Intro
Monitor water quality with 5 ways to check chloride levels, preventing corrosion and ensuring safety, using chloride test kits, meters, and other methods to detect excessive chloride ions.
Chloride is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions, including fluid balance, blood pressure regulation, and nerve function. Abnormal chloride levels can indicate underlying health issues, making it essential to monitor them regularly. In this article, we will explore the importance of checking chloride levels and discuss five ways to do so.
Checking chloride levels is vital because it helps diagnose and manage various medical conditions. For instance, low chloride levels can be a sign of dehydration, while high levels can indicate kidney disease or heart failure. Moreover, monitoring chloride levels can help healthcare professionals adjust treatment plans and prevent complications. With the advancement of medical technology, there are now various methods to check chloride levels, ranging from simple blood tests to more complex diagnostic procedures.
The human body relies heavily on chloride to function properly. Chloride helps maintain the balance of fluids within the body, which is essential for proper blood circulation, nerve function, and muscle contraction. Additionally, chloride plays a critical role in the production of digestive fluids, such as stomach acid and bile, which are necessary for nutrient absorption. Given the importance of chloride, it is essential to monitor its levels to ensure optimal health. In the following sections, we will delve into the different methods of checking chloride levels, including their benefits, limitations, and applications.
Understanding Chloride Levels
To appreciate the significance of checking chloride levels, it is essential to understand what chloride is and how it functions within the body. Chloride is an electrolyte, a type of mineral that carries an electric charge. It is the most abundant anion in the human body, making up approximately 70% of the body's total anion content. Chloride is found in various bodily fluids, including blood, sweat, and digestive juices. Its primary function is to maintain fluid balance and regulate blood pressure. Chloride also plays a crucial role in the transmission of nerve impulses and the contraction of muscles.
Normal Chloride Levels
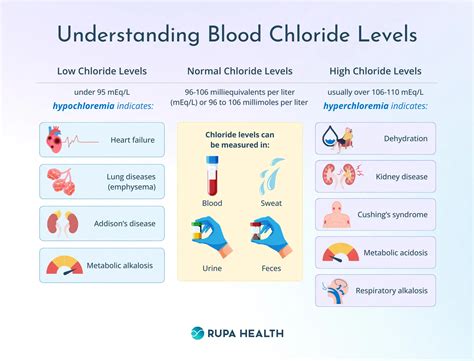
Normal chloride levels typically range from 96 to 106 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L) of blood. However, these values can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and medical history. It is essential to note that chloride levels can fluctuate throughout the day due to various factors, such as diet, hydration, and physical activity. Therefore, healthcare professionals often consider multiple test results and medical history when interpreting chloride levels.Method 1: Blood Tests

One of the most common methods of checking chloride levels is through blood tests. A blood test, also known as a serum chloride test, measures the amount of chloride in the blood. This test is typically performed as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP), which evaluates various aspects of metabolism, including electrolyte levels, kidney function, and liver function. To perform a blood test, a healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The benefits of blood tests include their non-invasive nature, relatively low cost, and quick results. However, blood tests may not always provide accurate results, especially if the sample is contaminated or if the individual has recently eaten a meal high in chloride. Additionally, blood tests may not detect mild changes in chloride levels, which can be a limitation in certain medical conditions.
Preparation and Results
To prepare for a blood test, individuals are usually required to fast for 8-12 hours before the test. This ensures that the results are not affected by recent food or drink consumption. After the test, the blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis, and the results are typically available within 24 hours. The results will indicate the chloride level in the blood, which can be used to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions.Method 2: Urine Tests

Another method of checking chloride levels is through urine tests. A urine test, also known as a urine chloride test, measures the amount of chloride in the urine. This test is often used to evaluate kidney function, as the kidneys play a critical role in regulating electrolyte levels, including chloride. To perform a urine test, an individual will collect a urine sample over a 24-hour period, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The benefits of urine tests include their non-invasive nature and ability to detect changes in chloride levels over an extended period. However, urine tests may not always provide accurate results, especially if the individual has kidney disease or is taking certain medications that affect kidney function.
Interpretation and Limitations
The results of a urine test will indicate the amount of chloride in the urine, which can be used to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. However, the results must be interpreted in conjunction with other medical tests and the individual's medical history. Urine tests may not detect mild changes in chloride levels, and the results can be affected by various factors, such as diet, hydration, and physical activity.Method 3: Sweat Tests
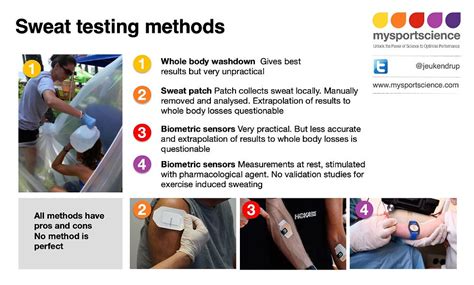
A sweat test, also known as a sweat chloride test, measures the amount of chloride in sweat. This test is often used to diagnose cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder that affects the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems. To perform a sweat test, a healthcare professional will apply a small amount of pilocarpine to the skin, which stimulates sweat production. The sweat is then collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The benefits of sweat tests include their non-invasive nature and ability to detect changes in chloride levels in individuals with cystic fibrosis. However, sweat tests may not always provide accurate results, especially if the individual has recently taken certain medications or has a skin condition that affects sweat production.
Applications and Limitations
Sweat tests are primarily used to diagnose cystic fibrosis in individuals who are suspected of having the condition. The results of a sweat test will indicate the amount of chloride in the sweat, which can be used to confirm or rule out a diagnosis of cystic fibrosis. However, sweat tests may not detect mild changes in chloride levels, and the results can be affected by various factors, such as age, sex, and medical history.Method 4: Stool Tests

A stool test, also known as a stool chloride test, measures the amount of chloride in stool. This test is often used to evaluate digestive function, as the digestive system plays a critical role in absorbing chloride and other essential nutrients. To perform a stool test, an individual will collect a stool sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The benefits of stool tests include their non-invasive nature and ability to detect changes in chloride levels in individuals with digestive disorders. However, stool tests may not always provide accurate results, especially if the individual has recently taken certain medications or has a condition that affects stool production.
Preparation and Results
To prepare for a stool test, individuals are usually required to follow a specific diet and avoid certain medications that can affect stool production. After the test, the stool sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis, and the results are typically available within 24 hours. The results will indicate the amount of chloride in the stool, which can be used to diagnose and monitor various digestive disorders.Method 5: Saliva Tests

A saliva test, also known as a saliva chloride test, measures the amount of chloride in saliva. This test is often used to evaluate oral health, as the mouth plays a critical role in maintaining proper chloride levels. To perform a saliva test, an individual will collect a saliva sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The benefits of saliva tests include their non-invasive nature and ability to detect changes in chloride levels in individuals with oral health disorders. However, saliva tests may not always provide accurate results, especially if the individual has recently eaten or drunk something that affects saliva production.
Applications and Limitations
Saliva tests are primarily used to evaluate oral health and detect changes in chloride levels in individuals with conditions such as dry mouth or oral infections. The results of a saliva test will indicate the amount of chloride in the saliva, which can be used to diagnose and monitor various oral health disorders. However, saliva tests may not detect mild changes in chloride levels, and the results can be affected by various factors, such as age, sex, and medical history.In conclusion, checking chloride levels is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing various medical conditions. The five methods discussed in this article, including blood tests, urine tests, sweat tests, stool tests, and saliva tests, each have their benefits and limitations. By understanding the different methods of checking chloride levels, individuals can take a proactive approach to their health and work with their healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage various medical conditions.
What is the normal range for chloride levels in the blood?
+The normal range for chloride levels in the blood is typically between 96 and 106 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
What are the symptoms of low chloride levels?
+The symptoms of low chloride levels can include dehydration, muscle weakness, and fatigue.
How often should I check my chloride levels?
+The frequency of checking chloride levels depends on various factors, including age, medical history, and underlying medical conditions. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for individual circumstances.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the importance of checking chloride levels and the various methods available. If you have any questions or concerns about chloride levels or would like to share your experiences, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote optimal health and well-being for everyone.
