Intro
Discover how beta blockers work to reduce blood pressure, alleviate anxiety, and regulate heart rate, exploring their mechanisms, benefits, and uses in managing hypertension, angina, and heart failure.
The importance of beta blockers cannot be overstated, as they have revolutionized the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions. These medications have been widely used for decades to manage conditions such as high blood pressure, angina, and certain heart rhythm disorders. By understanding how beta blockers work, individuals can better appreciate the significance of these medications and how they can improve overall health. Beta blockers have been a cornerstone in the management of cardiovascular diseases, and their mechanisms of action are multifaceted, involving various physiological processes.
The role of beta blockers in modern medicine is undeniable, with millions of people worldwide relying on these medications to manage their conditions. From reducing blood pressure to alleviating symptoms of anxiety, beta blockers have proven to be versatile and effective. However, their benefits extend beyond just treating cardiovascular conditions, as they can also be used to manage certain neurological and endocrine disorders. By exploring the different ways beta blockers work, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the complex mechanisms involved in their therapeutic effects.
Beta blockers have become an essential part of many treatment regimens, and their impact on public health has been significant. By reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events, beta blockers have helped to improve the quality of life for countless individuals. Moreover, their ability to manage symptoms of anxiety and tremors has made them a valuable tool in the treatment of various neurological and psychiatric conditions. As research continues to uncover the full potential of beta blockers, it is clear that these medications will remain a vital component of modern medicine for years to come.
Introduction to Beta Blockers
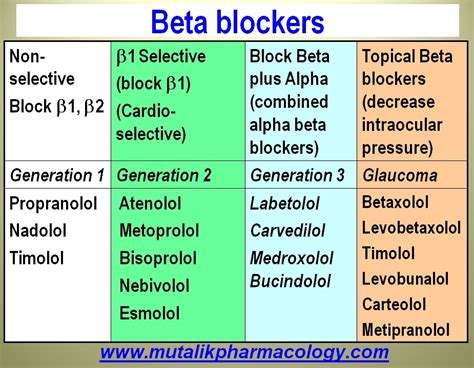
Types of Beta Blockers
There are several types of beta blockers, each with its own unique characteristics and mechanisms of action. Some of the most common types of beta blockers include: * Non-selective beta blockers, which block both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors * Selective beta blockers, which block only beta-1 receptors * Combined alpha and beta blockers, which block both alpha and beta receptors Each type of beta blocker has its own specific uses and benefits, and the choice of which one to use will depend on the individual's specific condition and needs.Mechanism of Action

Effects on the Heart
The effects of beta blockers on the heart are complex and multifaceted. Some of the key effects include: * Reduced heart rate: Beta blockers can help to slow the heart rate, which can reduce the workload on the heart and improve its efficiency. * Reduced contractility: Beta blockers can help to reduce the force of the heart's contractions, which can reduce the amount of oxygen the heart needs and improve its overall function. * Improved cardiac output: Beta blockers can help to improve the heart's ability to pump blood effectively, which can improve overall cardiovascular function.Benefits of Beta Blockers
Common Uses of Beta Blockers
Beta blockers are commonly used to manage a variety of conditions, including: * High blood pressure: Beta blockers can help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke. * Angina: Beta blockers can help to improve symptoms of angina by reducing the frequency and severity of chest pain. * Heart failure: Beta blockers can help to improve survival rates and reduce symptoms of heart failure. * Arrhythmias: Beta blockers can help to regulate abnormal heart rhythms and improve overall cardiovascular function.Side Effects of Beta Blockers
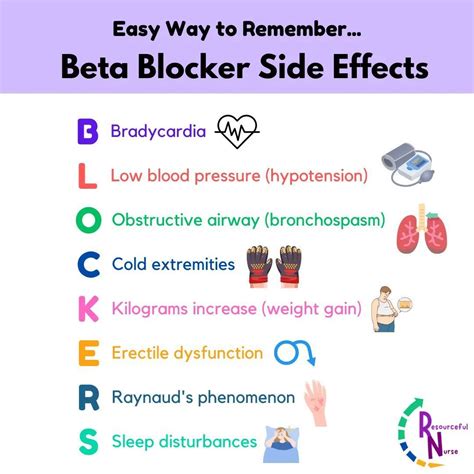
Interactions with Other Medications
Beta blockers can interact with a variety of other medications, including: * Calcium channel blockers: Beta blockers can interact with calcium channel blockers to increase the risk of certain side effects, such as dizziness and lightheadedness. * Anti-arrhythmic medications: Beta blockers can interact with anti-arrhythmic medications to increase the risk of certain side effects, such as abnormal heart rhythms. * Blood thinners: Beta blockers can interact with blood thinners to increase the risk of bleeding.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with beta blockers in the comments below. Have you or a loved one used beta blockers to manage a cardiovascular condition? What benefits or side effects have you experienced? By sharing your story, you can help to raise awareness and promote greater understanding of the importance of beta blockers in modern medicine.
What are the most common uses of beta blockers?
+Beta blockers are commonly used to manage a variety of conditions, including high blood pressure, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
What are the potential side effects of beta blockers?
+Beta blockers can cause a variety of side effects, including fatigue and drowsiness, dizziness and lightheadedness, shortness of breath, and cold hands and feet.
Can beta blockers be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, beta blockers can be used in combination with other medications, such as calcium channel blockers, anti-arrhythmic medications, and blood thinners. However, it is essential to carefully monitor for potential interactions and side effects.
What are the benefits of using beta blockers to manage cardiovascular conditions?
+The benefits of using beta blockers to manage cardiovascular conditions include reduced risk of heart attack and stroke, improved symptoms of angina, and improved survival rates in individuals with certain cardiovascular conditions.
How do beta blockers work to reduce blood pressure?
+Beta blockers work to reduce blood pressure by blocking the effects of epinephrine on the heart and blood vessels, which can help to slow the heart rate and reduce the force of the heart's contractions.
