Intro
Discover 5 essential tips for appendix removal, including pre-surgery prep, recovery strategies, and post-operative care, to ensure a smooth laparoscopic appendectomy and minimize complications, promoting a speedy appendicitis treatment and optimal healing process.
The appendix is a small, tube-like structure attached to the large intestine, and its function in the human body is still somewhat of a mystery. While it's not essential for our survival, there are instances where its removal becomes necessary due to conditions like appendicitis. Understanding the process and what to expect before, during, and after an appendectomy (the surgical removal of the appendix) is crucial for individuals facing this situation. The importance of being informed about the procedure, recovery, and potential complications cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the patient's ability to make informed decisions about their care and to navigate the recovery process effectively.
The decision to remove the appendix is typically made when the appendix becomes inflamed, a condition known as appendicitis. This inflammation can lead to severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. If left untreated, an inflamed appendix can rupture, leading to a potentially life-threatening infection. Therefore, understanding the signs and symptoms of appendicitis and seeking immediate medical attention if they occur is vital. Moreover, advancements in surgical techniques, including laparoscopic surgery, have made the appendectomy process less invasive and have reduced recovery times, making it a relatively safe procedure for those who require it.
For individuals considering or facing an appendectomy, it's essential to have a comprehensive understanding of what the procedure entails, the benefits and risks associated with it, and how to prepare for and recover from the surgery. This knowledge empowers patients to ask the right questions, make informed decisions about their care, and take proactive steps towards a smooth and successful recovery. Whether you're looking to understand the basics of appendicitis, the appendectomy procedure itself, or the post-operative care instructions, having detailed and accurate information at your disposal is key to navigating this medical situation effectively.
Understanding Appendicitis
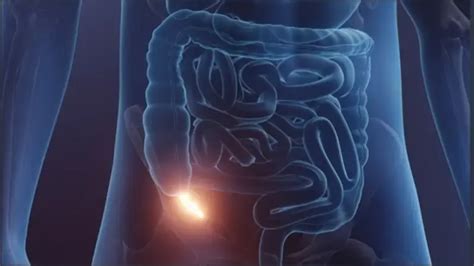
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The diagnosis of appendicitis is based on a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A healthcare provider will typically start by asking about the patient's symptoms and performing a physical examination, which may include pressing on the abdomen to check for tenderness. Blood tests may be ordered to check for signs of infection, such as an elevated white blood cell count. Imaging tests, like computed tomography (CT) scans or ultrasound, can help confirm the diagnosis by visualizing the appendix and any signs of inflammation.Appendectomy Procedure

Laparoscopic vs. Open Surgery
Both laparoscopic and open appendectomies are effective for treating appendicitis, but they have different recovery times and potential risks. Laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, leading to smaller scars, less pain post-operatively, and a faster return to normal activities. However, it requires specialized equipment and expertise, and the surgeon must be experienced in laparoscopic techniques. Open surgery, while more invasive, may be necessary in cases where the appendix has ruptured or if the patient has other complications that make laparoscopic surgery unsafe.Preparation and Recovery

Post-Operative Care
After an appendectomy, it's essential to monitor for signs of complications, such as infection, abscess, or bowel obstruction. Patients should follow up with their healthcare provider as instructed to ensure they are healing properly. Keeping the incision site clean and dry, taking medications as prescribed, and gradually returning to normal activities can help prevent complications and promote healing. It's also crucial to recognize the signs of potential problems, such as increasing pain, redness around the incision, fever, or difficulty urinating, and to seek medical attention immediately if these symptoms occur.Risks and Complications

Minimizing Risks
To minimize the risks associated with an appendectomy, patients should be proactive in their care. This includes asking questions before the procedure, such as what to expect during recovery, how to manage pain, and what signs of complications to watch for. After the surgery, adhering to the post-operative instructions, maintaining good hygiene, and avoiding strenuous activities until cleared by the healthcare provider can significantly reduce the risk of complications.5 Tips for a Successful Recovery

Conclusion and Next Steps
Understanding the process of appendectomy, from the diagnosis of appendicitis to the recovery after surgery, is essential for individuals facing this medical situation. By being informed and proactive in their care, patients can navigate the process more effectively, minimize the risk of complications, and ensure a successful recovery. Whether you're dealing with appendicitis or supporting a loved one through this experience, having the right information and resources can make a significant difference in outcomes and quality of life.What are the symptoms of appendicitis?
+The symptoms of appendicitis include sudden onset of abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and in some cases, constipation or diarrhea.
What is the difference between open and laparoscopic appendectomy?
+Open appendectomy involves a single incision in the abdomen, while laparoscopic appendectomy involves several small incisions through which a laparoscope and surgical tools are inserted. Laparoscopic surgery is less invasive and generally results in less pain and a quicker recovery.
How long does it take to recover from an appendectomy?
+The recovery time from an appendectomy can vary depending on the individual and the type of surgery performed. Generally, patients can return to normal activities within a few weeks after laparoscopic surgery and within 4-6 weeks after open surgery.
