Intro
Learn about 5 blood sugar levels, normal range, and fluctuations. Understand blood glucose monitoring, diabetes management, and healthy targets to control glucose levels effectively.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts the body's ability to function properly. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, serves as the primary source of energy for the cells in the body. When blood sugar levels are within a normal range, the body can efficiently utilize insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, to facilitate glucose uptake by cells. However, when blood sugar levels become imbalanced, it can lead to various health complications, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and nerve damage. Therefore, understanding the importance of monitoring and managing blood sugar levels is essential for preventing and mitigating these conditions.
The human body has a natural regulatory system to maintain blood sugar levels within a narrow range. After consuming a meal, the digestive system breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. In response, the pancreas releases insulin to help cells absorb glucose, thereby reducing blood sugar levels. Conversely, when blood sugar levels drop, the pancreas produces glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. This delicate balance is vital for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, and any disruptions can have severe consequences.
Blood sugar levels are typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, but generally, they should be between 70 mg/dL and 140 mg/dL. Levels above 140 mg/dL may indicate hyperglycemia, a condition characterized by high blood sugar, while levels below 70 mg/dL may indicate hypoglycemia, a condition marked by low blood sugar. It is essential to monitor blood sugar levels regularly, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition, to prevent complications and ensure timely intervention.
Blood Sugar Level Ranges

Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including: * Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause blood sugar levels to rise. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can raise blood sugar levels. * Stress: Stress can cause the body to release stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can increase blood sugar levels. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation. * Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can affect blood sugar levels.Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
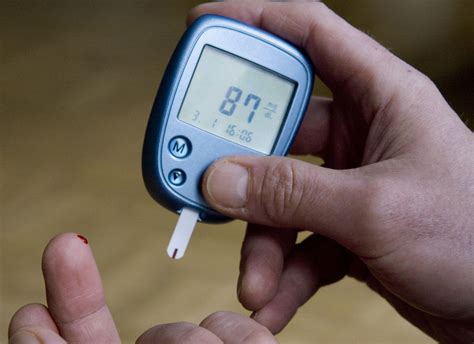
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Some strategies for managing blood sugar levels include: * Healthy eating: Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. * Stress management: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. * Medications: Take medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider to help regulate blood sugar levels. * Regular monitoring: Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to track progress and make adjustments to the management plan as needed.Complications of Unmanaged Blood Sugar Levels
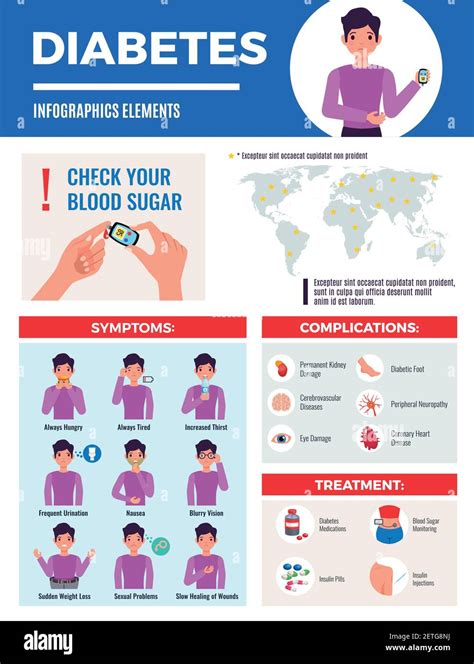
Preventing Blood Sugar Level Complications
Preventing complications related to unmanaged blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Some strategies for preventing complications include: * Regular monitoring: Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to track progress and make adjustments to the management plan as needed. * Healthy eating: Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. * Stress management: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. * Medications: Take medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider to help regulate blood sugar levels.Blood Sugar Level Management Tips

Blood Sugar Level Monitoring Devices
There are several devices available to monitor blood sugar levels, including: * Glucose meters: These devices measure the amount of glucose in a blood sample. * Continuous glucose monitors: These devices track blood sugar levels throughout the day. * Insulin pumps: These devices deliver insulin continuously throughout the day. * Smart insulin pens: These devices track insulin doses and provide reminders for future doses.Blood Sugar Level Management Apps
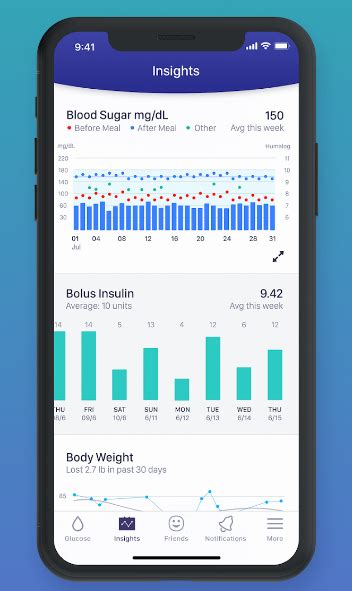
Blood Sugar Level Management Resources
Here are some additional resources for managing blood sugar levels: * American Diabetes Association (ADA): This organization provides information, support, and resources for individuals with diabetes. * Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): This organization provides information, support, and resources for individuals with diabetes. * National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): This organization provides information, support, and resources for individuals with diabetes. * Diabetes Education Program: This program provides education, support, and resources for individuals with diabetes.What are normal blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 mg/dL and 140 mg/dL.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood sugar levels depends on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, medication, and lifestyle. Generally, it is recommended to monitor blood sugar levels at least 4-6 times per day.
What are the complications of unmanaged blood sugar levels?
+Unmanaged blood sugar levels can lead to various complications, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, blindness, and amputations.
How can I prevent blood sugar level complications?
+Preventing complications related to unmanaged blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, such as regular monitoring, healthy eating, regular physical activity, stress management, and medications.
What are some tips for managing blood sugar levels?
+Some tips for managing blood sugar levels include staying hydrated, getting enough sleep, managing stress, being mindful of portion sizes, and choosing low-glycemic index foods.
In conclusion, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being. By understanding the importance of monitoring and managing blood sugar levels, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent complications and ensure timely intervention. We invite readers to share their experiences and tips for managing blood sugar levels in the comments below. Additionally, we encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote awareness and education about the importance of blood sugar level management and support individuals in their journey towards optimal health.
