis, to understand its significance in healthcare and laboratory results.
The medical field is filled with abbreviations, and understanding them is crucial for effective communication among healthcare professionals. One such abbreviation is CBC, which stands for Complete Blood Count. The Complete Blood Count, also known as a full blood count, is a laboratory test that examines the different components of blood to diagnose and monitor various health conditions.
In the medical field, a Complete Blood Count is a routine test that measures several components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelets. The test provides valuable information about the overall health of a patient, helping doctors diagnose conditions such as anemia, infection, and blood clotting disorders.
A Complete Blood Count is typically performed as part of a routine medical examination or when a patient presents with symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or bleeding. The test involves a simple blood draw, and the sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of a Complete Blood Count can help doctors identify abnormalities in the blood, which can indicate underlying health issues.
What is a Complete Blood Count?
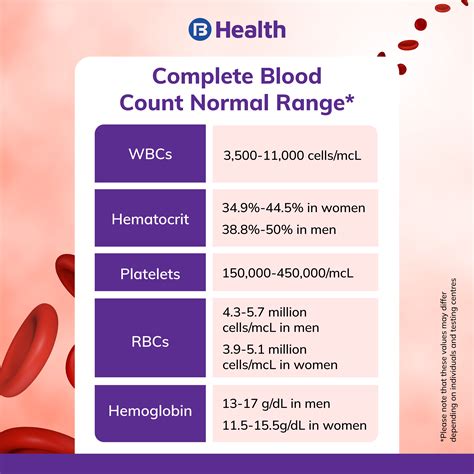
A Complete Blood Count is a comprehensive test that measures various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelets. The test provides a detailed picture of the blood's cellular composition, helping doctors diagnose and monitor a range of health conditions.
The different components of a Complete Blood Count include:
- Red blood cells: These cells carry oxygen throughout the body. A low red blood cell count can indicate anemia, while a high count can indicate dehydration or other conditions.
- White blood cells: These cells play a crucial role in the immune system, fighting off infections and diseases. An abnormal white blood cell count can indicate an underlying infection or condition.
- Hemoglobin: This protein carries oxygen in the blood. Low hemoglobin levels can indicate anemia or other conditions.
- Hematocrit: This measures the proportion of red blood cells in the blood. A low hematocrit can indicate anemia, while a high hematocrit can indicate dehydration or other conditions.
- Platelets: These cells help the blood to clot, preventing excessive bleeding. A low platelet count can indicate a bleeding disorder or other condition.
Why is a Complete Blood Count Performed?
A Complete Blood Count is performed for various reasons, including: - To diagnose and monitor anemia and other blood disorders - To evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for blood disorders - To screen for underlying infections or conditions - To monitor patients with a history of blood disorders - To evaluate the overall health of a patientComponents of a Complete Blood Count
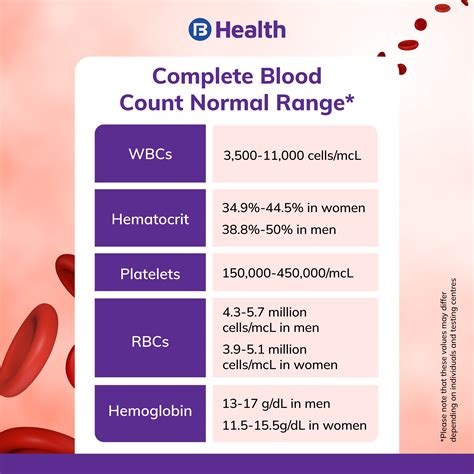
The components of a Complete Blood Count provide valuable information about the blood's cellular composition. The different components include:
- Red blood cell count: This measures the number of red blood cells in the blood.
- White blood cell count: This measures the number of white blood cells in the blood.
- Hemoglobin: This measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Hematocrit: This measures the proportion of red blood cells in the blood.
- Platelet count: This measures the number of platelets in the blood.
Interpreting the Results of a Complete Blood Count
The results of a Complete Blood Count are interpreted by a doctor or other healthcare professional. The results can indicate various health conditions, including: - Anemia: A low red blood cell count or low hemoglobin level can indicate anemia. - Infection: An abnormal white blood cell count can indicate an underlying infection. - Blood clotting disorders: A low platelet count can indicate a bleeding disorder or other condition. - Dehydration: A high hematocrit can indicate dehydration or other conditions.Abnormal Results

Abnormal results on a Complete Blood Count can indicate various health conditions. The different types of abnormal results include:
- Low red blood cell count: This can indicate anemia or other conditions.
- High red blood cell count: This can indicate dehydration or other conditions.
- Low white blood cell count: This can indicate a weakened immune system or other conditions.
- High white blood cell count: This can indicate an underlying infection or condition.
- Low platelet count: This can indicate a bleeding disorder or other condition.
- High platelet count: This can indicate a blood clotting disorder or other condition.
Treatments for Abnormal Results
The treatment for abnormal results on a Complete Blood Count depends on the underlying condition. The different treatments include: - Iron supplements: These can help treat anemia or other conditions. - Antibiotics: These can help treat underlying infections. - Blood transfusions: These can help treat severe anemia or other conditions. - Medications: These can help treat blood clotting disorders or other conditions.Preparation for a Complete Blood Count
To prepare for a Complete Blood Count, patients should:
- Avoid eating or drinking for several hours before the test
- Avoid taking certain medications that can affect the results
- Inform their doctor about any underlying medical conditions
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing to facilitate the blood draw
Risks and Complications
The risks and complications associated with a Complete Blood Count are minimal. The different risks and complications include: - Bleeding or bruising at the site of the blood draw - Infection at the site of the blood draw - Dizziness or lightheadedness after the blood drawBenefits of a Complete Blood Count

The benefits of a Complete Blood Count include:
- Early detection of health conditions: A Complete Blood Count can help diagnose health conditions early, allowing for prompt treatment.
- Monitoring of treatments: A Complete Blood Count can help monitor the effectiveness of treatments for blood disorders.
- Evaluation of overall health: A Complete Blood Count can provide valuable information about a patient's overall health.
Limitations of a Complete Blood Count
The limitations of a Complete Blood Count include: - Limited information: A Complete Blood Count provides limited information about the blood's cellular composition. - False results: The results of a Complete Blood Count can be affected by various factors, including medications or underlying medical conditions.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, a Complete Blood Count is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides information about the blood's cellular composition. The test can help diagnose and monitor various health conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood clotting disorders. If you have any concerns about your blood health, consult with your doctor or other healthcare professional.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Complete Blood Counts in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
What is a Complete Blood Count?
+A Complete Blood Count is a laboratory test that examines the different components of blood to diagnose and monitor various health conditions.
Why is a Complete Blood Count performed?
+A Complete Blood Count is performed to diagnose and monitor anemia and other blood disorders, evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, screen for underlying infections or conditions, and monitor patients with a history of blood disorders.
What are the components of a Complete Blood Count?
+The components of a Complete Blood Count include red blood cell count, white blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelet count.
How is a Complete Blood Count performed?
+A Complete Blood Count is performed by drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What are the benefits of a Complete Blood Count?
+The benefits of a Complete Blood Count include early detection of health conditions, monitoring of treatments, and evaluation of overall health.
