Intro
Discover 10 cognitive distortions examples, including all-or-nothing thinking, overgeneralization, and magnification, to understand mental biases and irrational thoughts, improving emotional regulation and mental health through cognitive behavioral therapy and mindfulness.
Cognitive distortions are irrational or exaggerated thought patterns that can influence our perceptions, emotions, and behaviors. These distortions can lead to negative consequences, such as anxiety, depression, and relationship problems. Understanding cognitive distortions is essential to recognize and challenge them, promoting more balanced and constructive thinking. In this article, we will delve into the world of cognitive distortions, exploring their importance, types, and examples, as well as strategies for overcoming them.
Cognitive distortions are not just minor flaws in our thinking; they can have a significant impact on our mental health and well-being. By becoming aware of these distortions, we can take the first step towards changing our thought patterns and improving our overall quality of life. The concept of cognitive distortions was first introduced by psychologist Aaron Beck, who identified several common patterns of distorted thinking that contribute to emotional distress. Since then, researchers have expanded on this work, identifying numerous types of cognitive distortions that can affect individuals in various ways.
The study of cognitive distortions has become a crucial aspect of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), a widely used approach to treating mental health conditions. CBT helps individuals identify and challenge their negative thought patterns, replacing them with more balanced and constructive ones. By learning to recognize and overcome cognitive distortions, people can develop more adaptive coping strategies, improve their relationships, and enhance their overall mental health. In the following sections, we will explore 10 common cognitive distortions, providing examples and explanations to help readers understand these concepts better.
Introduction to Cognitive Distortions
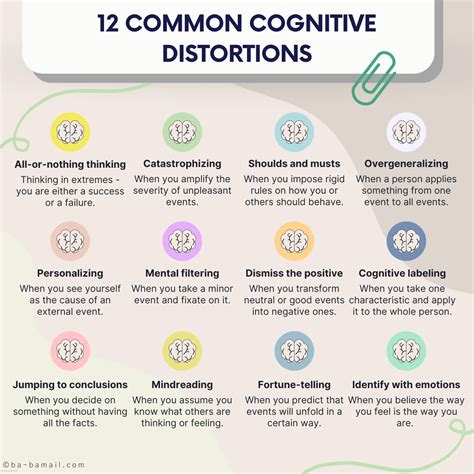
Cognitive distortions can be categorized into several types, each with its unique characteristics and effects on our thinking and behavior. Some common types of cognitive distortions include all-or-nothing thinking, overgeneralization, and emotional reasoning. These distortions can lead to negative consequences, such as increased stress, anxiety, and depression. By understanding the different types of cognitive distortions, we can develop more effective strategies for overcoming them and promoting more balanced thinking.
Types of Cognitive Distortions

The following are 10 examples of cognitive distortions, along with explanations and examples to illustrate each concept:
- All-or-nothing thinking: This distortion involves seeing things in absolute terms, with no middle ground. For example, "If I don't get this job, I'll never find a good career."
- Overgeneralization: This distortion involves making sweeping conclusions based on a single event or experience. For example, "I had a bad day today, so I'll always have bad days."
- Mental filtering: This distortion involves focusing on the negative aspects of a situation while ignoring the positive ones. For example, "I got a good grade on my exam, but I still made some mistakes."
- Disqualifying the positive: This distortion involves downplaying or dismissing positive experiences or achievements. For example, "I only got an A on that test because it was easy."
- Jumping to conclusions: This distortion involves making assumptions or drawing conclusions without sufficient evidence. For example, "I didn't get a call back from the interview, so I must not have gotten the job."
- Magnification or minimization: This distortion involves exaggerating or downplaying the significance of an event or situation. For example, "This mistake is going to ruin my entire career."
- Emotional reasoning: This distortion involves assuming that one's emotions reflect the way things really are. For example, "I feel anxious, so I must be in danger."
- Should statements: This distortion involves using words like "should" or "must" to impose unrealistic expectations on oneself or others. For example, "I should be able to handle this situation without any help."
- Labeling: This distortion involves assigning a negative label to oneself or others based on a single event or characteristic. For example, "I'm a failure because I made a mistake."
- Personalization: This distortion involves taking things personally or assuming that events or situations are directly related to oneself. For example, "My friend didn't call me back, so they must be mad at me."
Understanding Cognitive Distortions

To overcome cognitive distortions, it's essential to develop a greater awareness of our thoughts and emotions. This can involve practicing mindfulness, keeping a thought journal, or seeking feedback from others. By becoming more aware of our thought patterns, we can identify areas where we may be engaging in distorted thinking and develop strategies for challenging and changing these patterns.
Overcoming Cognitive Distortions

Some effective strategies for overcoming cognitive distortions include:
- Cognitive restructuring: This involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns, replacing them with more balanced and constructive ones.
- Mindfulness: This involves practicing present-moment awareness, allowing us to become more aware of our thoughts and emotions without judgment.
- Self-compassion: This involves treating oneself with kindness and understanding, rather than self-criticism or judgment.
- Social support: This involves seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist, who can provide guidance and encouragement in overcoming cognitive distortions.
Strategies for Change

In addition to these strategies, it's essential to practice self-care and stress management techniques, such as exercise, meditation, or deep breathing. By taking care of our physical and emotional needs, we can reduce our vulnerability to cognitive distortions and promote more balanced thinking.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, cognitive distortions are common patterns of irrational or exaggerated thinking that can have a significant impact on our mental health and well-being. By understanding the different types of cognitive distortions and developing strategies for overcoming them, we can promote more balanced and constructive thinking. We encourage readers to take the next step by practicing mindfulness, seeking social support, and developing self-compassion. By working together, we can create a more supportive and understanding community that fosters positive change and personal growth.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with cognitive distortions in the comments section below. How have you overcome negative thought patterns in your life? What strategies have you found most effective? By sharing our stories and insights, we can learn from each other and promote a greater understanding of cognitive distortions and their impact on our lives.
What are cognitive distortions?
+Cognitive distortions are irrational or exaggerated thought patterns that can influence our perceptions, emotions, and behaviors.
How can I overcome cognitive distortions?
+Effective strategies for overcoming cognitive distortions include cognitive restructuring, mindfulness, self-compassion, and social support.
What is the impact of cognitive distortions on mental health?
+Cognitive distortions can contribute to negative consequences, such as anxiety, depression, and relationship problems, and can have a significant impact on our mental health and well-being.
