Intro
Discover 5 uses of lactulose, a versatile sugar, for constipation relief, liver disease treatment, and gut health management, promoting digestive balance and overall well-being.
The importance of maintaining a healthy digestive system cannot be overstated. A well-functioning gut is essential for the proper absorption of nutrients, the elimination of waste, and the prevention of various diseases. One substance that has gained significant attention in recent years for its potential benefits in supporting gut health is lactulose. Lactulose is a synthetic sugar that is not absorbed by the body but instead serves as a food source for the beneficial bacteria in the gut, promoting a healthy gut microbiome. Its uses extend beyond just digestive health, encompassing various medical applications.
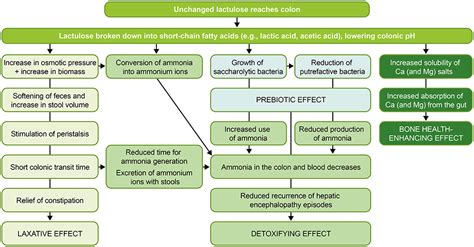
Lactulose has been widely recognized for its role in managing constipation. By drawing water into the bowel from the surrounding body tissues, it softens stools and makes them easier to pass. This mechanism of action not only provides relief from constipation but also helps in preventing complications such as hemorrhoids and anal fissures that can arise from straining during bowel movements. Moreover, its prebiotic properties support the growth of beneficial bacteria, which can enhance the immune system and produce certain vitamins.
The application of lactulose is not limited to gastrointestinal issues. It has also been used in the management of hepatic encephalopathy, a condition characterized by brain dysfunction that occurs when the liver is unable to remove toxins from the blood effectively. Lactulose works by reducing the production of ammonia in the gut, which is a major contributor to the development of hepatic encephalopathy. By promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and reducing the pH of the gut contents, lactulose inhibits the growth of bacteria that produce ammonia, thereby reducing its absorption into the bloodstream and subsequent effects on the brain.
Introduction to Lactulose

Benefits of Lactulose for Gut Health
The benefits of lactulose for gut health are multifaceted. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, lactulose enhances the gut barrier function, reducing the permeability of the gut wall and preventing the translocation of harmful bacteria and toxins into the bloodstream. This can lead to a reduction in systemic inflammation and an improvement in overall health. Additionally, the fermentation of lactulose by gut bacteria produces short-chain fatty acids, which serve as an energy source for the cells lining the colon and help maintain a healthy colonic environment.Medical Applications of Lactulose

Role of Lactulose in Hepatic Encephalopathy
In the context of hepatic encephalopathy, lactulose is considered a first-line treatment. By reducing the amount of ammonia produced in the gut and decreasing its absorption into the bloodstream, lactulose helps in preventing the neurological complications associated with ammonia toxicity. The reduction in gut pH due to lactulose fermentation also inhibits the activity of urease-producing bacteria, which are responsible for the breakdown of urea into ammonia. This dual mechanism of action makes lactulose an effective therapy for managing the symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy and improving the quality of life for patients with liver disease.Prebiotic Properties of Lactulose
Enhancing Immune System with Lactulose
The impact of lactulose on the immune system is another area of interest. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, lactulose can enhance the immune response and increase the production of antibodies, which are vital for fighting off infections. The short-chain fatty acids produced during the fermentation of lactulose can also stimulate the immune system, promoting the activity of immune cells such as macrophages and T-cells. This immunomodulatory effect of lactulose makes it a potential adjunctive therapy for conditions characterized by impaired immune function.Practical Applications and Dosage

Side Effects and Contraindications
While generally considered safe, lactulose can cause side effects, particularly when first starting therapy. These may include bloating, gas, and diarrhea, which usually resolve on their own as the body adjusts to the increased fermentation in the gut. In some cases, lactulose may not be suitable, such as in patients with galactosemia, a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to metabolize galactose. It is also important to monitor blood sugar levels in diabetic patients, as lactulose can affect glucose metabolism.Future Perspectives and Research

Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, lactulose is a versatile compound with a range of applications in supporting gut health and managing various medical conditions. Its prebiotic properties, ability to reduce ammonia production, and potential to enhance immune function make it a valuable therapeutic agent. As with any medical treatment, it is crucial to use lactulose under the guidance of a healthcare provider, adhering to recommended dosages and monitoring for side effects. By integrating lactulose into treatment plans and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can harness its benefits to promote a healthy gut microbiome and overall well-being.To further explore the benefits and applications of lactulose, we invite readers to share their experiences and insights in the comments section below. For those interested in learning more about gut health and the role of prebiotics in maintaining a balanced gut microbiome, we recommend exploring reputable sources and consulting with healthcare professionals. By engaging in open discussions and staying informed, we can work together to advance our understanding of lactulose and its potential to improve human health.
What is lactulose used for?
+Lactulose is used for the treatment of constipation and hepatic encephalopathy, and it has potential benefits in supporting gut health and enhancing immune function.
How does lactulose work?
+Lactulose works by drawing water into the bowel, softening stools, and promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which helps in reducing ammonia production and enhancing immune function.
What are the side effects of lactulose?
+Common side effects of lactulose include bloating, gas, and diarrhea, which usually resolve on their own as the body adjusts to the treatment.
