Intro
Monitor your health with the 5 Vital Signs: pulse, breathing rate, blood pressure, temperature, and oxygen saturation, key indicators of overall well-being, tracking health status, and detecting potential medical issues.
Monitoring vital signs is a crucial aspect of healthcare, as it provides essential information about a patient's overall health and well-being. The five vital signs are temperature, pulse, breathing rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation. These signs are called "vital" because they are critical indicators of life, and changes in these signs can signal the presence of illness, injury, or other health issues. In this article, we will delve into the importance of each vital sign, how they are measured, and what the normal ranges are.
The importance of monitoring vital signs cannot be overstated. By tracking these signs, healthcare professionals can quickly identify any abnormalities or changes that may indicate a patient is at risk for a particular condition. For example, an elevated temperature can be a sign of infection, while an irregular pulse can indicate a heart problem. Regular monitoring of vital signs also allows healthcare professionals to track the effectiveness of treatments and make adjustments as needed.
Vital signs are an essential part of healthcare, and their importance extends beyond the medical field. Understanding vital signs can also help individuals take control of their own health and well-being. By knowing what their normal vital sign ranges are, individuals can quickly identify any changes that may indicate a health issue. This knowledge can also help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle and health choices, such as exercise and diet.
Temperature

Measuring Temperature
Temperature can be measured using a variety of methods, including oral, rectal, and axillary thermometers. Oral thermometers are the most common type and are placed under the tongue to measure temperature. Rectal thermometers are used to measure temperature in infants and young children, while axillary thermometers are used to measure temperature in the armpit.Pulse

Measuring Pulse
Pulse can be measured using a variety of methods, including manual and electronic methods. Manual pulse measurement involves placing the fingers on the wrist or neck to feel the pulse. Electronic pulse measurement involves using a device that detects the pulse and displays the rate on a screen.Breathing Rate
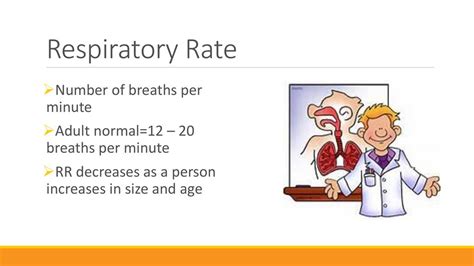
Measuring Breathing Rate
Breathing rate can be measured by counting the number of breaths taken per minute. This can be done manually by observing the patient's chest rise and fall or using a device that detects breathing rate.Blood Pressure
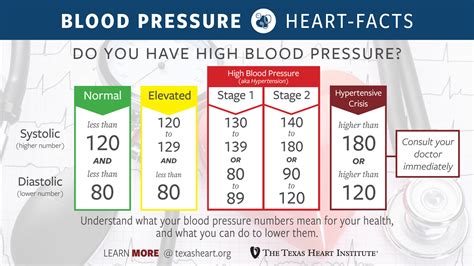
Measuring Blood Pressure
Blood pressure can be measured using a variety of methods, including manual and electronic methods. Manual blood pressure measurement involves using a sphygmomanometer and stethoscope to listen to the sounds of the blood flowing through the arteries. Electronic blood pressure measurement involves using a device that detects the blood pressure and displays the reading on a screen.Oxygen Saturation

Measuring Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen saturation can be measured using a pulse oximeter. This device emits light through the skin and detects the changes in light absorption that occur as oxygen binds to hemoglobin in the blood.Some of the key benefits of monitoring vital signs include:
- Early detection of health problems
- Improved patient outcomes
- Enhanced patient safety
- Better management of chronic conditions
- Increased patient engagement and empowerment
To get the most out of vital sign monitoring, it's essential to:
- Use accurate and reliable equipment
- Follow proper measurement techniques
- Take multiple readings to ensure accuracy
- Track changes in vital signs over time
- Communicate effectively with healthcare professionals
In addition to these benefits, monitoring vital signs can also help individuals take control of their own health and well-being. By understanding what their normal vital sign ranges are, individuals can quickly identify any changes that may indicate a health issue. This knowledge can also help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle and health choices, such as exercise and diet.
Some examples of how vital sign monitoring can be used in real-life scenarios include:
- Athletes using heart rate monitors to track their physical activity and optimize their training
- Individuals with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, using vital sign monitoring to manage their condition and prevent complications
- Healthcare professionals using vital sign monitoring to quickly identify patients who are at risk for certain conditions and provide targeted interventions
What are the normal ranges for vital signs?
+Normal ranges for vital signs vary depending on the individual and the specific vital sign being measured. However, general guidelines include: temperature 97.7-99.5°F (36.5-37.5°C), pulse 60-100 bpm, breathing rate 12-20 breaths per minute, blood pressure 90/60-120/80 mmHg, and oxygen saturation 95-100%.
How often should vital signs be monitored?
+The frequency of vital sign monitoring depends on the individual's health status and the specific vital sign being measured. For example, individuals with chronic conditions may need to monitor their vital signs daily, while healthy individuals may only need to monitor their vital signs occasionally.
What are some common causes of abnormal vital signs?
+Common causes of abnormal vital signs include infection, injury, dehydration, and chronic conditions such as diabetes or hypertension. Other factors, such as age, lifestyle, and environmental factors, can also affect vital signs.
How can I take control of my own vital sign monitoring?
+Individuals can take control of their own vital sign monitoring by investing in a home vital sign monitoring device, such as a blood pressure monitor or pulse oximeter. They can also work with their healthcare professional to develop a personalized vital sign monitoring plan.
What are some tips for accurate vital sign measurement?
+Tips for accurate vital sign measurement include using high-quality equipment, following proper measurement techniques, taking multiple readings to ensure accuracy, and tracking changes in vital signs over time.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the importance of monitoring vital signs. By understanding what their normal vital sign ranges are and how to monitor them effectively, individuals can take control of their own health and well-being. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with vital sign monitoring in the comments below. Additionally, if you have any questions or topics you'd like to discuss, please don't hesitate to reach out. Let's work together to prioritize our health and well-being by making informed decisions about our vital signs.
