Intro
Unlock the secrets of a Complete Blood Count (CBC), a vital blood test analyzing red and white blood cell counts, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, to diagnose anemia, infection, and blood disorders, revealing overall health and wellness.
The complete blood count, or CBC, is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in the medical field to assess a patient's overall health. It is a common blood test that provides valuable information about the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. A CBC is often used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions, from anemia and infection to cancer and blood disorders. In this article, we will delve into the world of complete blood counts, exploring what they are, how they work, and what the results can tell us about our health.
A complete blood count is a simple yet powerful test that can reveal a great deal about a person's health. It is typically performed as part of a routine medical examination or when a patient is experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or bruising. The test involves taking a small sample of blood from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of a CBC can help healthcare providers diagnose and monitor a variety of health conditions, making it an essential tool in the diagnosis and treatment of many diseases.
The importance of complete blood counts cannot be overstated. They provide healthcare providers with a wealth of information about a patient's blood cells, including their size, shape, and quantity. This information can be used to diagnose a range of health conditions, from mild to severe. For example, a CBC can help diagnose anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood. It can also help diagnose infections, such as pneumonia or meningitis, by detecting an increase in white blood cells. Additionally, a CBC can help monitor the progression of diseases such as cancer, HIV, and AIDS, making it a crucial tool in the management of these conditions.
What is a Complete Blood Count?
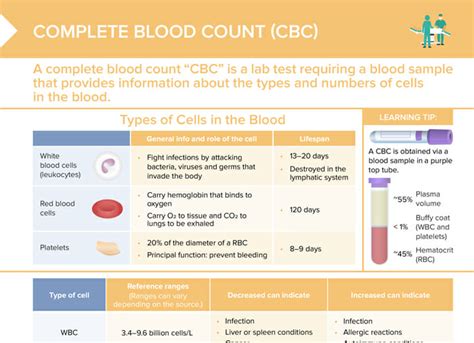
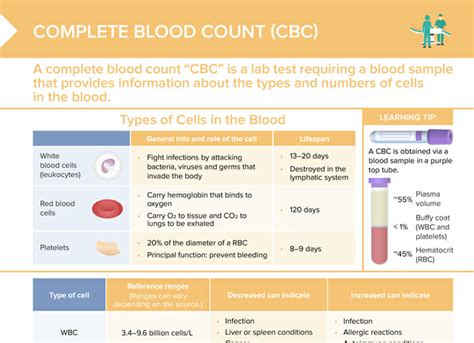
A complete blood count is a blood test that measures the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The test provides a comprehensive overview of a patient's blood cells, including their size, shape, and quantity. The results of a CBC can help healthcare providers diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions, from anemia and infection to cancer and blood disorders. The test is typically performed using a automated analyzer, which provides rapid and accurate results.
Components of a Complete Blood Count
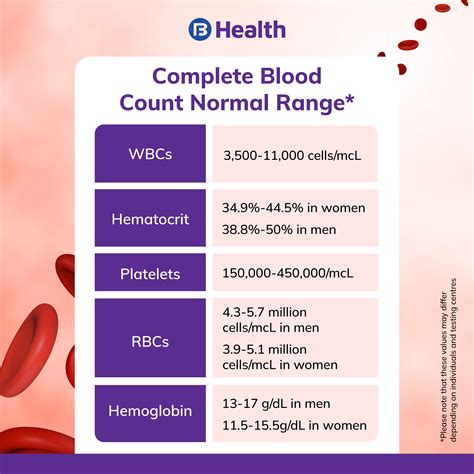
A complete blood count includes several components, each of which provides valuable information about a patient's blood cells. These components include: * Red blood cell count: This measures the number of red blood cells in the blood. * Hemoglobin: This measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood, which is a protein that carries oxygen to the body's tissues. * Hematocrit: This measures the proportion of red blood cells in the blood. * White blood cell count: This measures the number of white blood cells in the blood, which help fight infection. * Platelet count: This measures the number of platelets in the blood, which help the blood to clot.How is a Complete Blood Count Performed?
A complete blood count is typically performed in a healthcare provider's office or laboratory. The test involves taking a small sample of blood from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The blood sample is usually taken from the median cubital vein, which is located in the crook of the elbow. The procedure is relatively painless and only takes a few minutes to complete.
Step-by-Step Guide to a Complete Blood Count
Here is a step-by-step guide to how a complete blood count is performed: 1. The healthcare provider will clean the area where the blood sample will be taken with an antiseptic solution. 2. A tourniquet will be applied to the upper arm to help the vein become more visible. 3. A needle will be inserted into the vein and a small sample of blood will be taken. 4. The blood sample will be collected in a tube and sent to a laboratory for analysis. 5. The results of the test will be provided to the healthcare provider, who will interpret the results and provide a diagnosis or recommendation for further testing.What Do the Results of a Complete Blood Count Mean?
The results of a complete blood count can provide valuable information about a patient's health. The results are typically reported in a series of numbers and percentages, which can be confusing for patients who are not familiar with medical terminology. Here is a breakdown of what the results of a complete blood count mean:
- Red blood cell count: A low red blood cell count can indicate anemia, while a high count can indicate dehydration or other conditions.
- Hemoglobin: A low hemoglobin level can indicate anemia, while a high level can indicate dehydration or other conditions.
- Hematocrit: A low hematocrit can indicate anemia, while a high hematocrit can indicate dehydration or other conditions.
- White blood cell count: A high white blood cell count can indicate infection or inflammation, while a low count can indicate a weakened immune system.
- Platelet count: A low platelet count can indicate a bleeding disorder, while a high count can indicate a blood clotting disorder.
Interpreting the Results of a Complete Blood Count
Interpreting the results of a complete blood count requires a thorough understanding of medical terminology and the normal ranges for each component of the test. Here are some tips for interpreting the results of a complete blood count: * Red blood cell count: The normal range for red blood cells is 4.32-5.72 million cells per microliter (mcL) for men and 3.90-5.30 million cells per mcL for women. * Hemoglobin: The normal range for hemoglobin is 13.5-17.5 grams per deciliter (g/dL) for men and 12-16 g/dL for women. * Hematocrit: The normal range for hematocrit is 40.7-50.3% for men and 36.1-48.3% for women. * White blood cell count: The normal range for white blood cells is 3,500-10,500 cells per mcL. * Platelet count: The normal range for platelets is 150,000-450,000 platelets per mcL.Common Conditions Diagnosed with a Complete Blood Count
A complete blood count is a versatile test that can help diagnose a wide range of health conditions. Here are some common conditions that can be diagnosed with a complete blood count:
- Anemia: A complete blood count can help diagnose anemia by detecting a low red blood cell count or low hemoglobin level.
- Infection: A complete blood count can help diagnose infection by detecting an increase in white blood cells.
- Blood disorders: A complete blood count can help diagnose blood disorders such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
- Cancer: A complete blood count can help diagnose cancer by detecting abnormal blood cells or a low platelet count.
- HIV/AIDS: A complete blood count can help diagnose HIV/AIDS by detecting a low white blood cell count or a low platelet count.
Limitations of a Complete Blood Count
While a complete blood count is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations. Here are some of the limitations of a complete blood count: * A complete blood count may not detect all types of anemia or blood disorders. * A complete blood count may not detect cancer or other serious health conditions in their early stages. * A complete blood count may not provide a definitive diagnosis, but rather suggest the need for further testing.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, a complete blood count is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide valuable information about a patient's health. The test is simple, painless, and relatively inexpensive, making it a popular choice for healthcare providers. While a complete blood count has several limitations, it can help diagnose a wide range of health conditions, from anemia and infection to cancer and blood disorders. If you have any concerns about your health or would like to learn more about complete blood counts, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of complete blood counts and their role in diagnosing and monitoring health conditions. If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences with complete blood counts, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with your friends and family on social media.
What is a complete blood count?
+A complete blood count is a blood test that measures the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What are the components of a complete blood count?
+The components of a complete blood count include red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, white blood cell count, and platelet count.
What do the results of a complete blood count mean?
+The results of a complete blood count can provide valuable information about a patient's health, including the presence of anemia, infection, or blood disorders.
