Intro
Discover 5 life-saving uses of Clopidogrel, a potent antiplatelet medication, including preventing blood clots, strokes, and heart attacks, while managing cardiovascular diseases, coronary artery disease, and peripheral artery disease.
Clopidogrel, commonly known by its brand name Plavix, is a medication that plays a crucial role in preventing blood clots in patients who are at risk of heart attack or stroke. It belongs to a class of drugs known as antiplatelet agents, which work by preventing platelets in the blood from clumping together to form clots. The importance of clopidogrel lies in its ability to reduce the risk of major vascular events in patients with a history of heart disease or those who have had a heart attack or stroke. Understanding the uses of clopidogrel is essential for managing cardiovascular health effectively.
The mechanism by which clopidogrel works is complex and involves the inhibition of the P2Y12 receptor on platelets, a key component in the process of platelet activation and aggregation. By inhibiting this receptor, clopidogrel effectively reduces the likelihood of blood clots forming. This is particularly beneficial for patients who have undergone certain medical procedures, such as the placement of a coronary stent, or those with specific medical conditions that increase their risk of developing dangerous blood clots.
Given its critical role in managing and preventing cardiovascular events, clopidogrel has become a staple in the treatment regimen of many patients at risk. Its use is tailored to the individual patient's needs, taking into account their medical history, current health status, and other medications they may be taking. The versatility and efficacy of clopidogrel have made it a widely prescribed medication, with its applications extending across various aspects of cardiovascular disease management.
Prevention of Heart Attack and Stroke

Benefits for Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) benefit significantly from clopidogrel, as it reduces the risk of clot formation in the coronary arteries, which could lead to a heart attack. The medication is particularly beneficial for those who have undergone procedures such as angioplasty or stenting to open up blocked coronary arteries. By preventing clot formation on the stent, clopidogrel helps to ensure the long-term patency of the coronary artery, reducing the need for further interventions.Treatment After Coronary Stent Placement
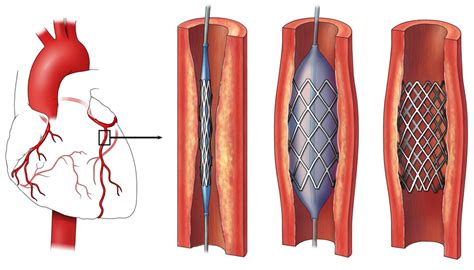
Management of Peripheral Artery Disease
Clopidogrel is also used in the management of peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the blood vessels outside of the heart, leading to reduced blood flow to the limbs. Patients with PAD are at an increased risk of developing blood clots, which can lead to serious complications such as limb ischemia or even the need for amputation. By preventing blood clot formation, clopidogrel helps to reduce these risks, improving outcomes for patients with PAD.Use in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Combination Therapy with Aspirin
Clopidogrel is often prescribed in combination with aspirin, another antiplatelet agent, for patients at high risk of cardiovascular events. This dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) is particularly beneficial for patients who have undergone coronary stent placement, as it provides a synergistic effect in preventing blood clot formation. However, the duration of DAPT can vary based on the type of stent used (bare-metal vs. drug-eluting) and the patient's individual risk profile.Considerations and Precautions

Dosing and Administration
The dosing of clopidogrel is typically standardized, with most patients receiving a loading dose followed by a maintenance dose. However, the specific dosing regimen can vary based on the patient's condition and the presence of other medications that may interact with clopidogrel. It is essential for patients to follow the prescribed dosing regimen closely and to discuss any concerns or questions with their healthcare provider.Monitoring and Follow-Up

Patient Education and Adherence
Educating patients about the role of clopidogrel in their treatment plan, its potential side effects, and the importance of adherence is crucial for maximizing the benefits of the medication. Patients should be encouraged to ask questions and to report any concerns or side effects to their healthcare provider. Additionally, strategies to improve adherence, such as pill boxes or reminders, can be helpful in ensuring that patients take their medication as prescribed.Future Directions and Research

Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine
The field of pharmacogenomics holds promise for the personalized use of clopidogrel, allowing for the identification of genetic variations that may affect how patients respond to the medication. By understanding these genetic differences, healthcare providers may be able to tailor clopidogrel therapy to the individual, maximizing its benefits while minimizing risks. This approach represents a significant advancement in the management of cardiovascular disease, offering the potential for more effective and safer treatment strategies.As the medical community continues to learn more about clopidogrel and its applications, it is essential for patients to remain informed and engaged in their care. By understanding the role of clopidogrel in managing cardiovascular health, patients can better navigate their treatment options and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve the best possible outcomes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about the uses of clopidogrel and its role in cardiovascular health. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most accurate and helpful information. Please consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from understanding the importance of clopidogrel in preventing heart attacks and strokes.
What is clopidogrel used for?
+Clopidogrel is used to prevent blood clots that cause heart attacks and strokes. It is often prescribed to patients who have had a heart attack or stroke, those with peripheral artery disease, and patients who have undergone coronary stent placement.
How does clopidogrel work?
+Clopidogrel works by inhibiting the P2Y12 receptor on platelets, which prevents platelets from clumping together to form blood clots. This action reduces the risk of heart attacks and strokes in patients at high risk.
What are the potential side effects of clopidogrel?
+The most significant risk associated with clopidogrel is bleeding, as it affects the body's ability to form clots. Patients should be monitored for signs of bleeding and should report any unusual bleeding to their healthcare provider immediately.
