Intro
Discover the Computed Tomography Angiography Scan, a medical imaging technique using CT scans and contrast agents to visualize blood vessels, diagnose vascular diseases, and detect blockages, aneurysms, and tumors, aiding in precise cardiovascular treatment and patient care.
The use of medical imaging has revolutionized the field of healthcare, enabling doctors to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions with greater accuracy and precision. One of the most powerful diagnostic tools available today is the Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) scan. This non-invasive imaging test uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the blood vessels and surrounding tissues, allowing doctors to visualize the vascular system in unprecedented detail. In this article, we will explore the importance of CTA scans, their benefits, and how they work, as well as provide practical examples and statistical data to illustrate their effectiveness.
The CTA scan has become an essential tool in the diagnosis and treatment of various vascular conditions, including coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, and cerebral vasculature disorders. By providing high-resolution images of the blood vessels, CTA scans enable doctors to identify blockages, aneurysms, and other abnormalities that can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. The test is also useful in planning surgical interventions, such as angioplasty and stenting, and in monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
The CTA scan is a relatively quick and painless procedure that involves injecting a contrast agent into the bloodstream to highlight the blood vessels. The contrast agent, typically a iodine-based substance, is injected through a vein in the arm, and the X-ray machine rotates around the body to capture images from multiple angles. The resulting images are then reconstructed into detailed 3D models, allowing doctors to visualize the vascular system from any angle. This level of detail is essential in diagnosing complex vascular conditions, such as atherosclerosis, which can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other life-threatening complications.
How CTA Scans Work
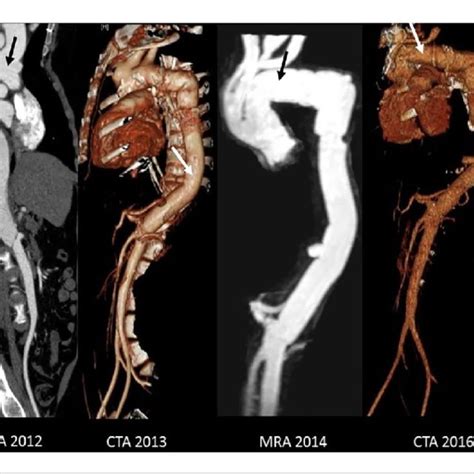
Benefits of CTA Scans
The benefits of CTA scans are numerous, and they have revolutionized the field of vascular medicine. Some of the key advantages of CTA scans include: * High-resolution images: CTA scans provide detailed images of the blood vessels, allowing doctors to diagnose complex vascular conditions with greater accuracy. * Non-invasive: CTA scans are a non-invasive procedure, eliminating the need for surgical intervention or other invasive tests. * Quick and painless: The CTA scan is a relatively quick procedure, typically taking around 10-30 minutes to complete, and is painless, except for the injection of the contrast agent. * Low risk: CTA scans are generally safe, with a low risk of complications, such as allergic reactions to the contrast agent.Preparation and Procedure
CTA Scan Results
The results of a CTA scan are typically available within a few hours, and they are usually interpreted by a radiologist or a vascular specialist. The results may show: * Blockages or narrowing of the blood vessels * Aneurysms or other abnormalities * Blood clots or other vascular conditions * The effectiveness of treatment, such as angioplasty or stentingCommon Applications of CTA Scans
Limitations and Risks
While CTA scans are generally safe and effective, there are some limitations and risks to consider: * Radiation exposure: CTA scans use X-rays, which can expose patients to radiation. * Contrast agent reactions: Some patients may be allergic to the contrast agent, which can cause an allergic reaction. * Kidney damage: The contrast agent can cause kidney damage in patients with pre-existing kidney disease. * Claustrophobia: Some patients may experience claustrophobia or anxiety during the test.Future Developments
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, CTA scans are a powerful diagnostic tool that has revolutionized the field of vascular medicine. They provide high-resolution images of the blood vessels, allowing doctors to diagnose complex vascular conditions with greater accuracy. While there are some limitations and risks to consider, the benefits of CTA scans far outweigh the risks. If you are experiencing symptoms of a vascular condition, such as chest pain or leg pain, it is essential to consult with your doctor to determine if a CTA scan is right for you.To learn more about CTA scans and their applications, we invite you to comment below or share this article with your friends and family. You can also take specific actions, such as consulting with your doctor or scheduling a CTA scan, to take control of your vascular health.
What is a CTA scan?
+A CTA scan is a medical imaging test that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of the blood vessels and surrounding tissues.
What are the benefits of CTA scans?
+The benefits of CTA scans include high-resolution images, non-invasive procedure, quick and painless, and low risk of complications.
What are the common applications of CTA scans?
+CTA scans have a wide range of applications in vascular medicine, including diagnosing coronary artery disease, evaluating peripheral artery disease, and diagnosing cerebral vasculature disorders.
