Intro
Discover Clonidines role in the alpha-2 adrenergic agonist drug class, treating hypertension, ADHD, and anxiety with its sedative properties, while exploring side effects and interactions.
Clonidine is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various medical conditions. It is essential to understand the clonidine drug class, its mechanism of action, and its applications to appreciate its significance in the pharmaceutical industry. Clonidine belongs to a class of medications known as centrally acting alpha-2 adrenergic agonists. This classification is crucial in understanding how clonidine works and its effects on the body.
The importance of clonidine drug class cannot be overstated, as it has been used to treat conditions such as hypertension, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and certain pain disorders. Its unique mechanism of action, which involves stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, makes it an effective treatment option for these conditions. Furthermore, clonidine has been used off-label for various other conditions, including anxiety disorders, insomnia, and migraine headaches. The versatility of clonidine in treating a range of medical conditions makes it a valuable medication in the pharmaceutical arsenal.
Understanding the clonidine drug class is also essential for healthcare professionals, as it enables them to make informed decisions about its use, potential side effects, and interactions with other medications. Clonidine's pharmacological properties, including its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, are critical in determining its efficacy and safety profile. Additionally, the clonidine drug class has undergone extensive research, and numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate its effectiveness and safety in various patient populations. The findings of these studies have contributed significantly to our understanding of clonidine's therapeutic potential and its limitations.
Introduction to Clonidine
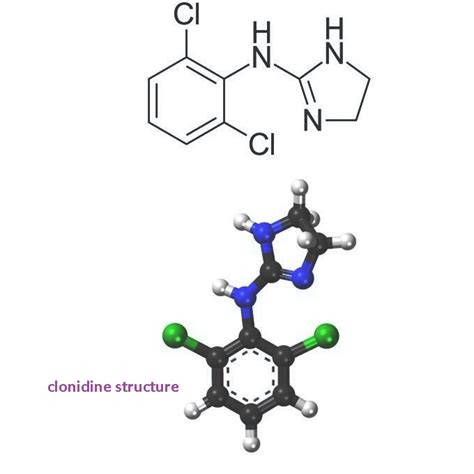
Pharmacological Properties of Clonidine
The pharmacological properties of clonidine are essential in understanding its mechanism of action and its effects on the body. Clonidine is a lipophilic medication, which means it can cross the blood-brain barrier and interact with alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain. This interaction leads to a decrease in sympathetic outflow, resulting in a decrease in blood pressure, heart rate, and peripheral resistance. Clonidine also has a sedative effect, which makes it useful in treating conditions such as ADHD and insomnia.Mechanism of Action of Clonidine

Applications of Clonidine
Clonidine has several applications, including: * Treatment of hypertension: Clonidine is used to treat hypertension, either as a monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive medications. * Treatment of ADHD: Clonidine is used to treat ADHD, particularly in children who have not responded to other treatments. * Treatment of pain disorders: Clonidine is used to treat certain pain disorders, including complex regional pain syndrome and neuropathic pain. * Treatment of anxiety disorders: Clonidine is used off-label to treat anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder and panic disorder. * Treatment of insomnia: Clonidine is used off-label to treat insomnia, particularly in patients who have not responded to other treatments.Benefits of Clonidine

Risks and Side Effects of Clonidine
The risks and side effects of clonidine include: * Hypotension: Clonidine can cause hypotension, particularly in patients who are taking other antihypertensive medications. * Sedation: Clonidine can cause sedation, particularly in patients who are taking other sedative medications. * Dry mouth: Clonidine can cause dry mouth, particularly in patients who are taking other medications that cause dry mouth. * Constipation: Clonidine can cause constipation, particularly in patients who are taking other medications that cause constipation. * Withdrawal symptoms: Clonidine can cause withdrawal symptoms, particularly in patients who have been taking it for an extended period.Interactions with Other Medications
Dosage and Administration of Clonidine
The dosage and administration of clonidine depend on the condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication. The usual dosage of clonidine for hypertension is 0.1-0.3 mg twice daily, while the usual dosage for ADHD is 0.1-0.2 mg three times daily. Clonidine should be taken orally, and it should be swallowed whole with water. The medication should not be crushed or chewed, as this can affect its absorption and efficacy.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
Clonidine is an essential medication that has been used for several decades to treat various medical conditions. Its unique mechanism of action and its applications make it a valuable treatment option for patients who have not responded to other treatments. However, clonidine can also cause side effects, and its interactions with other medications should be carefully evaluated. As research continues to uncover the benefits and risks of clonidine, healthcare professionals should stay up-to-date with the latest findings to provide the best possible care for their patients.What is clonidine used for?
+Clonidine is used to treat various medical conditions, including hypertension, ADHD, and pain disorders.
How does clonidine work?
+Clonidine works by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, which leads to a decrease in sympathetic outflow and a decrease in blood pressure, heart rate, and peripheral resistance.
What are the side effects of clonidine?
+The side effects of clonidine include hypotension, sedation, dry mouth, constipation, and withdrawal symptoms.
