Intro
The human body is a complex system that relies on a delicate balance of various substances to function properly. One such substance is chloride, an essential electrolyte that plays a vital role in maintaining the body's fluid balance and facilitating various bodily functions. Chloride concentration in blood is a critical aspect of human health, and understanding its importance can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain their overall well-being. In this article, we will delve into the world of chloride concentration in blood, exploring its significance, normal levels, factors that influence it, and the implications of abnormal levels.
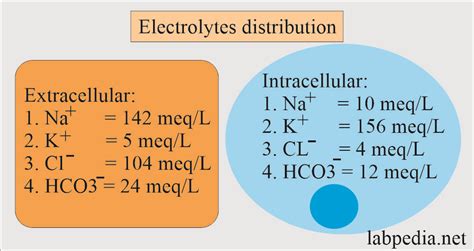
Chloride is the most abundant anion in the human body, accounting for approximately 70% of the total anion content in the blood. It is an essential component of various bodily fluids, including blood, sweat, and tears. Chloride helps regulate the balance of fluids within the body, maintaining proper blood pressure, and facilitating the transmission of nerve impulses. Moreover, chloride is involved in the production of digestive fluids, such as stomach acid, which is essential for breaking down food in the digestive system. Given its widespread involvement in various bodily functions, it is crucial to maintain optimal chloride levels in the blood.
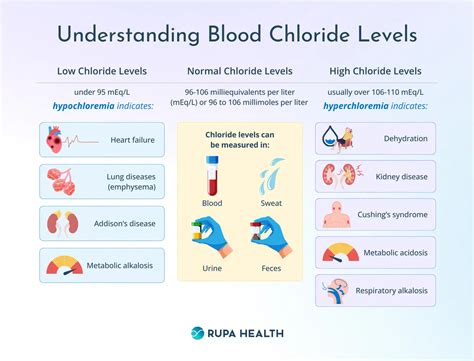
The normal chloride concentration in blood ranges from 96 to 106 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). This range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method used. Chloride levels in the blood are tightly regulated by the kidneys, which adjust the amount of chloride excreted in the urine to maintain a stable balance. Various factors can influence chloride levels, including diet, hydration status, and certain medical conditions. For instance, a diet high in salt can lead to increased chloride levels, while dehydration can cause a decrease in chloride concentration. Understanding these factors can help individuals take steps to maintain optimal chloride levels and prevent potential health issues.
Importance of Chloride Concentration in Blood
Factors That Influence Chloride Concentration
Several factors can influence chloride concentration in blood, including: * Diet: A diet high in salt can lead to increased chloride levels, while a diet low in salt can cause a decrease in chloride concentration. * Hydration status: Dehydration can cause a decrease in chloride concentration, while overhydration can lead to an increase in chloride levels. * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, heart failure, and liver disease, can affect chloride levels in the blood. * Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can influence chloride levels by increasing or decreasing the amount of chloride excreted in the urine.Normal Chloride Levels in Blood
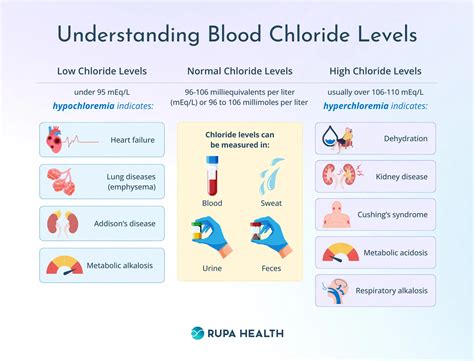
Consequences of Abnormal Chloride Levels
Abnormal chloride levels can have significant consequences on overall health. Hyperchloremia, or elevated chloride levels, can lead to: * Dehydration * Electrolyte imbalance * Metabolic acidosis * Respiratory problems Hypochloremia, or decreased chloride levels, can cause: * Muscle weakness * Fatigue * Seizures * Respiratory problems It is crucial to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.Causes of Abnormal Chloride Levels
Treatment Options for Abnormal Chloride Levels
Treatment options for abnormal chloride levels depend on the underlying cause. In some cases, treatment may involve: * Dietary changes: Adjusting salt intake or increasing fluid consumption can help regulate chloride levels. * Medications: Medications, such as diuretics or electrolyte supplements, can help restore normal chloride levels. * Medical procedures: In severe cases, medical procedures, such as dialysis, may be necessary to restore normal chloride levels.Prevention and Management

Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, chloride concentration in blood is a critical aspect of human health. Maintaining optimal chloride levels is essential for regulating various bodily functions, including fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contraction. By understanding the factors that influence chloride levels and taking proactive steps to prevent and manage abnormal levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing related health issues. If you have concerns about your chloride levels or overall health, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.What is the normal range for chloride concentration in blood?
+The normal range for chloride concentration in blood is 96 to 106 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
What are the consequences of abnormal chloride levels?
+Abnormal chloride levels can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, metabolic acidosis, respiratory problems, muscle weakness, fatigue, seizures, and other health issues.
How can I prevent and manage abnormal chloride levels?
+Preventing and managing abnormal chloride levels requires a comprehensive approach, including maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, monitoring electrolyte levels, and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
What are the causes of abnormal chloride levels?
+Causes of abnormal chloride levels include kidney disease, heart failure, liver disease, medications, and dietary factors.
How can I get my chloride levels checked?
+You can get your chloride levels checked by consulting with a healthcare professional, who will perform a blood test to determine your chloride levels.
