Intro
Discover key Clindamycin Hcl facts, including its antibiotic uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand this medications benefits and risks for bacterial infections treatment.
Clindamycin HCl, a medication belonging to the lincosamide class of antibiotics, has been widely used to treat various bacterial infections. Its effectiveness against a range of bacteria, including those resistant to other antibiotics, has made it a staple in both human and veterinary medicine. However, like all medications, it's crucial to understand its properties, uses, and potential side effects to ensure safe and effective treatment. The importance of Clindamycin HCl lies not only in its antibacterial properties but also in its ability to penetrate into bones, making it particularly useful for treating osteomyelitis, a bone infection. Moreover, its application extends beyond treating infections, with potential uses in managing acne and other skin conditions due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
The mechanism of action of Clindamycin HCl involves binding to the bacterial ribosome, which is essential for protein synthesis. By inhibiting this process, the medication effectively stops the growth of bacteria, leading to their death. This action is primarily bacteriostatic, meaning it inhibits the growth of bacteria, but it can be bactericidal (killing bacteria) against certain susceptible strains. Understanding how Clindamycin HCl works is vital for healthcare providers to prescribe it appropriately and for patients to understand the importance of completing the full treatment course as directed.
Clindamycin HCl's broad spectrum of activity includes effectiveness against Gram-positive cocci, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and certain Gram-negative bacteria. It is also active against anaerobic bacteria, which are bacteria that do not require oxygen to grow. This makes Clindamycin HCl particularly useful in treating infections where anaerobes are suspected or confirmed, such as in abdominal, skin, and soft tissue infections. Furthermore, its ability to concentrate in various body tissues, including bone, makes it an option for treating infections in these areas.
Introduction to Clindamycin HCl

Benefits of Clindamycin HCl

Key Uses of Clindamycin HCl
Some of the key uses of Clindamycin HCl include: - Treating bacterial infections of the skin and soft tissues - Managing infections of the respiratory tract - Treating infections of the bones and joints - Treating certain types of intra-abdominal infections - Managing acne and other skin conditions when caused by bacteria susceptible to Clindamycin HClWorking Mechanism of Clindamycin HCl
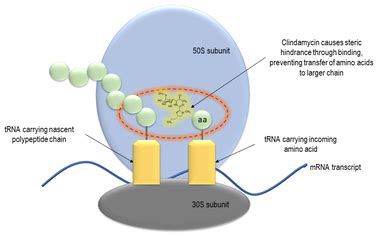
Steps for Effective Use
For the effective use of Clindamycin HCl, the following steps should be considered: 1. **Consult a Healthcare Provider**: Before starting treatment with Clindamycin HCl, it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure the medication is appropriate for the specific infection being treated. 2. **Complete the Full Treatment Course**: To ensure the infection is fully cleared and to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance, it's crucial to complete the full treatment course as directed by the healthcare provider. 3. **Monitor for Side Effects**: While Clindamycin HCl is generally well-tolerated, monitoring for potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions, is important.Potential Side Effects of Clindamycin HCl

Precautions and Warnings
Precautions and warnings associated with Clindamycin HCl include: - **Allergic Reactions**: Patients with a history of allergy to Clindamycin or lincomycin should avoid using Clindamycin HCl. - **Gastrointestinal Diseases**: Patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease, especially colitis, should use Clindamycin HCl with caution. - **Pregnancy and Breastfeeding**: Clindamycin HCl should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed, and caution is advised when used by breastfeeding mothers.FAQs About Clindamycin HCl
What is Clindamycin HCl used for?
+Clindamycin HCl is used to treat various bacterial infections, including those of the skin, respiratory tract, and bones.
How does Clindamycin HCl work?
+Clindamycin HCl works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, effectively stopping their growth.
What are the potential side effects of Clindamycin HCl?
+Potential side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, allergic reactions, and pseudomembranous colitis.
In conclusion, Clindamycin HCl is a valuable antibiotic for treating various bacterial infections, offering a broad spectrum of activity and the ability to penetrate into different tissues. However, its use must be guided by a thorough understanding of its benefits, working mechanisms, potential side effects, and precautions. By judiciously using Clindamycin HCl and adhering to prescribed treatment regimens, patients can effectively manage bacterial infections while minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance. We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about Clindamycin HCl in the comments section, and we encourage the sharing of this article with others who may benefit from this information.
