Intro
Unlock insights into CBC with differential and platelet count, a comprehensive blood test analyzing white blood cells, red blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelets to diagnose conditions like anemia, infection, and bleeding disorders.
The complete blood count (CBC) with differential and platelet count is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in the medical field to assess various components of the blood. It is a crucial test that provides valuable information about the overall health of an individual, helping doctors diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, from anemia and infection to bleeding disorders and cancer. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the CBC with differential and platelet count, its components, and how it is used in clinical practice.
The CBC is a comprehensive test that measures the levels of different blood cells, including red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets. The differential count, also known as the diff, provides a detailed breakdown of the different types of WBCs present in the blood, while the platelet count measures the number of platelets. These components are essential for maintaining proper blood function, and any abnormalities can indicate underlying health issues.
The CBC with differential and platelet count is a commonly ordered test, and its results can be used to diagnose and monitor various conditions, such as anemia, infection, inflammation, and bleeding disorders. For example, a low RBC count can indicate anemia, while an elevated WBC count can suggest infection or inflammation. A low platelet count, also known as thrombocytopenia, can increase the risk of bleeding, while an elevated platelet count can increase the risk of blood clots.
Cbc Components
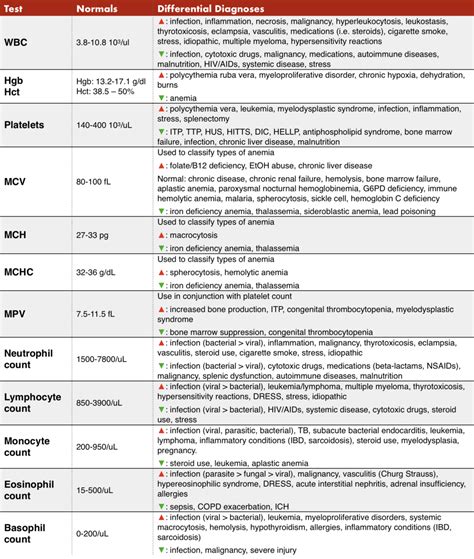
The CBC with differential and platelet count consists of several components, each providing valuable information about the blood. These components include:
- Red blood cell (RBC) count: measures the number of RBCs in the blood
- Hemoglobin (Hb) level: measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood
- Hematocrit (Hct) level: measures the proportion of RBCs in the blood
- White blood cell (WBC) count: measures the number of WBCs in the blood
- Differential count: provides a detailed breakdown of the different types of WBCs present in the blood, including:
- Neutrophils
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
- Platelet count: measures the number of platelets in the blood
How Cbc Is Performed

The CBC with differential and platelet count is typically performed using a blood sample drawn from a vein in the arm. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where it is examined using specialized equipment and techniques. The results are usually available within a few hours, although this may vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test.
The test is usually performed in the following steps:
- Blood sample collection: a healthcare professional draws a blood sample from a vein in the arm using a needle and syringe.
- Sample preparation: the blood sample is prepared for analysis by adding anticoagulants to prevent clotting.
- Analysis: the prepared sample is then analyzed using specialized equipment, such as a hematology analyzer.
- Result interpretation: the results are interpreted by a healthcare professional, who will look for any abnormalities or patterns that may indicate underlying health issues.
Cbc Results Interpretation
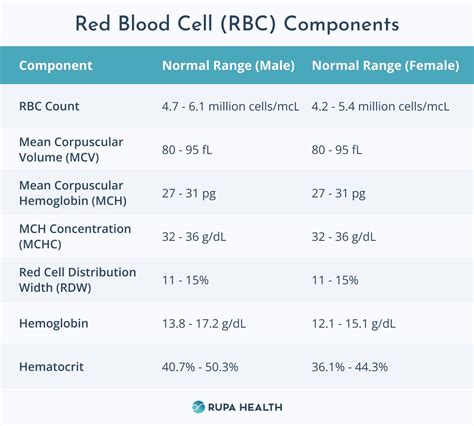
Interpreting the results of a CBC with differential and platelet count requires a thorough understanding of the different components and their normal ranges. The results are usually presented in a table or graph, with each component listed separately. The healthcare professional will look for any abnormalities or patterns that may indicate underlying health issues.
For example:
- A low RBC count may indicate anemia, while a high RBC count may indicate dehydration or polycythemia.
- A low WBC count may indicate a weakened immune system, while a high WBC count may indicate infection or inflammation.
- A low platelet count may indicate thrombocytopenia, while a high platelet count may indicate thrombocytosis.
Cbc And Differential Count
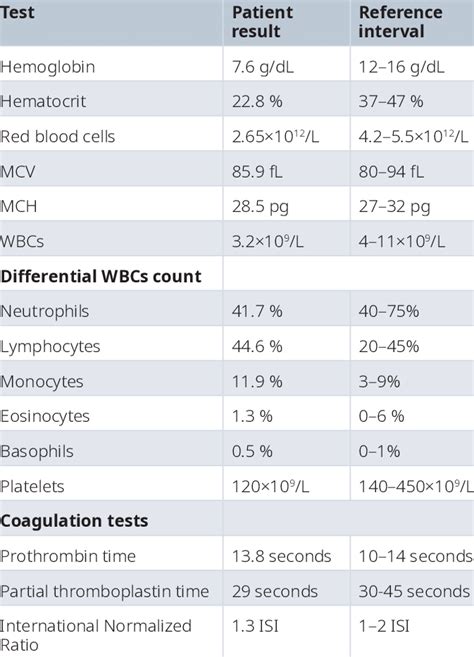
The differential count is an essential component of the CBC, providing a detailed breakdown of the different types of WBCs present in the blood. The differential count is usually expressed as a percentage of the total WBC count, and it can help diagnose and monitor various conditions, such as infection, inflammation, and cancer.
The differential count typically includes the following components:
- Neutrophils: 45-75% of total WBCs
- Lymphocytes: 20-40% of total WBCs
- Monocytes: 5-10% of total WBCs
- Eosinophils: 1-4% of total WBCs
- Basophils: 0.5-1% of total WBCs
Any abnormalities in the differential count can indicate underlying health issues, such as:
- Neutrophilia: an increase in neutrophils, which can indicate infection or inflammation
- Lymphocytosis: an increase in lymphocytes, which can indicate viral infection or cancer
- Monocytosis: an increase in monocytes, which can indicate chronic infection or inflammation
- Eosinophilia: an increase in eosinophils, which can indicate allergic reaction or parasitic infection
- Basophilia: an increase in basophils, which can indicate allergic reaction or cancer
Platelet Count And Its Importance
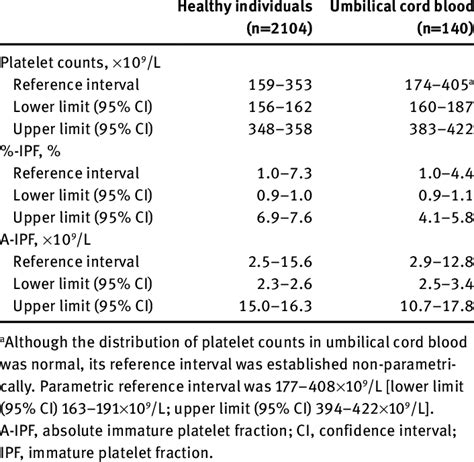
The platelet count is a critical component of the CBC, measuring the number of platelets in the blood. Platelets play a vital role in blood clotting, and any abnormalities in the platelet count can increase the risk of bleeding or blood clots.
A low platelet count, also known as thrombocytopenia, can increase the risk of bleeding, while a high platelet count, also known as thrombocytosis, can increase the risk of blood clots. The normal range for platelet count is usually between 150,000 and 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood.
Any abnormalities in the platelet count can indicate underlying health issues, such as:
- Thrombocytopenia: a low platelet count, which can increase the risk of bleeding
- Thrombocytosis: a high platelet count, which can increase the risk of blood clots
- Bleeding disorders: such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease
- Cancer: such as leukemia or lymphoma
Clinical Applications Of Cbc

The CBC with differential and platelet count has numerous clinical applications, including:
- Diagnosing and monitoring anemia, infection, inflammation, and bleeding disorders
- Evaluating the effectiveness of treatment for various conditions, such as cancer or autoimmune disorders
- Monitoring blood cell production in patients with bone marrow disorders
- Detecting blood cell abnormalities in patients with genetic disorders
The CBC is a widely used test, and its results can be used to guide clinical decision-making, such as:
- Ordering additional tests or procedures, such as bone marrow biopsy or imaging studies
- Initiating or adjusting treatment, such as antibiotics or transfusions
- Monitoring patient response to treatment, such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy
Limitations And Potential Interferences

While the CBC with differential and platelet count is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations and potential interferences, including:
- Sample collection and handling errors, which can affect the accuracy of the results
- Instrumental errors, such as calibration or maintenance issues
- Biological variability, such as diurnal or circadian rhythms
- Medications or supplements that can affect blood cell production or function
It is essential to consider these limitations and potential interferences when interpreting the results of a CBC with differential and platelet count, and to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Future Directions And Emerging Trends
The CBC with differential and platelet count is a constantly evolving field, with emerging trends and technologies that are improving its accuracy and usefulness. Some of the future directions and emerging trends include:
- Point-of-care testing, which allows for rapid and convenient testing at the bedside or in the clinic
- Molecular diagnostics, which can detect specific genetic or molecular abnormalities
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning, which can improve the accuracy and interpretation of CBC results
- Personalized medicine, which can tailor treatment to an individual's unique genetic and molecular profile
These emerging trends and technologies have the potential to revolutionize the field of hematology and improve patient outcomes, and it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments and advancements.
What is a CBC with differential and platelet count?
+A CBC with differential and platelet count is a blood test that measures the levels of different blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, and provides a detailed breakdown of the different types of white blood cells present in the blood.
What are the components of a CBC with differential and platelet count?
+The components of a CBC with differential and platelet count include red blood cell count, hemoglobin level, hematocrit level, white blood cell count, differential count, and platelet count.
What are the clinical applications of a CBC with differential and platelet count?
+The clinical applications of a CBC with differential and platelet count include diagnosing and monitoring anemia, infection, inflammation, and bleeding disorders, evaluating the effectiveness of treatment, and monitoring blood cell production in patients with bone marrow disorders.
What are the limitations and potential interferences of a CBC with differential and platelet count?
+The limitations and potential interferences of a CBC with differential and platelet count include sample collection and handling errors, instrumental errors, biological variability, and medications or supplements that can affect blood cell production or function.
What are the future directions and emerging trends in CBC with differential and platelet count?
+The future directions and emerging trends in CBC with differential and platelet count include point-of-care testing, molecular diagnostics, artificial intelligence and machine learning, and personalized medicine.
In conclusion, the CBC with differential and platelet count is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides essential information about the blood and its components. Its clinical applications are numerous, and it is widely used in the medical field to diagnose and monitor various conditions. While it has several limitations and potential interferences, emerging trends and technologies are improving its accuracy and usefulness. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the CBC with differential and platelet count, and we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below.
