Intro
Discover key 5 CBC blood test facts, including complete blood count results, hematocrit, hemoglobin, and white blood cell analysis, to understand your health and diagnose conditions like anemia and infection.
The complete blood count (CBC) test is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in medical settings to evaluate various aspects of a patient's health. It is a comprehensive test that measures different components of the blood, providing valuable insights into the body's overall condition. Understanding the significance and implications of a CBC test can empower individuals to take a more proactive approach to their health. In this article, we will delve into the importance of CBC tests, their components, and what the results can indicate about a person's health.
A CBC test is a routine procedure that can be performed as part of a regular health checkup or when a healthcare provider suspects an underlying condition that needs to be diagnosed or monitored. The test requires a small blood sample, usually drawn from a vein in the arm, which is then analyzed in a laboratory. The results of a CBC test can reveal a wealth of information about the blood's cellular composition, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Each component provides unique insights into different aspects of health, from the risk of infection to the presence of anemia or other blood disorders.
The importance of CBC tests cannot be overstated, as they offer a non-invasive and relatively simple method for detecting a range of health issues. By analyzing the different components of the blood, healthcare providers can identify abnormalities that may indicate the presence of a specific condition. For instance, an elevated white blood cell count can suggest an infection or inflammatory process, while a low red blood cell count may indicate anemia. Similarly, abnormalities in platelet counts can signal issues with blood clotting. Given the comprehensive nature of CBC tests, they are an indispensable tool in both preventive care and diagnostic medicine.
Understanding CBC Test Components
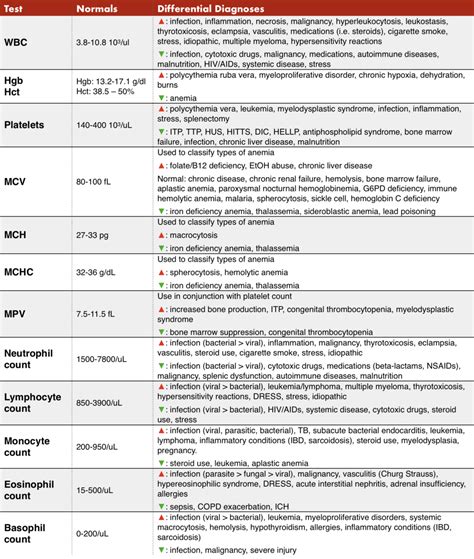
A CBC test evaluates several key components of the blood, each providing valuable information about the body's health status. These components include:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): These cells are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. Abnormalities in RBC counts can indicate conditions such as anemia or polycythemia.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): WBCs are crucial for the immune system, helping to fight off infections. An elevated WBC count can suggest the presence of an infection or inflammatory condition.
- Platelets: These small cells play a vital role in blood clotting. Abnormal platelet counts can indicate issues with bleeding or clotting.
- Hemoglobin (Hb) and Hematocrit (Hct): Hemoglobin is a protein in RBCs that carries oxygen, while hematocrit measures the proportion of blood volume made up of RBCs. These values can help diagnose anemia and other conditions affecting RBCs.
Interpreting CBC Test Results
Interpreting the results of a CBC test requires a comprehensive understanding of the normal ranges for each component and how they relate to overall health. Healthcare providers consider the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other diagnostic findings when interpreting CBC results. For example, a slightly elevated WBC count might not be concerning in someone who has recently recovered from an infection, but it could indicate a more serious issue in someone without a clear reason for such an elevation.Benefits of Regular CBC Tests

Regular CBC tests offer several benefits, particularly for individuals with chronic health conditions or those at risk of developing certain diseases. Some of the key advantages include:
- Early Detection of Health Issues: CBC tests can identify abnormalities in the blood that may indicate the presence of a health issue before symptoms become apparent.
- Monitoring of Chronic Conditions: For individuals with conditions like anemia, diabetes, or cardiovascular disease, regular CBC tests can help monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect any changes in condition.
- Prevention: By identifying risk factors or early signs of disease, individuals can take preventive measures to reduce their risk of developing more serious health problems.
Common Conditions Diagnosed with CBC Tests
CBC tests are instrumental in diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of health conditions. Some common conditions that can be identified or managed with CBC tests include: - Anemia: Characterized by low RBC counts or hemoglobin levels, anemia can result from iron deficiency, vitamin deficiencies, or chronic diseases. - Infections: Elevated WBC counts can indicate the presence of a bacterial or viral infection. - Blood Clotting Disorders: Abnormal platelet counts or function can signal issues with blood clotting, such as thrombocytopenia or thrombocytosis. - Leukemia: This type of cancer affects the blood and bone marrow, often leading to abnormal WBC counts.Preparation and Procedure for CBC Tests

Preparing for a CBC test is relatively straightforward. Individuals are usually advised to:
- Avoid eating for a certain period before the test, though this is not always required.
- Inform their healthcare provider about any medications or supplements they are taking.
- Avoid strenuous exercise before the test. The procedure itself involves a simple blood draw, typically from a vein in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Results are usually available within a day or two, though this can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific tests ordered.
Understanding CBC Test Results
When receiving the results of a CBC test, it's essential to understand what each component measures and what the normal ranges are. Results are often reported in a table or graph format, making it easier to visualize the different components and their values. Healthcare providers will discuss the results with the patient, explaining any abnormalities and what they might indicate. In some cases, additional testing may be necessary to further investigate any findings.Limitations and Potential Risks of CBC Tests

While CBC tests are highly valuable, they also have limitations. For instance:
- A single abnormal result does not necessarily indicate a serious health issue; it could be due to a temporary condition or laboratory error.
- CBC tests may not detect all types of health issues, particularly those that do not affect the blood cells directly.
- There is a small risk of bleeding, bruising, or infection at the blood draw site, though these complications are rare.
Future Directions in CBC Testing
Advancements in medical technology are continually improving the accuracy and scope of CBC tests. Future directions may include: - More sophisticated automated analyzers that can provide quicker and more detailed results. - The integration of CBC tests with other diagnostic tools, such as genetic testing, to offer a more comprehensive view of a patient's health. - Increased use of point-of-care testing, allowing for rapid CBC results in outpatient settings or even at home.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, CBC tests are a vital component of both preventive care and diagnostic medicine. By understanding the components of a CBC test, interpreting the results, and recognizing the benefits and limitations of these tests, individuals can better navigate their health care. Whether as part of a routine checkup or in response to specific symptoms, CBC tests offer a window into the body's health, guiding healthcare decisions and promoting overall well-being.
Final Thoughts on CBC Tests
As medical science continues to evolve, the role of CBC tests in healthcare will likely expand. With their ability to provide insights into various aspects of health, from infection and inflammation to anemia and blood clotting disorders, CBC tests will remain an essential diagnostic tool. By staying informed about CBC tests and their implications, individuals can take a more active role in their health management, fostering a collaborative approach to care that prioritizes prevention, early detection, and effective treatment.What does a CBC test measure?
+A CBC test measures various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, providing insights into the body's overall health and detecting potential health issues.
How often should I get a CBC test?
+The frequency of CBC tests depends on individual health needs. For healthy individuals, a yearly checkup may include a CBC test. However, those with chronic conditions or at risk of certain diseases may need more frequent testing as advised by their healthcare provider.
Can CBC tests diagnose all blood disorders?
+While CBC tests are highly useful for diagnosing many blood disorders, they may not detect all types of conditions. Additional tests, such as blood smears, bone marrow biopsies, or genetic tests, might be necessary for a comprehensive diagnosis.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with CBC tests in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from understanding the importance and implications of CBC tests in healthcare. Together, let's promote health awareness and empower individuals to take an active role in their well-being.
