Intro
Learn about high blood pressure, its symptoms, and causes. Understand hypertension, blood pressure readings, and cardiovascular risks to manage your health effectively.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is too high, which can lead to damage to the blood vessels, heart, and other organs. High blood pressure is often referred to as the "silent killer" because it can cause damage to the body without showing any symptoms. In fact, many people with high blood pressure do not even know they have it until it is too late.
The importance of understanding high blood pressure cannot be overstated. It is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease, which are among the leading causes of death worldwide. Furthermore, high blood pressure can also cause vision loss, cognitive impairment, and peripheral artery disease, among other health problems. The good news is that high blood pressure is preventable and treatable, and by making lifestyle changes and working with a healthcare provider, individuals can manage their blood pressure and reduce their risk of developing these serious health conditions.
High blood pressure is a complex condition that is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While some people may be more prone to developing high blood pressure due to their family history or age, there are many things that individuals can do to reduce their risk. For example, eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can all help to lower blood pressure and improve overall health. Additionally, working with a healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure and make lifestyle changes can help individuals to manage their condition and prevent complications.
What Causes High Blood Pressure
Risk Factors for High Blood Pressure
Some of the key risk factors for high blood pressure include: * Age: The risk of developing high blood pressure increases with age. * Family history: Individuals with a family history of high blood pressure are more likely to develop the condition. * Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure. * Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure. * Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of developing high blood pressure. * Diet: A diet that is high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure.How is High Blood Pressure Diagnosed

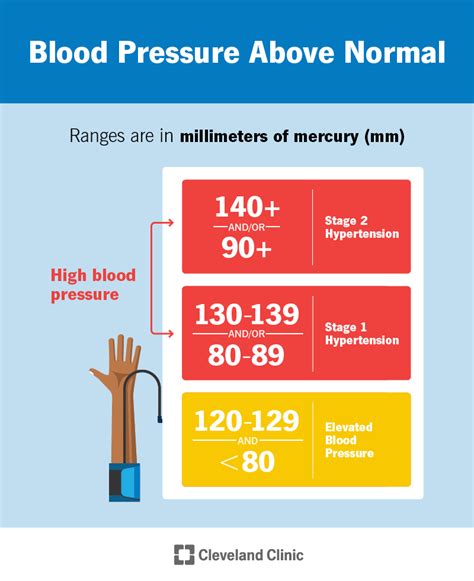
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings
Blood pressure readings are typically expressed as a ratio of the systolic pressure to the diastolic pressure, with the systolic pressure listed first. For example, a blood pressure reading of 120/80 mmHg indicates a systolic pressure of 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of 80 mmHg. The American Heart Association defines the following blood pressure categories: * Normal blood pressure: Less than 120/80 mmHg * Elevated blood pressure: 120-129/80 mmHg * Stage 1 hypertension: 130-139/80-89 mmHg * Stage 2 hypertension: 140 or higher/90 or higher mmHgTreatment Options for High Blood Pressure
Medications for High Blood Pressure
There are many different types of medications that can be used to treat high blood pressure, including diuretics, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers. The type of medication that is prescribed will depend on the individual's specific needs and medical history. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment and to monitor blood pressure regularly.Complications of Untreated High Blood Pressure
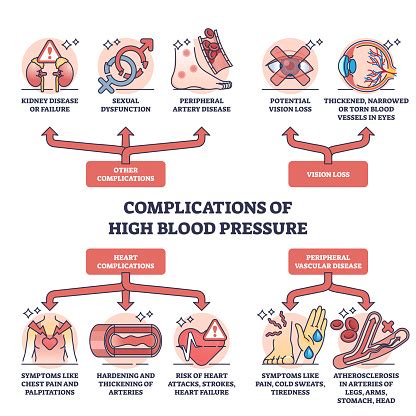
Reducing the Risk of Complications
There are many things that individuals can do to reduce their risk of developing complications from high blood pressure. Some of the most effective ways to reduce this risk include: * Working with a healthcare provider to manage blood pressure * Making lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise * Monitoring blood pressure regularly * Taking medications as prescribed * Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumptionLifestyle Changes for Managing High Blood Pressure
Additional Tips for Managing High Blood Pressure
Some additional tips for managing high blood pressure include: * Monitoring blood pressure regularly * Working with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan * Taking medications as prescribed * Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water * Getting enough potassium, calcium, and magnesium through diet or supplementsConclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with high blood pressure in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may be interested in learning more about high blood pressure.
What is the normal range for blood pressure?
+Normal blood pressure is typically defined as a systolic pressure of less than 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of less than 80 mmHg.
What are the symptoms of high blood pressure?
+High blood pressure often does not have any symptoms, but it can cause headaches, dizziness, and nosebleeds in some individuals.
How can I lower my blood pressure?
+There are many ways to lower blood pressure, including eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, and taking medications as prescribed.
What are the risks of untreated high blood pressure?
+Untreated high blood pressure can lead to many serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and vision loss.
How often should I have my blood pressure checked?
+It is recommended to have blood pressure checked at least once per year, or more often if you have a history of high blood pressure or other health conditions.
