Intro
Relieve knee pain with effective Knee Bursitis Treatment, including physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes to reduce inflammation and prevent future flare-ups, promoting joint health and mobility.
Knee bursitis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility in the knee joint. It occurs when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints and reduce friction between bones, tendons, and ligaments, become inflamed or irritated. This condition can be debilitating, making everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or even standing for long periods of time a challenge. Understanding the importance of effective treatment for knee bursitis is crucial for managing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving quality of life.
The prevalence of knee bursitis is significant, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. It is particularly common among athletes, individuals who engage in repetitive knee movements, and those who have suffered knee injuries or have underlying conditions such as arthritis. Given its widespread impact, it is essential to explore the various treatment options available for knee bursitis, from conservative management to surgical interventions. By delving into the details of these treatments, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and work towards achieving optimal knee health.
Effective management of knee bursitis involves a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying causes of the condition, alleviates symptoms, and promotes healing. This may include a combination of rest, physical therapy, medication, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Understanding the benefits and limitations of each treatment option is vital for developing a personalized treatment plan that meets the unique needs and circumstances of each individual. Moreover, staying informed about the latest advancements in knee bursitis treatment can empower individuals to take an active role in their recovery, fostering a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers.
Knee Bursitis Overview
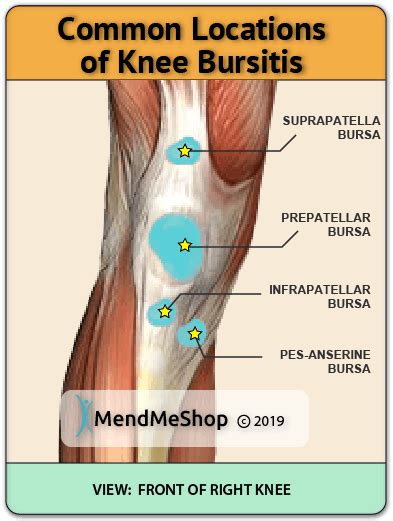
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of knee bursitis are diverse, ranging from direct trauma to the knee to underlying conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Repetitive activities that involve kneeling, squatting, or climbing stairs can also contribute to the development of knee bursitis. Additionally, individuals with poor posture, muscle imbalances, or previous knee injuries may be more susceptible to this condition. Recognizing these risk factors can help in the prevention and early detection of knee bursitis, facilitating prompt intervention and reducing the risk of complications.Symptoms and Diagnosis

Physical Examination and Imaging Studies
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider may look for signs of swelling, redness, and warmth around the knee, as well as assess the range of motion and strength of the surrounding muscles. Imaging studies can provide valuable information about the extent of bursitis and help identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the symptoms. Understanding the diagnostic process is essential for individuals to navigate their care effectively and make informed decisions about their treatment.Treatment Options
Conservative Management
Conservative management of knee bursitis focuses on reducing inflammation, promoting healing, and improving function. This may involve modifying activities to avoid exacerbating the condition, using assistive devices such as crutches or knee braces, and engaging in exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee. By adopting a conservative approach, many individuals can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and avoid the need for more invasive treatments.Surgical Intervention
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Following surgery, it is essential to follow a structured rehabilitation program to ensure proper healing and regain strength and mobility in the knee. This may include physical therapy exercises, pain management strategies, and gradual progression of activities to avoid overloading the knee. By adhering to postoperative care and rehabilitation guidelines, individuals can minimize the risk of complications and achieve optimal outcomes from their surgical treatment.Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications

Exercise and Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for maintaining knee health and preventing bursitis. Exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee, such as squats, lunges, and leg press, can help absorb shock and reduce stress on the bursae. Low-impact activities such as cycling or swimming are also beneficial, as they promote cardiovascular fitness without exerting excessive stress on the knee joint.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your experiences or ask questions about knee bursitis treatment in the comments below. Your input can help others better understand this condition and the various treatment options available. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
What are the common causes of knee bursitis?
+Knee bursitis can be caused by direct trauma to the knee, repetitive activities, or underlying conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout.
How is knee bursitis diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of knee bursitis typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI scans to confirm the presence of bursitis and rule out other conditions.
What are the treatment options for knee bursitis?
+Treatment options for knee bursitis include conservative management with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, medication, and in some cases, surgical intervention to remove the inflamed bursa.
